Types Of Force We Discussed Friction Force Gravity Applied Force

Types Of Force We Discussed Friction Force Gravity Applied Force A force is a push or pull acting upon an object as a result of its interaction with another object. there are a variety of types of forces. previously in this lesson, a variety of force types were placed into two broad category headings on the basis of whether the force resulted from the contact or non contact of the two interacting objects. Treating displacement from the equilibrium as a vector, we see that the direction of the force is in exactly the opposite direction, regardless of whether the spring is stretched or expanded. accordingly, we can write: f→ elastic = −kΔx→ (2.3.6) (2.3.6) f → e l a s t i c = − k Δ x →. this equation is commonly known as hooke's law.
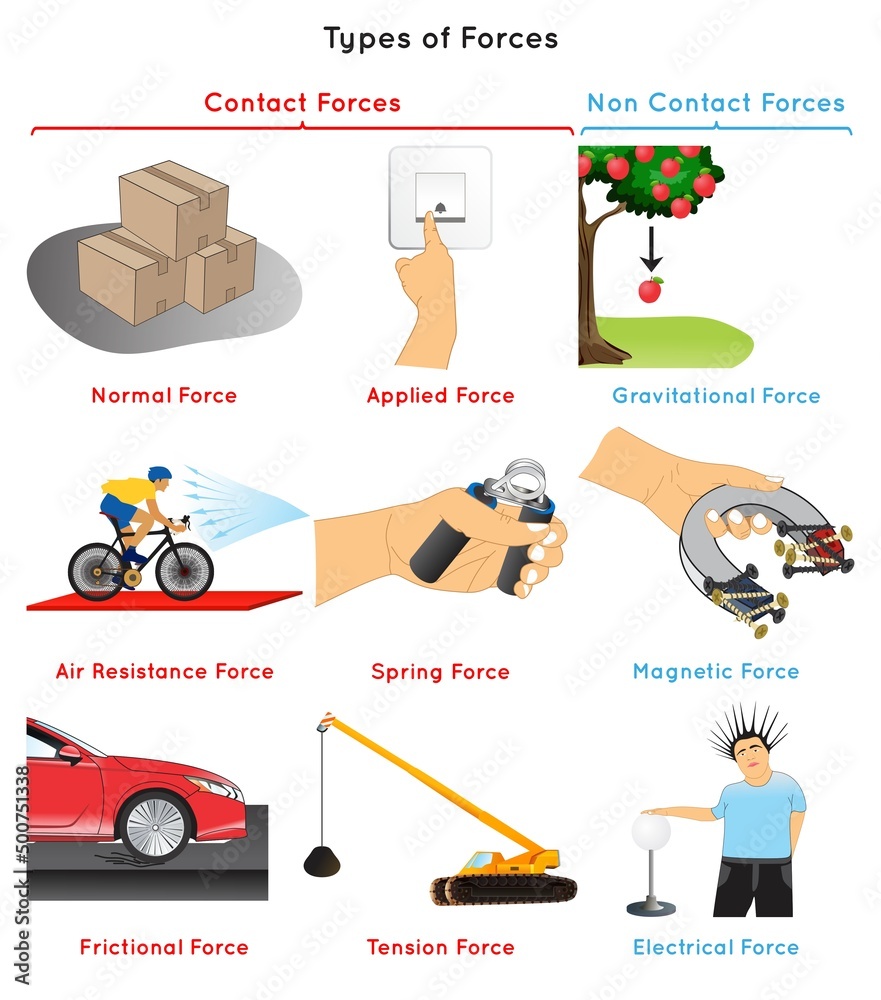
Types Of Forces Infographic Diagram Normal Applied Air Resistance Examples of static friction include the force that resists. a person from slipping while walking and running. a heavy object from moving while pushing or pulling. 2. kinetic friction. kinetic friction arises when the object moves relative to the surface after the applied force overcomes the static friction. kinetic friction can be of two types. 1. a mass is suspended from the ceiling by a spring. the spring exerts an upward pull upon the mass. friction force (ffrict) the force between two surfaces that are sliding (or attempting to slide) across each other. friction opposes the motion of the sliding object. a truck skids to a stop along a road. A catalog of forces will be useful for reference as we solve various problems involving force and motion. these forces include normal force, tension, friction, and spring force. normal force. weight (also called the force of gravity) is a pervasive force that acts at all times and must be counteracted to keep an object from falling. Free body diagrams represent a picture of the forces that are acting on a body or a system. in the examples below, the forces illustrated are friction, applied forces, the normal force and weight. you can see for these situations that the angle of the incline is 0° and as such cos 0° = 1.
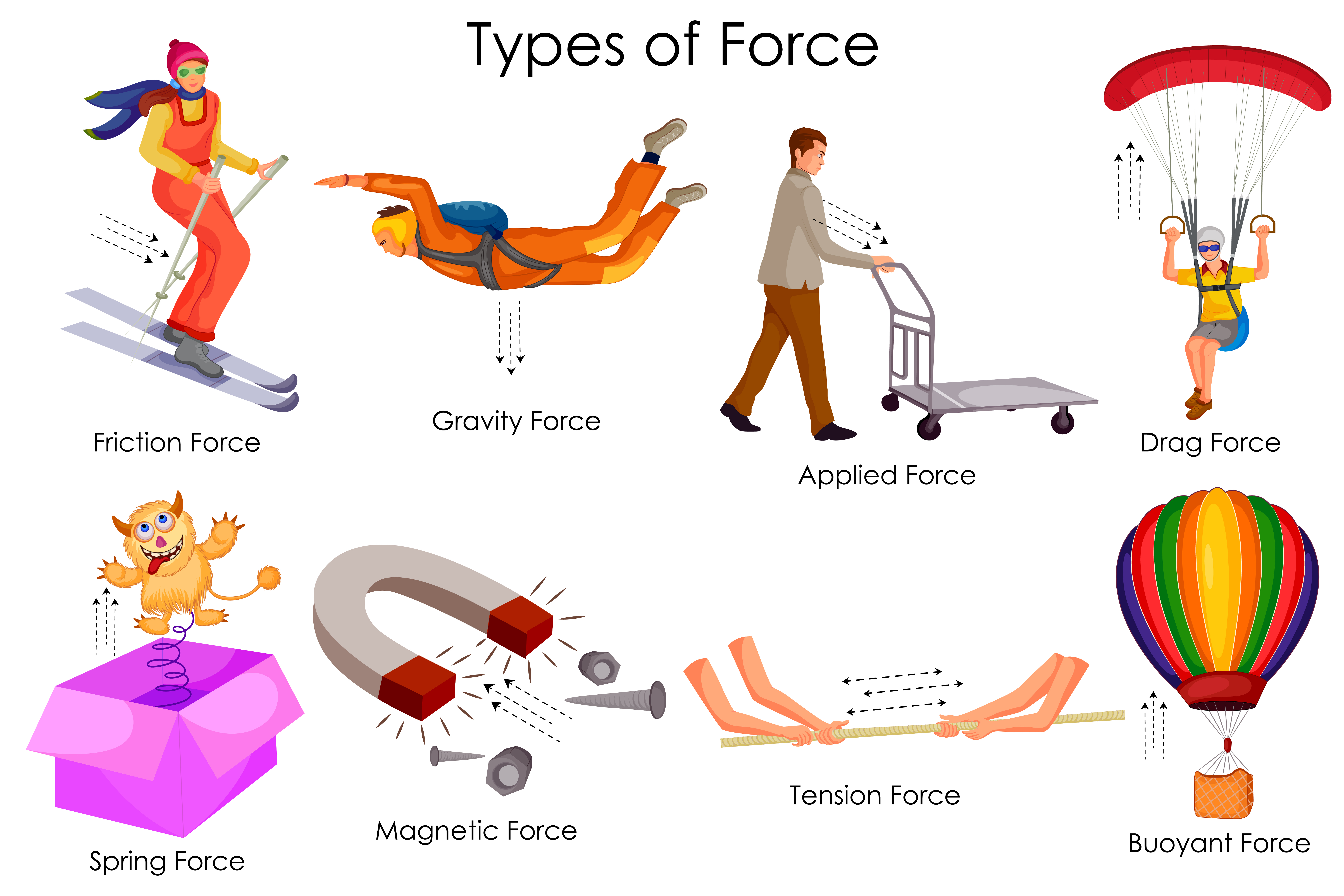
Types Of Forces Ks3 Science A catalog of forces will be useful for reference as we solve various problems involving force and motion. these forces include normal force, tension, friction, and spring force. normal force. weight (also called the force of gravity) is a pervasive force that acts at all times and must be counteracted to keep an object from falling. Free body diagrams represent a picture of the forces that are acting on a body or a system. in the examples below, the forces illustrated are friction, applied forces, the normal force and weight. you can see for these situations that the angle of the incline is 0° and as such cos 0° = 1. Forces are classified and given names based on their source, how they are transmitted, or their effects. in previous sections, we discussed the forces called push, weight, and friction. in this section, applying newton’s third law of motion will allow us to explore three more forces: the normal force, tension, and thrust. however, because we. At small but nonzero speeds, friction is nearly independent of speed. figure 5.4.1: frictional forces, such as →f , always oppose motion or attempted motion between objects in contact. friction arises in part because of the roughness of the surfaces in contact, as seen in the expanded view.
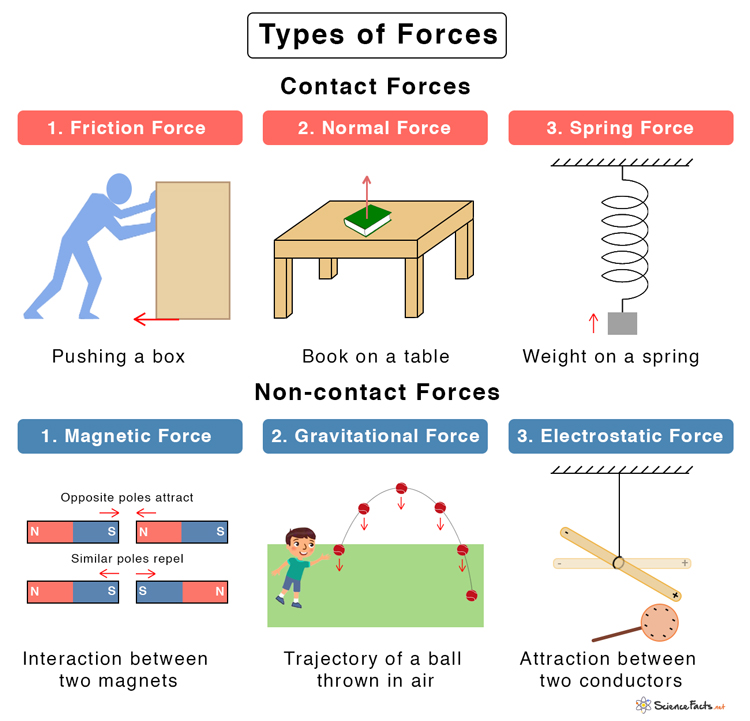
What Is Force Motion Examples Types Of Forces Diagrams Forces are classified and given names based on their source, how they are transmitted, or their effects. in previous sections, we discussed the forces called push, weight, and friction. in this section, applying newton’s third law of motion will allow us to explore three more forces: the normal force, tension, and thrust. however, because we. At small but nonzero speeds, friction is nearly independent of speed. figure 5.4.1: frictional forces, such as →f , always oppose motion or attempted motion between objects in contact. friction arises in part because of the roughness of the surfaces in contact, as seen in the expanded view.
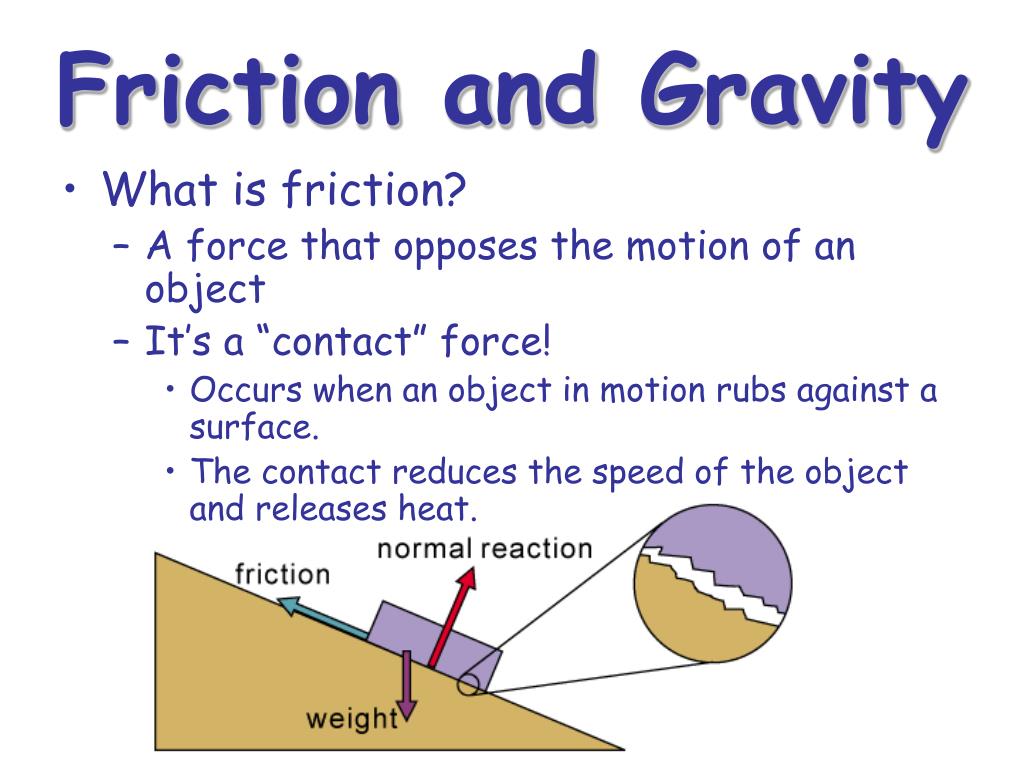
Ppt Force And Motion Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6854836

Comments are closed.