Why Does Convection Take Place
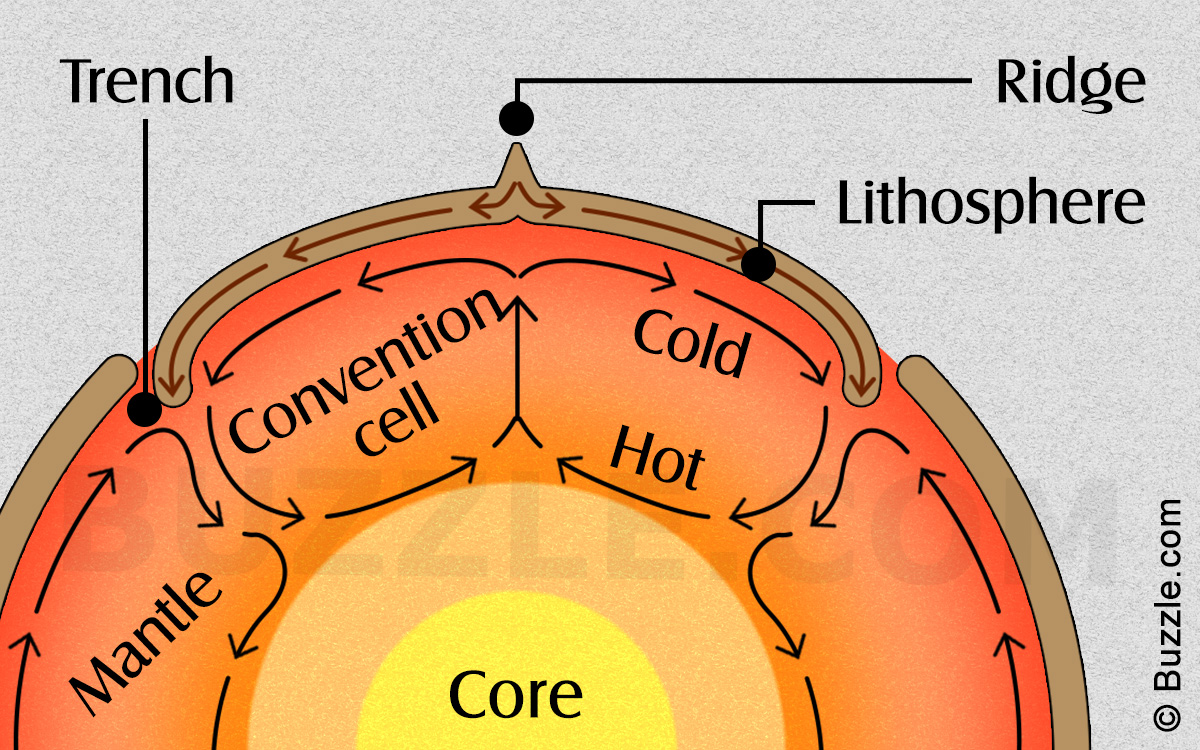
Why Does Convection Take Place Convection is a type of heat transfer that occurs via fluid motion caused by density differences. learn how convection works in nature, examples of convection in everyday life and the sun, and the difference between convection and conduction. Convection, process by which heat is transferred by movement of a heated fluid such as air or water. natural convection results from the tendency of most fluids to expand when heated—i.e., to become less dense and to rise as a result of the increased buoyancy. circulation caused by this effect accounts for the uniform heating of water in a.

Why Does Convection Take Place Convection is often categorised or described by the main effect causing the convective flow; for example, thermal convection. convection cannot take place in most solids because neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion of matter can take place. granular convection is a similar phenomenon in granular material instead of fluids. Convection currents in science: definition and examples. convection currents are heat driven cycles that move energy from one location to another. because particles within a solid are fixed in place, convection currents are seen only in gases and liquids. a temperature difference leads to an energy transfer from an area of higher energy to one. This difference in density causes the warm air to rise while colder air falls to take its place. as this process repeats, it creates a circulation loop within the column of air that helps distribute heat evenly. forced convection. forced convection is the process of moving fluids (liquids or gases) using external forces, such as fans, pumps, or. A hot, less dense material at the bottom moves upwards, and likewise, cold material from the top moves downwards. convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combined.
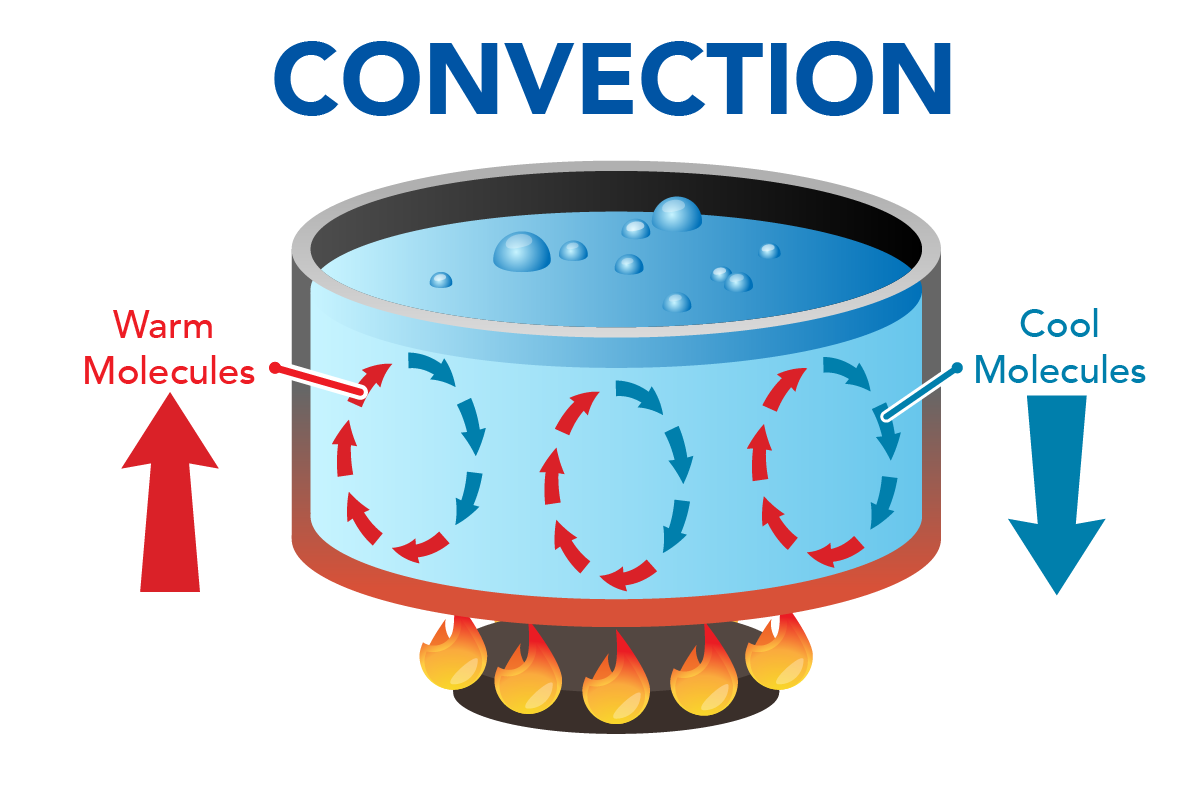
Introduction To Heat Transfer Let S Talk Science This difference in density causes the warm air to rise while colder air falls to take its place. as this process repeats, it creates a circulation loop within the column of air that helps distribute heat evenly. forced convection. forced convection is the process of moving fluids (liquids or gases) using external forces, such as fans, pumps, or. A hot, less dense material at the bottom moves upwards, and likewise, cold material from the top moves downwards. convection (or convective heat transfer) is the transfer of heat from one place to another due to the movement of fluid. although often discussed as a distinct method of heat transfer, convective heat transfer involves the combined. Convection is the movement of particles through a substance, transporting their heat energy from hotter areas to cooler areas. conduction however, doesn’t necessarily involve particles moving. instead energy is passed from one particle to another upon contact, transferring heat. as a result, conduction in liquids and gases is a much slower. Take home experiment: convection rolls in a heated pan. take two small pots of water and use an eye dropper to place a drop of food coloring near the bottom of each. leave one on a bench top and heat the other over a stovetop. watch how the color spreads and how long it takes the color to reach the top. watch how convective loops form.

Comments are closed.