Ventricular Septal Defect Vsd With Pulmonary Stenosis Yashoda Hospitals Hyderabad

Ventricular Septal Defect Vsd With Pulmonary Stenosis Yashoda A ventricular septal defect (vsd) is a congenital condition in which there is a hole in the wall (septum) between the two lower chambers of the heart (the ve. According to the availability of size and number of pulmonary vascular segments, they had one of the following three options of surgical treatment: (1) final repair (closure of the vsd and rv to pulmonary artery conduit), (2) rv to pulmonary artery conduit alone (vsd left open), or (3) central shunt from ascending aorta to reconstructed new.
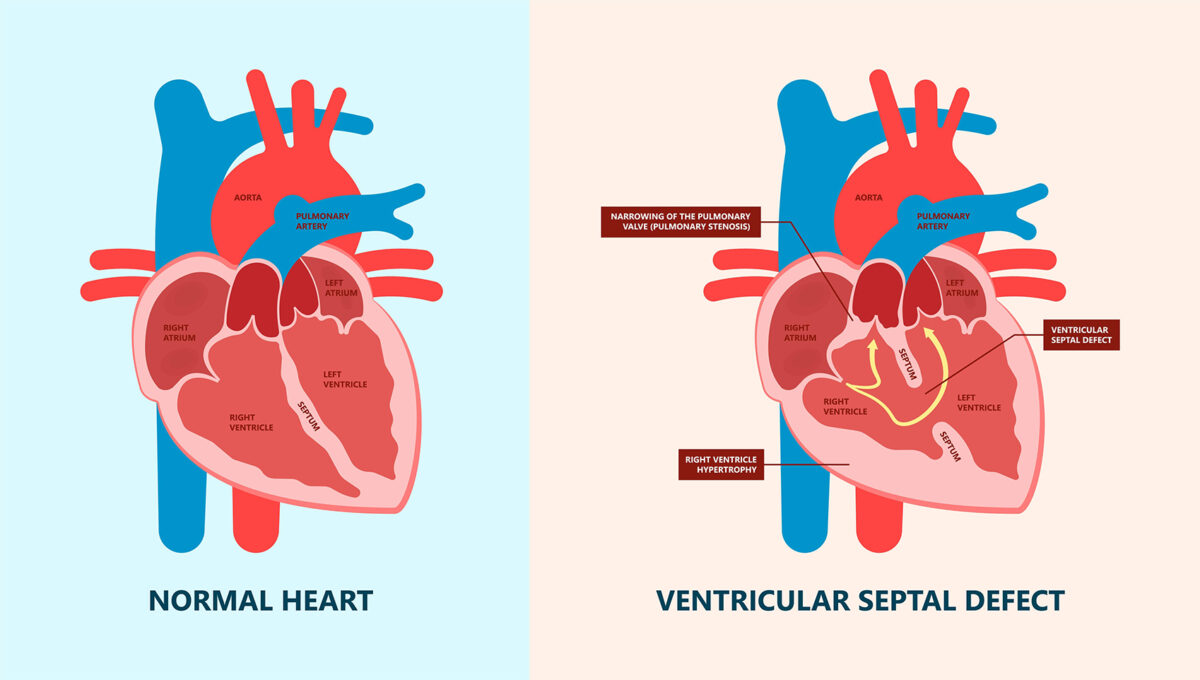
Ventricular Septal Defect вђ Symptoms Causes Closure In Hyderabad Ventricular septal defects (vsds) are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly in children and are the second most common congenital abnormality in adults, surpassed only by a bicuspid aortic valve. the primary pathophysiology involves an abnormal communication between the right and left ventricles, leading to shunt formation and subsequent hemodynamic compromise in vsd. while spontaneous. Introduction. ventricular septal defect (vsd) with pulmonary atresia (pa) consists of a spectrum of disorders ranging from atresia of right ventricle to pulmonary vasculature connection and presence of confluent or non confluent mediastinal branch pulmonary arteries to complete absence of mediastinal pulmonary arteries and major aorto pulmonary collateral arteries (mapcas), being the only. Introduction. a ventricular septal defect (vsd) is defined as a defect or opening in the interventricular septum. this results in a communication between the left and the right ventricles. a vsd may occur in isolation (single vsd), in association with other vsds (multiple vsds), or as one component of a more complex defect. Ventricular septal defect (vsd) is the commonest congenital heart disease (chd) at birth with a prevalence of 0.3% in children 0 to 6 years old. 1 unrepaired vsd carries a higher risk of death than repaired vsd; however, most children with unrepaired vsd survive to adulthood. 2 a common complication of chd is pulmonary hypertension which occurs in 4.2% of chd cases in general and 6.1% of.

Comments are closed.