What Are Price Controls Macroeconomics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/price-controls.asp-Final-a1ef396a73f54e5c9abf75b0f5c2df76.jpg)
Price Controls Explained Types Examples Pros Cons Price controls are government mandated minimum or maximum prices that can be charged for specified goods. price controls in economics are restrictions imposed by governments to ensure that. Lower output. with price controls, firms will have less incentive to produce goods, leading to lower employment. a study by paul evans found that wwii price controls were successful in keeping prices 30% lower than otherwise, but with a 12% reduction in employment and 7% lower output.
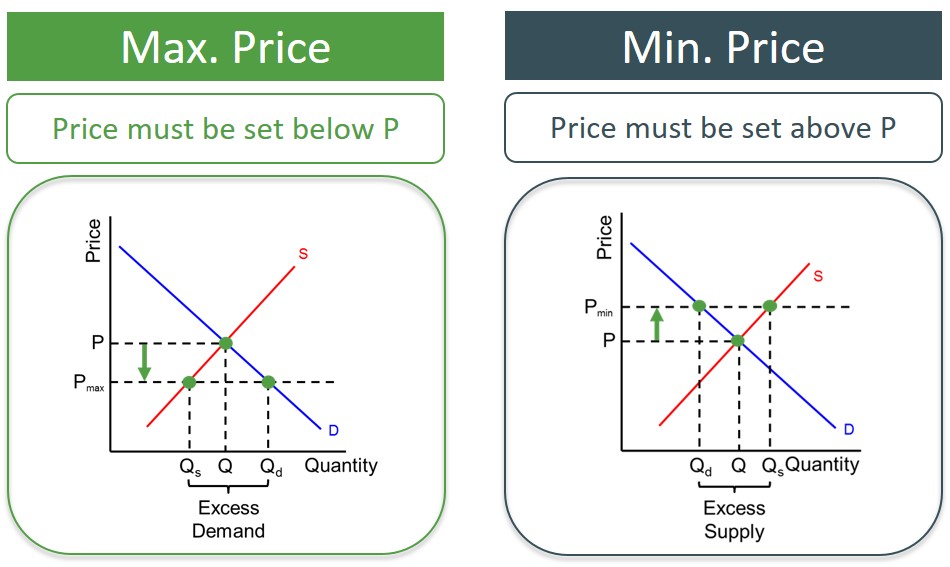
Education Resources For Teachers Schools Students Ezyeducation Price controls are government regulations on wages or prices or their rates of change. governments can impose such regulations on a broad range of goods and services or, more commonly, on a market for a single good. governments can either control the rise of prices with price ceilings, such as rent controls, or put a floor under prices with. Price controls in microeconomics and macroeconomics price controls, also known as government imposed limits on the prices of goods and services, have long been a controversial topic in economics. these policies are typically implemented in an attempt to protect consumers from high prices or to support struggling industries. Price controls. price controls are restrictions set in place and enforced by governments, on the prices that can be charged for goods and services in a market. the intent behind implementing such controls can stem from the desire to maintain affordability of goods even during shortages, and to slow inflation, or, alternatively, to ensure a. A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service, while a price floor is the legal minimum price. although both a price ceiling and a price floor can be imposed, the government usually only selects either a ceiling or a floor for particular goods or services. when prices are established by a free market, then there is a balance.

Comments are closed.