Trend Lines What Are Residual Values Expii

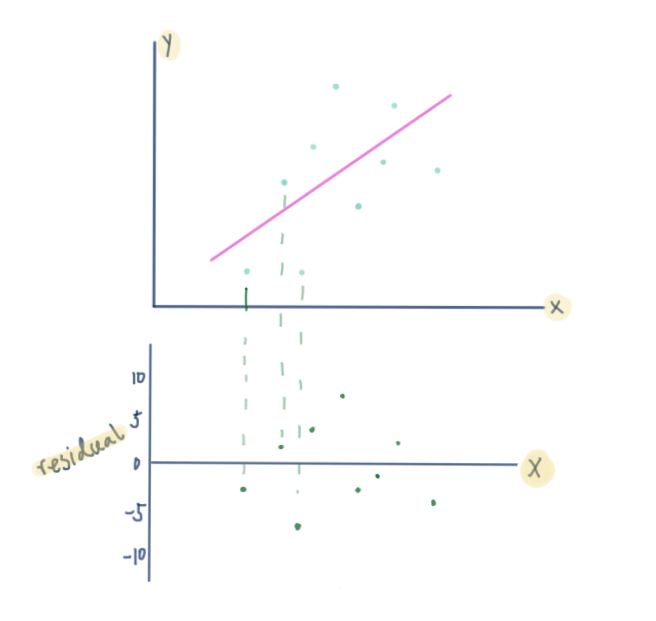
Trend Lines What Are Residual Values Expii A residual is a measurement to determine how well a scatter plot's data fits its trend line. to find a point's residual, we subtract the predicted y value from the actual y value. residual=actual y value−predicted y value. the actual value, is represented by the dot on the scatter plot. the predicted value is given by the trend line or line. Whenever we plot either a line of best fit or a trend line for a scatter plot, we find that not every point in the plot ends up on that line. the vertical difference between the **expected value ** (the point on the line) and the actual value (the value in the scatter plot) is called the residual value. residual=actual y value−predicted y value.

Residual Plots Definition Examples Expii Expii. trend lines and residuals expii. residuals are a way to measure how well a line of best fit fits a point of data. trend lines and residuals residual. Answer. residuals are helpful in evaluating how well a linear model fits a data set. we often display them in a residual plot such as the one shown in figure 7.2.6 for the regression line in figure 7.2.5. the residuals are plotted at their original horizontal locations but with the vertical coordinate as the residual. The fitted line plot suggests that one data point does not follow the trend in the rest of the data. here's what the residual vs. fits plot looks like: the ideal random pattern of the residual plot has disappeared, since the one outlier really deviates from the pattern of the rest of the data. Use residual plots to check the assumptions of an ols linear regression model. if you violate the assumptions, you risk producing results that you can’t trust. residual plots display the residual values on the y axis and fitted values, or another variable, on the x axis. after you fit a regression model, it is crucial to check the residual plots.

Residual Plots Definition Examples Expii The fitted line plot suggests that one data point does not follow the trend in the rest of the data. here's what the residual vs. fits plot looks like: the ideal random pattern of the residual plot has disappeared, since the one outlier really deviates from the pattern of the rest of the data. Use residual plots to check the assumptions of an ols linear regression model. if you violate the assumptions, you risk producing results that you can’t trust. residual plots display the residual values on the y axis and fitted values, or another variable, on the x axis. after you fit a regression model, it is crucial to check the residual plots. Step 3. calculate the residuals using the formula: residuals = y (actual) – y (predicted) for each column in the table, we subtract the y (predicted) from the y (actual) to obtain the residual for that given value of 𝑥. for 𝑥 = 1, the residual = 6 – 4.5 = 1.5. for 𝑥 = 2, the residual = 4.5 – 6.65 = 2.15. Example: interpreting a curved residual plot. suppose we collect the following data on the number of hours worked per week and the reported happiness level (on a scale of 0 100) for 11 different people in some office: if we create a simple scatter plot of hours worked vs. happiness level, here’s what it would look like: now suppose we would.

Residual Plots Definition Examples Expii Step 3. calculate the residuals using the formula: residuals = y (actual) – y (predicted) for each column in the table, we subtract the y (predicted) from the y (actual) to obtain the residual for that given value of 𝑥. for 𝑥 = 1, the residual = 6 – 4.5 = 1.5. for 𝑥 = 2, the residual = 4.5 – 6.65 = 2.15. Example: interpreting a curved residual plot. suppose we collect the following data on the number of hours worked per week and the reported happiness level (on a scale of 0 100) for 11 different people in some office: if we create a simple scatter plot of hours worked vs. happiness level, here’s what it would look like: now suppose we would.
Residual Plots Definition Examples Expii

Comments are closed.