What Are Primary And Secondary Consumers

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers for energy. they can be carnivores or omnivores, and they regulate the population of primary consumers and provide energy to tertiary consumers. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web.

The Food Chain For Kids Hubpages The organisms that consume the producers are herbivores: the primary consumers. secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the. These are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the herbivores. tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. there may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. trophic levels. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food through.

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores. A primary consumer is an organism that feeds on primary producers. organisms of this type make up the second trophic level and are consumed or predated by secondary consumers, tertiary consumers or apex predators. trophic levels. primary consumers are usually herbivores that feed on autotrophic plants, which produce their own food through. Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer the next one is the secondary consumer.
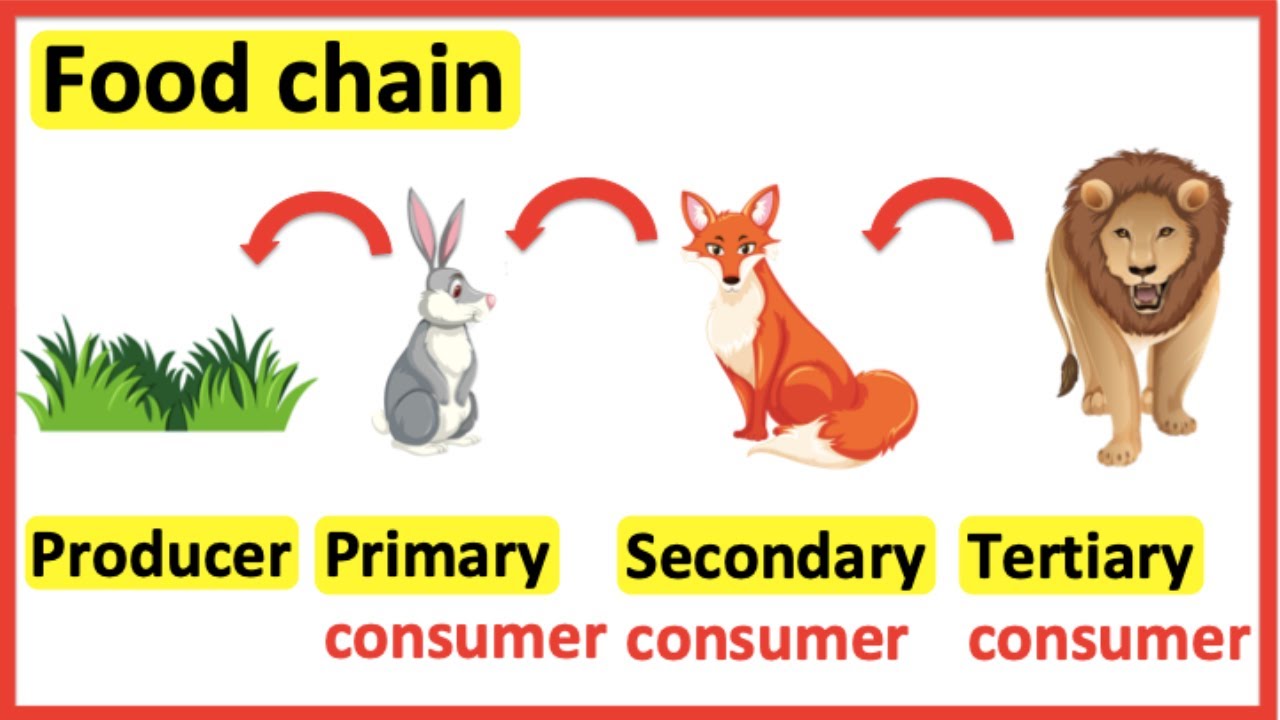
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Secondary consumers nearly always consume both producers and primary consumers and are therefore usually classed as omnivores. secondary consumers make up the third trophic level of the food chain and are – as are all consumers – heterotrophs. tertiary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers are hawks, snakes, crocodiles and some big cats. The grass is the producer, and the animals are consumers: the first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer the next one is the secondary consumer.

Comments are closed.