Tree Diagram Examples Probability
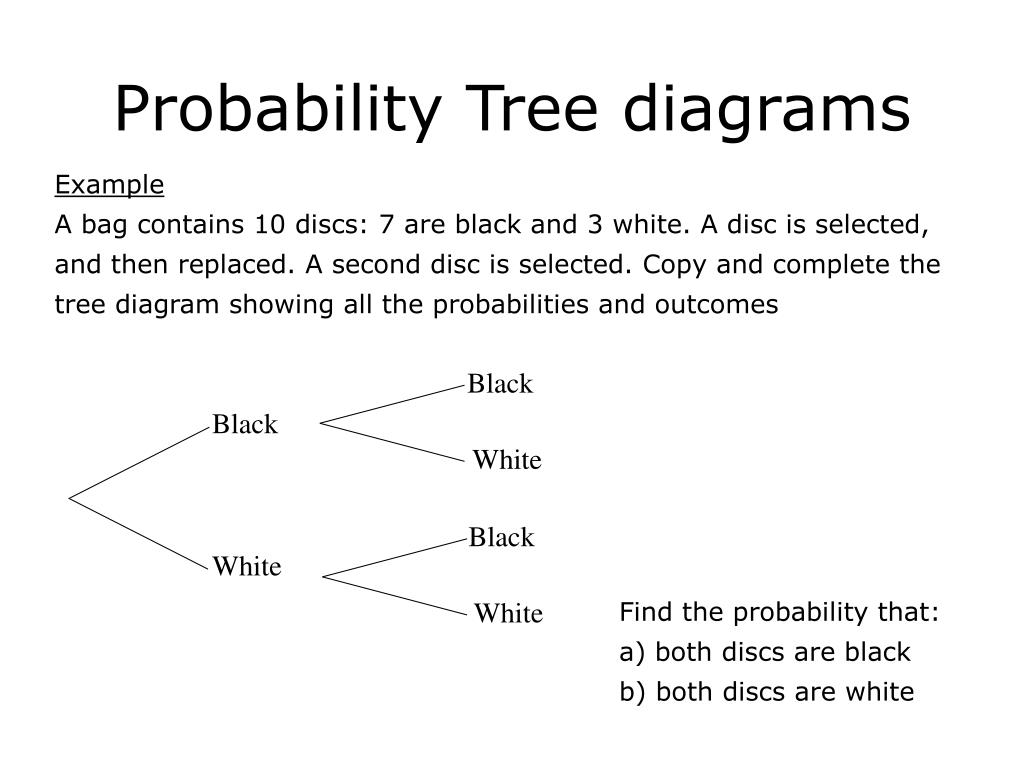
Ppt Probability Tree Diagrams Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The tree diagram is complete, now let's calculate the overall probabilities. this is done by multiplying each probability along the "branches" of the tree. here is how to do it for the "sam, yes" branch: (when we take the 0.6 chance of sam being coach and include the 0.5 chance that sam will let you be goalkeeper we end up with an 0.3 chance.). What is tree diagram probability? tree diagram probability is a way of organizing the information for two or more probability events. probability tree diagrams show all the possible outcomes of the events and can be used to solve probability questions. a simple tree diagram has branches that match each outcome. for example,.
Probability Tree Diagram Igcse At Mathematics Realm Examples on probability tree diagram. example 1: suppose a bag contains a total of 5 balls out of which 2 are blue and 3 are orange. using a probability tree diagram, find the conditional probability of drawing a blue ball given the first ball that was drawn was orange. the balls are drawn without replacement. Decimals can be used to represent probabilities on a probability tree diagram. simply multiply the decimals found on the branches of the required outcome. when multiplying decimals, the answer will always have the same number of decimal places as the decimals being multiplied combined. for example, a biased coin has a probability of heads = 0.9. The rule for finding the probability of a particular event in a probability tree diagram occurring is to multiply the probabilities of the corresponding branches. for example, to prove that there is 0.25 probability of getting two heads in a row, you would multiply 0.5 x 0.5 (since the probability of getting a heads on the first flip is 0.5 and. Example 3: two independent events. mary has to catch 2 2 buses to work. the probability the first bus will be late is 0.1 0.1 and the probability the second bus will be late is 0.3. 0.3. complete the tree diagram. work out the probability that at least one bus will be late. fill in the probabilities on the branches.
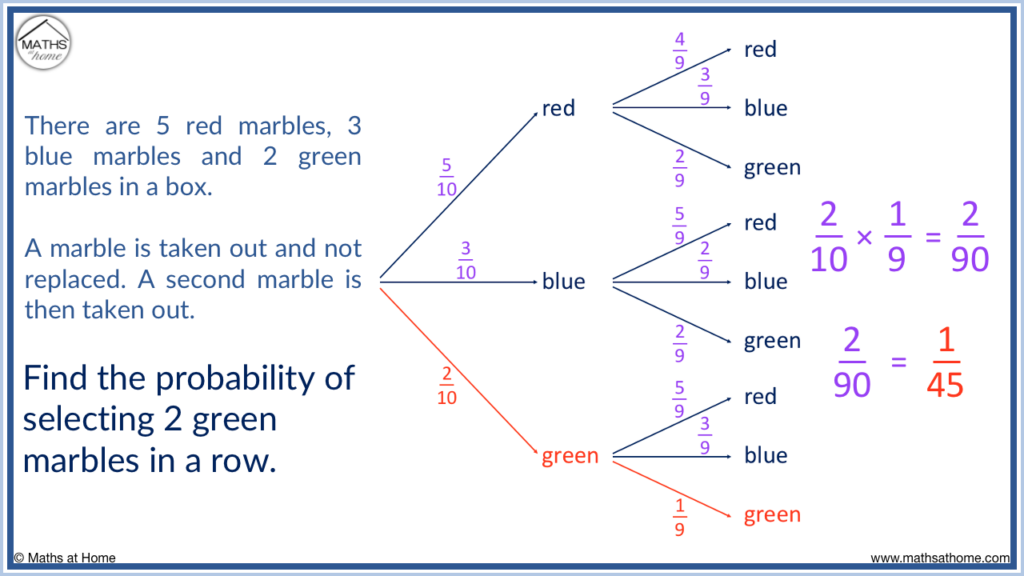
Draw A Probability Tree Diagram Online Johnson Weepty The rule for finding the probability of a particular event in a probability tree diagram occurring is to multiply the probabilities of the corresponding branches. for example, to prove that there is 0.25 probability of getting two heads in a row, you would multiply 0.5 x 0.5 (since the probability of getting a heads on the first flip is 0.5 and. Example 3: two independent events. mary has to catch 2 2 buses to work. the probability the first bus will be late is 0.1 0.1 and the probability the second bus will be late is 0.3. 0.3. complete the tree diagram. work out the probability that at least one bus will be late. fill in the probabilities on the branches. Solution. we illustrate using a tree diagram. the probability that we will get two black marbles in the first two tries is listed adjacent to the lowest branch, and it = 3 10. the probability of getting first black, second white, and third black = 3 20. similarly, the probability of getting first white, second black, and third black = 3 25. Suppose a jar contains 3 red and 4 white marbles. if two marbles are drawn without replacement, find the following probabilities using a tree diagram. the probability that both marbles are red. the probability that the first marble is red and the second white. the probability that one marble is red and the other white. solution.
Probability Tree Diagram Igcse At Mathematics Realm Solution. we illustrate using a tree diagram. the probability that we will get two black marbles in the first two tries is listed adjacent to the lowest branch, and it = 3 10. the probability of getting first black, second white, and third black = 3 20. similarly, the probability of getting first white, second black, and third black = 3 25. Suppose a jar contains 3 red and 4 white marbles. if two marbles are drawn without replacement, find the following probabilities using a tree diagram. the probability that both marbles are red. the probability that the first marble is red and the second white. the probability that one marble is red and the other white. solution.

Comments are closed.