What Is Pressure In Fluid Mechanics The Engineering Projects
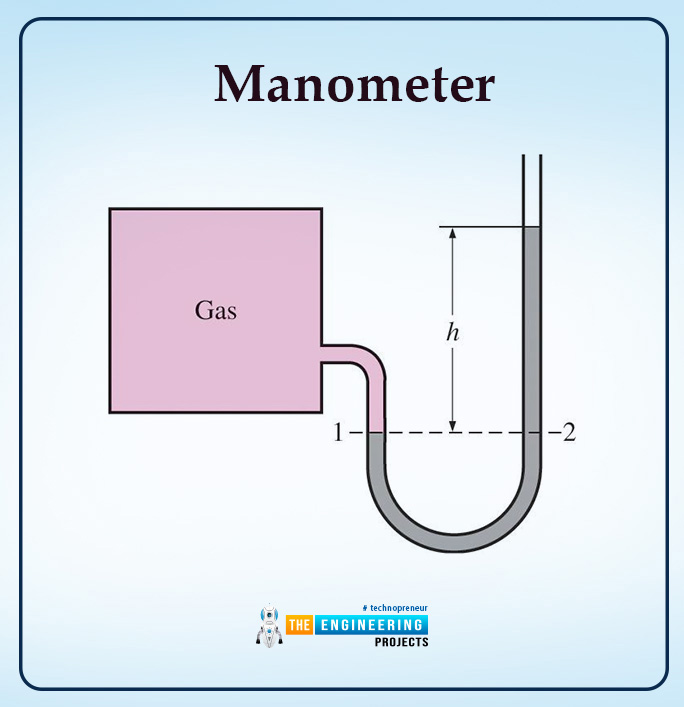
What Is Pressure In Fluid Mechanics The Engineering Projects The definition of pressure according to fluid mechanics is as follows: pressure is the normal force applied by a fluid per unit area. unit of pressure. the units of pressure pascal is too small to deal with in practical cases. for instance, kilopascal: 1kpa=103pa. mega pascal: 1mpa=106pa. Drag and lift in fluids. posted at: 06 nov 2022. category: fluid mechanics. author: syedzainnasir. 0 comment. departments:mechanical engineeringit is one of the most critical topics whenever. it is related to the resistance a fluid faces in motion. a fluid exerts a force on a body in a different direction.
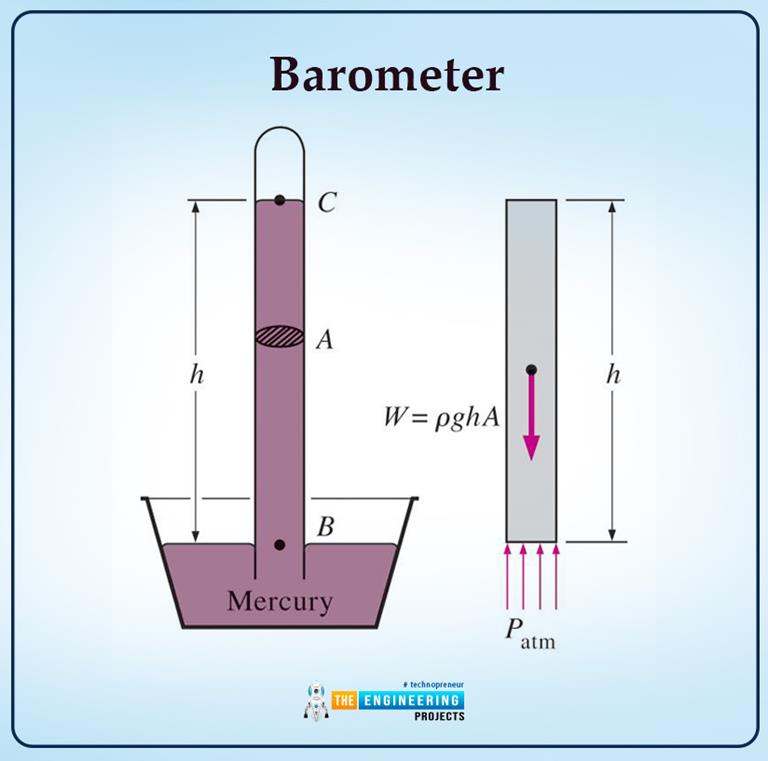
What Is Pressure In Fluid Mechanics The Engineering Projects Introduction to fluid mechanics. fluid mechanics is considered to be one of the essential branches of mechanical engineering. fluid mechanics comprises two words, fluid, and mechanics, with different meanings and research criteria. in this article, i will extensively introduce fluid mechanics and its importance in daily life. For a static fluid, the pressure only varies with elevation z and is constant in horizontal xy planes. the basic equation for pressure variation with elevation can be integrated depending on whether = constant or = (z), i.e., whether the fluid is incompressible (liquid or low speed gas) or compressible (high speed gas) since. g constant. Mechanical engineering. fluid mechanics is a key part of physics and engineering, especially for mechanical engineers. it’s about understanding how liquids and gases behave, whether they’re still or moving. grasping this subject is vital for mechanical engineers because it helps them design and improve systems like pumps, turbines, and. 14.1 fluids, density, and pressure. a fluid is a state of matter that yields to sideways or shearing forces. liquids and gases are both fluids. fluid statics is the physics of stationary fluids. density is the mass per unit volume of a substance or object, defined as ρ = m v ρ = m v. the si unit of density is kg m 3.
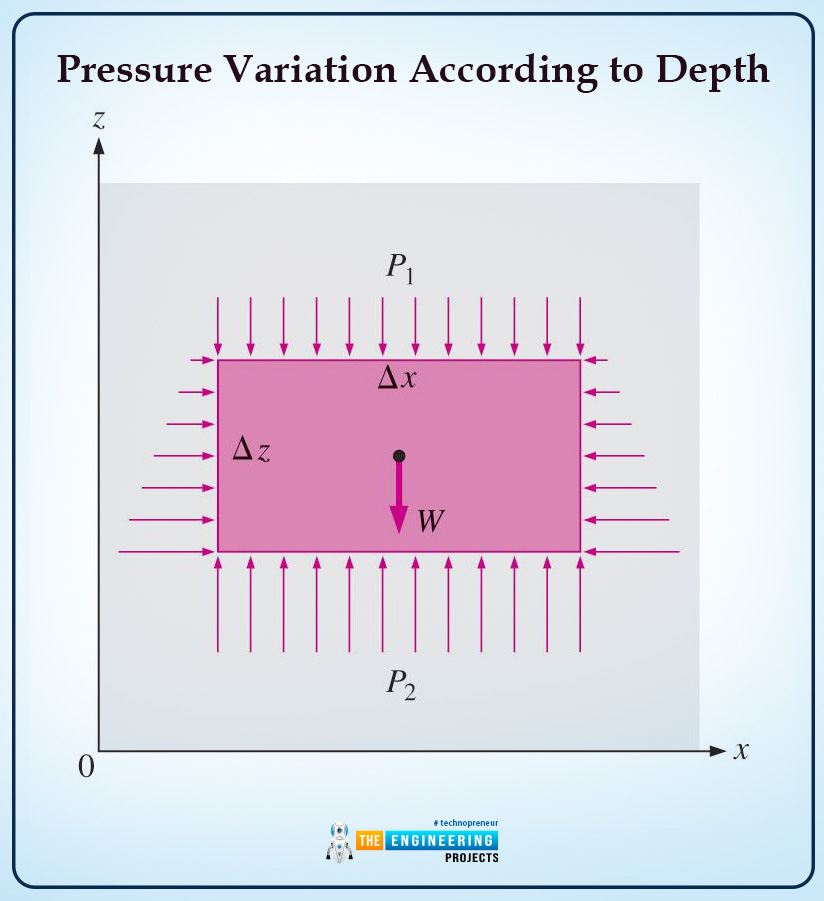
What Is Pressure In Fluid Mechanics The Engineering Projects Mechanical engineering. fluid mechanics is a key part of physics and engineering, especially for mechanical engineers. it’s about understanding how liquids and gases behave, whether they’re still or moving. grasping this subject is vital for mechanical engineers because it helps them design and improve systems like pumps, turbines, and. 14.1 fluids, density, and pressure. a fluid is a state of matter that yields to sideways or shearing forces. liquids and gases are both fluids. fluid statics is the physics of stationary fluids. density is the mass per unit volume of a substance or object, defined as ρ = m v ρ = m v. the si unit of density is kg m 3. This class provides students with an introduction to principal concepts and methods of fluid mechanics. topics covered in the course include pressure, hydrostatics, and buoyancy; open systems and control volume analysis; mass conservation and momentum conservation for moving fluids; viscous fluid flows, flow through pipes; dimensional analysis; boundary layers, and lift and drag on objects. 14.2: fluids, density, and pressure (part 1) a fluid is a state of matter that yields to sideways or shearing forces. liquids and gases are both fluids. fluid statics is the physics of stationary fluids. density is the mass per unit volume of a substance or object while pressure is the force per unit perpendicular area over which the force is.
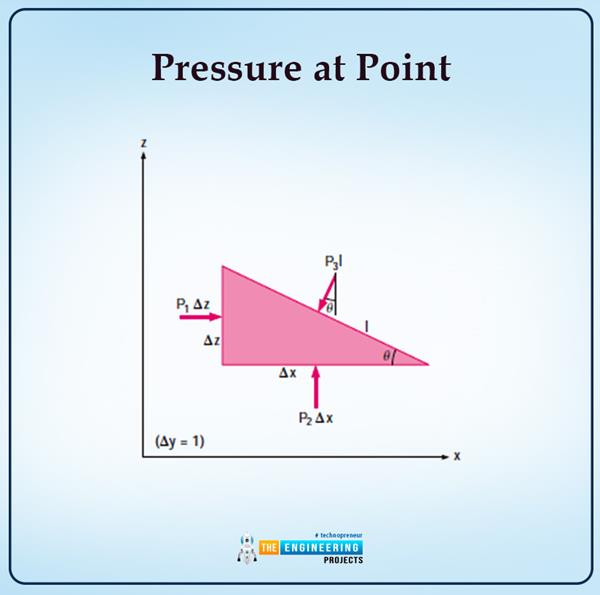
What Is Pressure In Fluid Mechanics The Engineering Projects This class provides students with an introduction to principal concepts and methods of fluid mechanics. topics covered in the course include pressure, hydrostatics, and buoyancy; open systems and control volume analysis; mass conservation and momentum conservation for moving fluids; viscous fluid flows, flow through pipes; dimensional analysis; boundary layers, and lift and drag on objects. 14.2: fluids, density, and pressure (part 1) a fluid is a state of matter that yields to sideways or shearing forces. liquids and gases are both fluids. fluid statics is the physics of stationary fluids. density is the mass per unit volume of a substance or object while pressure is the force per unit perpendicular area over which the force is.

Comments are closed.