What Is Schema Theory In Psychology

Schema Theory Psychology Schema theory is a branch of cognitive science concerned with how the brain structures knowledge. schema (plural: schemas or schemata) is an organized unit of knowledge for a subject or event based on past experience. individuals access schema to guide current understanding and action (pankin, 2013). for example, a student’s self schema of. Challenges. in psychology, a schema is a cognitive framework or concept that helps organize and interpret information. simply put, a schema describes patterns of thinking and behavior that people use to interpret the world. we use schemas because they allow us to take shortcuts in interpreting the vast amount of information that is available in.

15 Schema Examples In Learning Psychology 2024 Schema theory claims that our mind has mental frameworks that help organize information and influence cognition and behaviour. learn the key characteristics, functions, studies, applications and limitations of schema theory with examples and videos. Schema theory explains how people organize their knowledge into categories and use schemas to interpret new information. learn about the origins, types, and impacts of schemas on learning and memory. In psychology and cognitive science, a schema (pl.: schemata or schemas) describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. [1][2] it can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing. Schema theory jeff pankin fall 2013 basic concepts definition: schema theory is a branch of cognitive science concerned with how the brain structures knowledge. a schema is an organized unit of knowledge for a subject or event. it is based on past experience and is accessed to guide current understanding or action. characteristics:.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-schema-2795873_final-abab7e24079f4a1492ccc62b8cffa7f0.png)
Schema In Psychology Definition Types Examples In psychology and cognitive science, a schema (pl.: schemata or schemas) describes a pattern of thought or behavior that organizes categories of information and the relationships among them. [1][2] it can also be described as a mental structure of preconceived ideas, a framework representing some aspect of the world, or a system of organizing. Schema theory jeff pankin fall 2013 basic concepts definition: schema theory is a branch of cognitive science concerned with how the brain structures knowledge. a schema is an organized unit of knowledge for a subject or event. it is based on past experience and is accessed to guide current understanding or action. characteristics:. Schema theory describes how knowledge is acquired, processed and organized. the starting assumption of this theory is that “ very act of comprehension involves one’s knowledge of the world ” 4). according to this theory, knowledge is a network of mental frames or cognitive constructs called schema (pl. schemata). Schema, in social science, mental structures that an individual uses to organize knowledge and guide cognitive processes and behaviour. people use schemata (the plural of schema) to categorize objects and events based on common elements and characteristics and thus interpret and predict the world. new information is processed according to how.
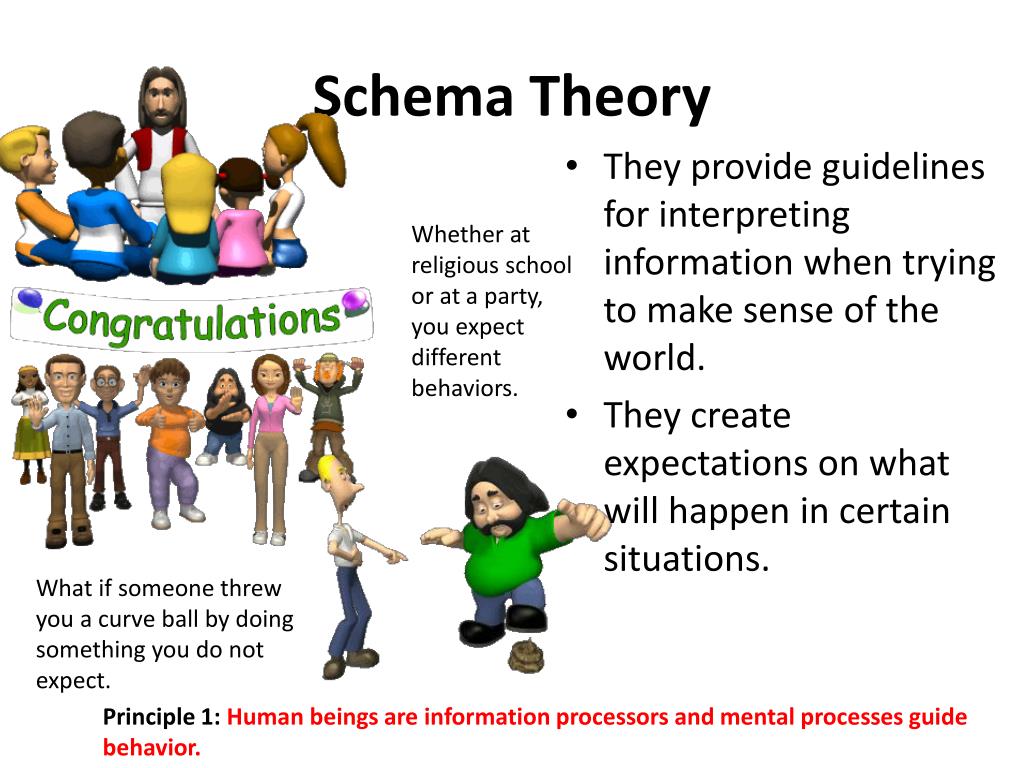
Schema Theory Psychology Schema theory describes how knowledge is acquired, processed and organized. the starting assumption of this theory is that “ very act of comprehension involves one’s knowledge of the world ” 4). according to this theory, knowledge is a network of mental frames or cognitive constructs called schema (pl. schemata). Schema, in social science, mental structures that an individual uses to organize knowledge and guide cognitive processes and behaviour. people use schemata (the plural of schema) to categorize objects and events based on common elements and characteristics and thus interpret and predict the world. new information is processed according to how.

Comments are closed.