Ventricular Septal Defect Congenital Heart Defects Ncbddd Cdc
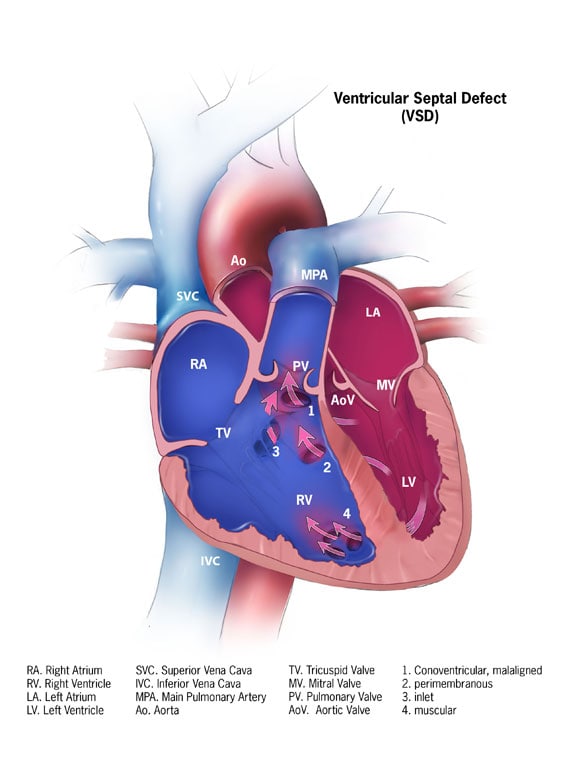
Ventricular Septal Defect Congenital Heart Defects Ncbddd Cdc A ventricular septal defect (vsd) happens during pregnancy if the wall that forms between the two ventricles does not fully develop. this leaves a hole. in babies without a heart defect, the right side of the heart pumps oxygen poor blood from the heart to the lungs. the left side of the heart pumps oxygen rich blood to the rest of the body. Overview and early presentation. congenital heart defects diseases (chd) are common, occurring in about one in 100 newborns. many types of chd require prompt diagnosis and care, both medical and surgical, to improve survival and health. in some of the milder cases, chd might resolve on its own (e.g. small ventricular septal defects) or require.
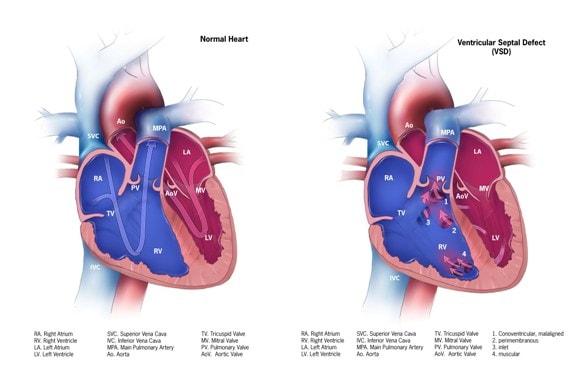
Ventricular Septal Defect Congenital Heart Defects Ncbddd Cdc To date, cdc researchers have found that. in 2010, about 1 million children and 1.4 million adults were living with a heart defect. 7. in 2010, 1 in 250 to 1 in 59 children and teens were living with a heart defect. 8. in addition, between 2011 and 2013, 1 in 157 children ages 1 10 years and 1 in 680 adolescents and adults ages 11 64 years had. Congenital means they are present at birth. heart defects can vary from mild (a small hole in the heart) to severe (missing parts of the heart). in the united states, heart defects affect nearly 1% of births, or about 40,000 babies, each year. 1 2 about 1 in 4 babies born with a heart defect has a critical heart defect. 3 babies with critical. Ventricular septal defects (vsds) are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly in children and are the second most common congenital abnormality in adults, surpassed only by a bicuspid aortic valve. the primary pathophysiology involves an abnormal communication between the right and left ventricles, leading to shunt formation and subsequent hemodynamic compromise in vsd. while spontaneous. Vsd is an opening or hole (defect) in the wall (septum) separating the two lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). in normal development, the wall between the chambers closes before the fetus is born, so that by birth, oxygen rich blood is kept from mixing with the oxygen poor blood. when the hole does not close, it may cause higher pressure.
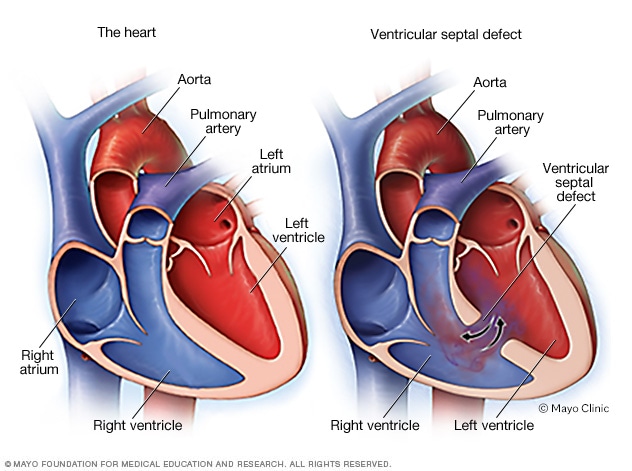
Ventricular Septal Defect Vsd Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic Ventricular septal defects (vsds) are the most common congenital cardiac anomaly in children and are the second most common congenital abnormality in adults, surpassed only by a bicuspid aortic valve. the primary pathophysiology involves an abnormal communication between the right and left ventricles, leading to shunt formation and subsequent hemodynamic compromise in vsd. while spontaneous. Vsd is an opening or hole (defect) in the wall (septum) separating the two lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). in normal development, the wall between the chambers closes before the fetus is born, so that by birth, oxygen rich blood is kept from mixing with the oxygen poor blood. when the hole does not close, it may cause higher pressure. Ventricular septal defect (see figure ventricular septal defect) is the 2nd most common congenital heart anomaly after bicuspid aortic valve, accounting for 20% of all defects. it can occur alone or with other congenital anomalies (eg, tetralogy of fallot, complete atrioventricular septal defects, transposition of the great arteries). Cdc works to identify causes of birth defects and opportunities to prevent them. by applying a public health approach incorporating three essential elements—surveillance or disease tracking, research to identify causes, and prevention research and programs—we can rapidly translate scientific findings into appropriate public health interventions.
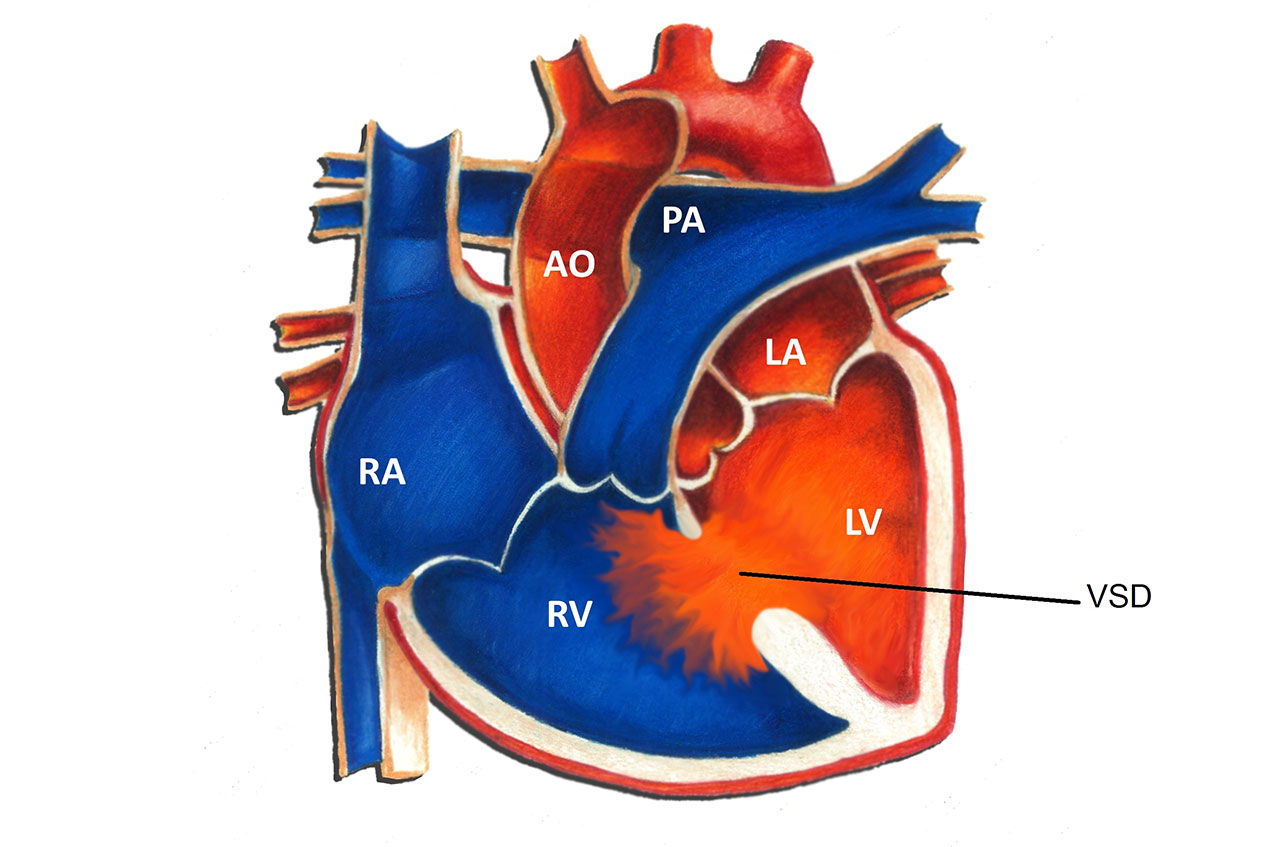
Anatomy Of The Ventricular Septal Defect In Congenital Heart Defect Ventricular septal defect (see figure ventricular septal defect) is the 2nd most common congenital heart anomaly after bicuspid aortic valve, accounting for 20% of all defects. it can occur alone or with other congenital anomalies (eg, tetralogy of fallot, complete atrioventricular septal defects, transposition of the great arteries). Cdc works to identify causes of birth defects and opportunities to prevent them. by applying a public health approach incorporating three essential elements—surveillance or disease tracking, research to identify causes, and prevention research and programs—we can rapidly translate scientific findings into appropriate public health interventions.

Comments are closed.