Wave Motion Waves And Tides
Wave Motion Waves And Tides This is a map ocean surface currents from 1877. (john james wild, 1877) at the surface, currents are mainly driven by four factors—wind, the sun’s radiation, gravity, and earth’s rotation. all of these factors are interconnected. the sun’s radiation creates prevailing wind patterns, which push ocean water to bunch in hills and valleys. The water molecules begin to move up and down in a circular orbit, creating a wave crest. this motion propagates energy through the water in the direction of the wind. once they have enough energy from the wind, these wave crests spread out and begin their journey across the open ocean as “swells”. these swells can travel uninterrupted for.

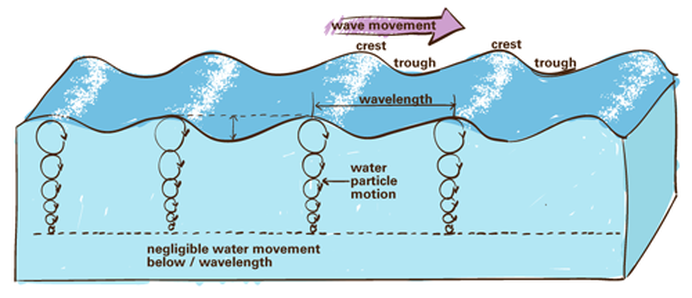
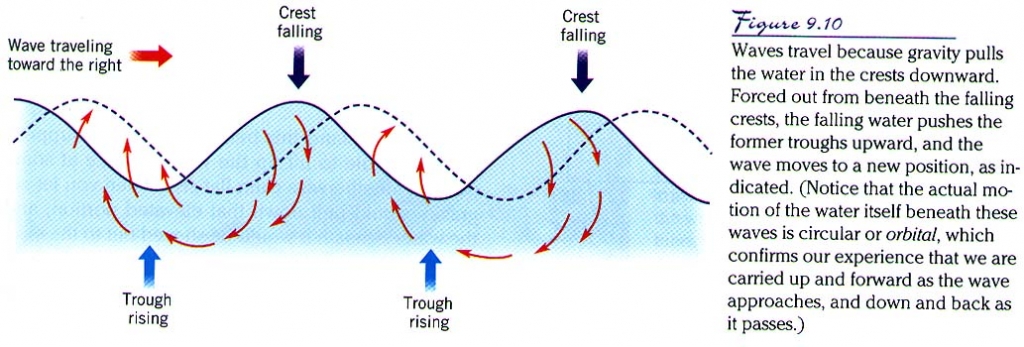
Wave Motion Waves And Tides There are several components to a basic wave (figure 10.1.2): still water level: where the water surface would be if there were no waves present and the sea was completely calm. crest: the highest point of the wave. trough: the lowest point of the wave. wave height: the distance between the crest and the trough. Learning objectives. after reading this chapter you should be able to: identify the parts of a basic wave. define the terminology used to describe the motion of a wave (i.e. period, frequency, speed etc.) explain the circular motion of water particles involved in wave motion. explain the difference between deep water waves and shallow water waves. Waves are most commonly caused by wind. wind driven waves, or surface waves, are created by the friction between wind and surface water. as wind blows across the surface of the ocean or a lake, the continual disturbance creates a wave crest. these types of waves are found globally across the open ocean and along the coast. Tides are another type of wave motion – a change in the ocean water level that typically reaches a high and low twice a day, about six hours apart (called a semi diurnal tide). the change from low to high tide is called the "flood tide" or “flow”. the change from high to low tide is called the "ebb tide". tides result from the pull of.
Movement Of Ocean Water Geography Study Material Notes Waves are most commonly caused by wind. wind driven waves, or surface waves, are created by the friction between wind and surface water. as wind blows across the surface of the ocean or a lake, the continual disturbance creates a wave crest. these types of waves are found globally across the open ocean and along the coast. Tides are another type of wave motion – a change in the ocean water level that typically reaches a high and low twice a day, about six hours apart (called a semi diurnal tide). the change from low to high tide is called the "flood tide" or “flow”. the change from high to low tide is called the "ebb tide". tides result from the pull of. Tides are the regular, alternating rise and fall of sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. the changing of the tide is often rapid and dramatic. on a smaller scale, similar motions occur on large lakes, in the atmosphere, and even within the solid earth. lesson. during a tidal cycle in the oceans, sea level rises, or. Tidal waves are formed by the gravitational forces of the earth, sun, and moon. the gravitational forces of the sun and (to a greater extent) the moon pull on the oceans causing the oceans to swell on either side of the earth (the side closest to the moon and the side farthest from the moon). as the earth rotates, the tides go 'in' and 'out.

Comments are closed.