Var Methods Calculating Value At Risk Method Master Class Education

Var Methods Calculating Value At Risk Method Master Class Education There are three primary methods used for calculating value at risk (var). a. the variance covariance method. b. the historical simulation method. c. the monte carlo simulation method. all var methods have a common base but diverge in how they actually calculate value at risk (var). they also have a common problem in assuming that the future. Specifically: value at risk (var) = λ × z value of standard normal cumulative distribution corresponding with a specified confidence level. for example for a confidence level of 99% the z value is 2.326 (excel’s function ‘normsinv (.99) may be used to determine the z value) and the. and the daily value at risk (var)=2.326 λ.

Master Class Calculating Value At Risk Var Final Steps Var. value at risk is a statistical metric to compute a portfolio's risk. it displays the highest possible loss and a given confidence level. it considers the market price and the volatility in a given time frame. investors, analysts, and regulators widely use var to measure the risks in their portfolios. Develop a thorough understanding of value at risk (var) and its significance in financial risk management. master the calculation and application of parametric, historical, and monte carlo var methods. gain insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each var methodology, enabling informed decision making. apply var techniques to various. We first calculate the mean and standard deviation of the returns. according to the assumption, for a 95% confidence level, the value at risk is calculated as a mean 1.65 * standard deviation. also, as per the assumption, for a 99% confidence level, the value at risk is calculated as mean 2.33* standard deviation. Value at risk. value at risk = vm (vi v (i 1)) m = the number of days from which historical data is taken. vi = the number of variables on the day i. in calculating each daily return, we.
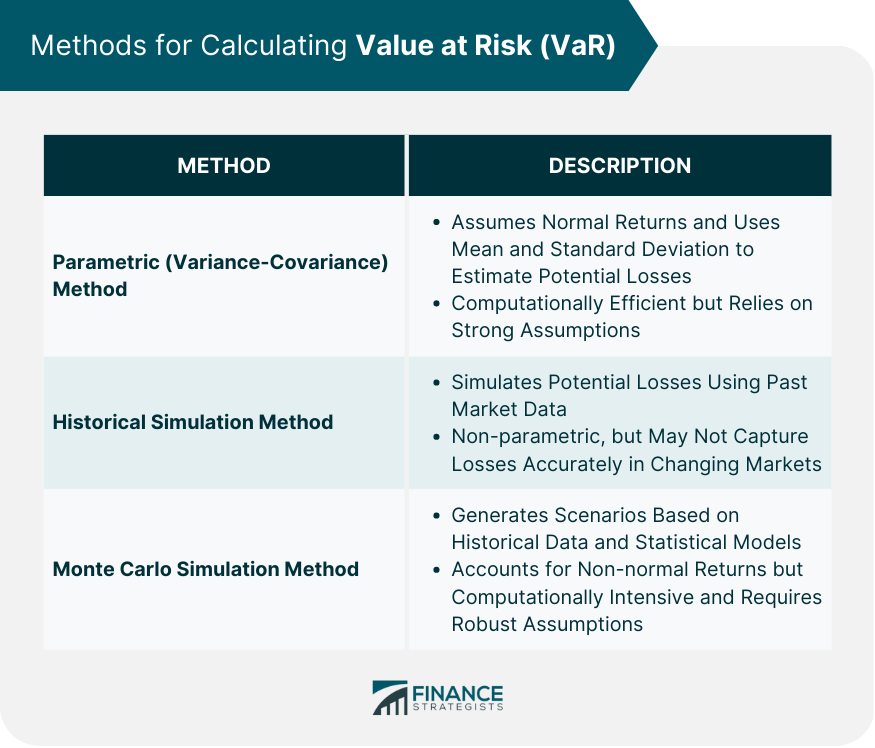
Value At Risk Var Definition Components Calculation We first calculate the mean and standard deviation of the returns. according to the assumption, for a 95% confidence level, the value at risk is calculated as a mean 1.65 * standard deviation. also, as per the assumption, for a 99% confidence level, the value at risk is calculated as mean 2.33* standard deviation. Value at risk. value at risk = vm (vi v (i 1)) m = the number of days from which historical data is taken. vi = the number of variables on the day i. in calculating each daily return, we. Conditional value at risk, also known as expected shortfall, is an alternative risk measure that addresses some of var's limitations by focusing on the expected loss beyond the var threshold. cvar provides a more comprehensive view of tail risk, as it considers the magnitude of losses in extreme events, rather than simply estimating the maximum loss within a given confidence level. Value at risk (var) is a risk management used to estimate the maximum potential loss within a specified time frame and confidence level. it is commonly employed to assess and manage risk exposure in institutional portfolios. var is determined by three factors a specific percentage or value of the loss, the period over which risk is evaluated.

Master Class Calculating Value At Risk Var Introduction Conditional value at risk, also known as expected shortfall, is an alternative risk measure that addresses some of var's limitations by focusing on the expected loss beyond the var threshold. cvar provides a more comprehensive view of tail risk, as it considers the magnitude of losses in extreme events, rather than simply estimating the maximum loss within a given confidence level. Value at risk (var) is a risk management used to estimate the maximum potential loss within a specified time frame and confidence level. it is commonly employed to assess and manage risk exposure in institutional portfolios. var is determined by three factors a specific percentage or value of the loss, the period over which risk is evaluated.
Ppt Value At Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 733643

Comments are closed.