Understanding Linux And Unix Inodes And File Metadata

Understanding Of Linux Inodes Welcome To Charanjit Cheema Blog The i (inodes) option of the. df. command instructs it to display its output in numbers of inodes. we're going to look at the file system on the first partition on the first hard drive, so we type the following: df i dev sda1. the output gives us: file system: the file system being reported on. Do you need a greater understanding of linux inodes and file metadata?here we take a tour to make sure that we do truly understand inodes in linux and what t.
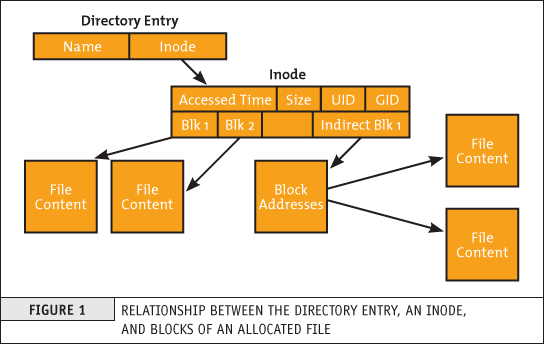
Increase Inodes On Linux Inode application. many commands used by system administrators in unix linux operating systems often give inode numbers to designate a file. let us see he practical application of inode number. type the following commands: $ cd tmp. $ touch \"la*. $ ls l. now try to remove file “la*. To summarize inode usage for an entire directory subtree, use du with i parameter: $ du ih var . 369218 var. this reveals the total inodes consumed under var for thorough tracking. as we can see, linux offers extensive visibility into inode consumption from high level overviews to file specific numbers. A block is the smallest unit of data storage in a filesystem. the block size determines the granularity of data storage and affects the performance and efficiency of the filesystem. typical block sizes are 512 bytes, 1 kb, 2 kb, 4 kb, and 8 kb. the block size you choose can significantly impact how the filesystem performs and how much storage. Linux filesystems are complicated things to understand, especially when you get down into the weeds of data and metadata. every time you run the ls command and see the output—files listed, permissions, account ownership, etc.—understand that the data about the files you see is stored somewhere separate from the files themselves, and must be called up.

Comments are closed.