Understanding Charts And Graphs
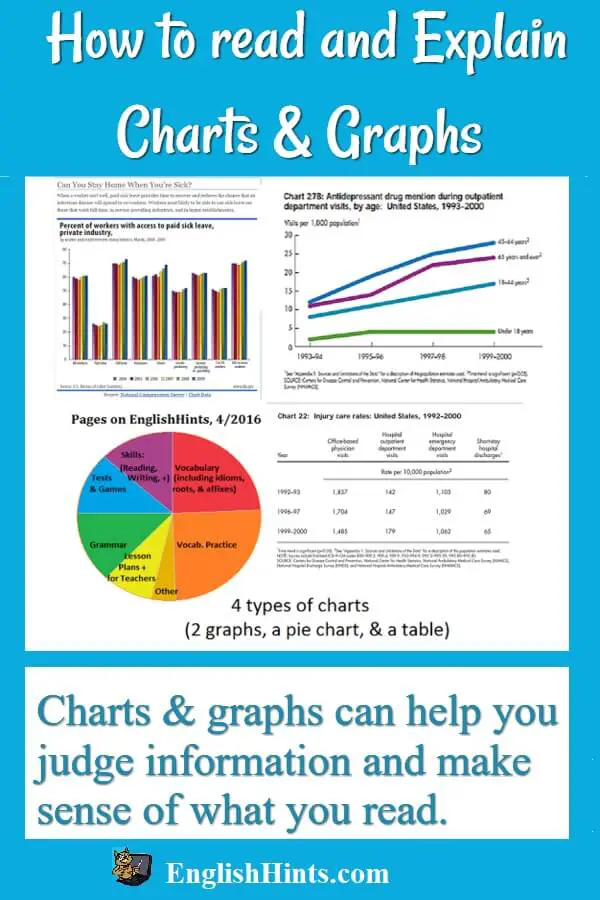
Understanding And Explaining Charts And Graphs Steps: open your google sheets application. paste the table in your worksheet. open the worksheet and click the extensions menu. then click charts, graphs, & visualizations by chartexpo. finally, click the open button in the dropdown. click the add new chart button to access your fully stocked library of charts. There are several different types of charts and graphs. the four most common are probably line graphs, bar graphs and histograms, pie charts, and cartesian graphs. they are generally used for, and are best for, quite different things. you would use: bar graphs to show numbers that are independent of each other. example data might include things.
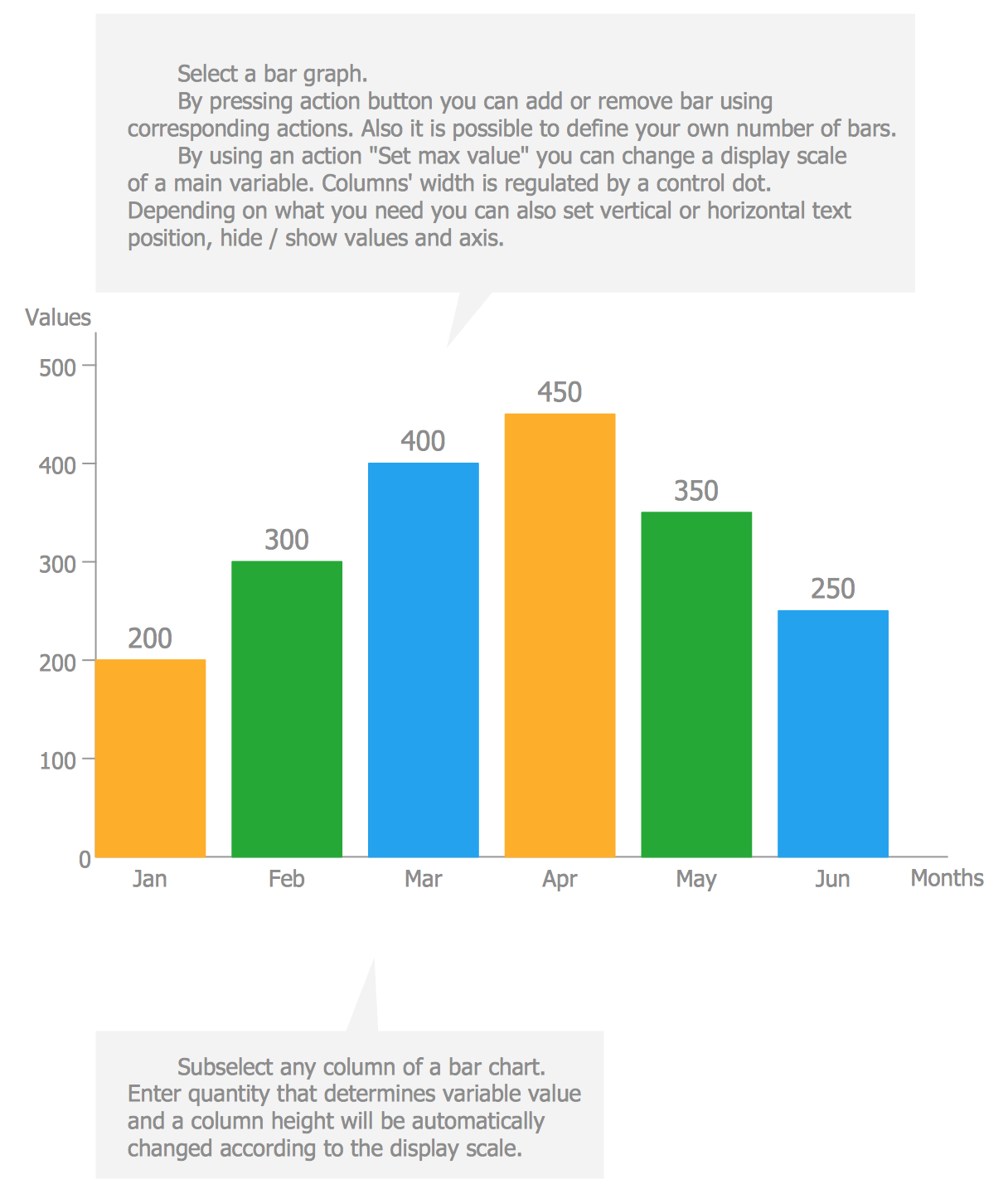
Understanding Charts And Graphs Graphs and charts includes: explanation and illustration of the different ways in which data is presented in charts and diagrams. worked examples of creating and interpreting a range of graphs and. How to use charts and graphs effectively. bring your data to life with engaging charts and graphs. visual representations help us to understand data quickly. when you show an effective graph or chart, your report or presentation gains clarity and authority, whether you're comparing sales figures or highlighting a trend. Market segments are often divided based on age and gender, and a population pyramid is an ideal visual representation of the two groups. the graph classically takes on the shape of a pyramid when a population is healthy and growing the largest groups are the youngest, and each gender dwindles somewhat equally as the population ages, leaving the smallest groups at the top of the graph. Creating & reading graphs for experiments. when collecting data from an experiment, different variables are discussed. an independent variable is the cause and what is being manipulated. it is.

Understanding Charts And Graphs Walmart Market segments are often divided based on age and gender, and a population pyramid is an ideal visual representation of the two groups. the graph classically takes on the shape of a pyramid when a population is healthy and growing the largest groups are the youngest, and each gender dwindles somewhat equally as the population ages, leaving the smallest groups at the top of the graph. Creating & reading graphs for experiments. when collecting data from an experiment, different variables are discussed. an independent variable is the cause and what is being manipulated. it is. 5. pie chart. pie charts highlight data and statistics in pie slice format. a pie chart represents numbers in percentages, and the total sum of all pies should equal 100 percent. when considering charts and graphs to employ to visualize data, pie charts are most impactful to your audience if you have a small data set. Consider the most common charts: scatterplots, bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts. these chart types, or a combination of them, provide answers to most questions with relational data. they are the backbone of performing visual analysis on non geospatial data. visualizing data with charts relies on drawing points using cartesian coordinates.
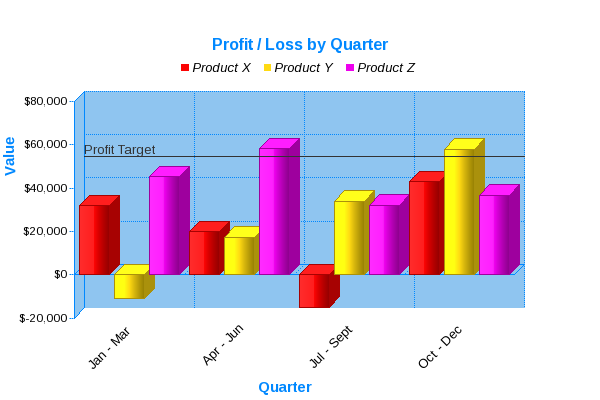
Understanding Diagrams And Graphs вђ Learning Center 5. pie chart. pie charts highlight data and statistics in pie slice format. a pie chart represents numbers in percentages, and the total sum of all pies should equal 100 percent. when considering charts and graphs to employ to visualize data, pie charts are most impactful to your audience if you have a small data set. Consider the most common charts: scatterplots, bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts. these chart types, or a combination of them, provide answers to most questions with relational data. they are the backbone of performing visual analysis on non geospatial data. visualizing data with charts relies on drawing points using cartesian coordinates.

Comments are closed.