Thrombus Shifts To Lcx Acute Anterior Mi Cardiogenic Shock Ostial Lad Occlusion How To Treat

Right And Left Coronary Trees Lad Left Anterior Descending Artery The study concluded that ostial lad lesions are no longer a risk factor for restenosis with des. in a large study with 162 ostial lad lesions, the use of des showed good outcomes with overall tlr rates of 8.3% . these results are similar to our study, as most of our patients were treated with des. The primary goal was to define the patient characteristics and procedural details for patients with ostial lad lesions. long term outcomes including all cause mortality, target lesion revascularization (tlr), target vessel revascularization (tvr) and instent restenosis (isr) were determined for the cohort.

Technical Feasibility And Safety Of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Major adverse cardiac events (mace) were defined as (1) cardiovascular death, and (2) nonfatal myocardial infarction (mi), and target vessel revascularization (tvr), defined as a repeated intervention (surgical or percutaneous) to treat a luminal stenosis within the stent or in the 5 mm distal or proximal segments adjacent to the stent. Introduction. coronary stenosis is often complicated with ostium of the left anterior descending (lad) or circumflex (lcx) artery. nonetheless, therapy is challenging owing to the complicated effects of the distal left main (lm) coronary artery, as revealed by prior intravascular ultrasound (ivus) studies []. Procedural success (defined as successful implantation of an lm stent and restoration of at least a thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (timi) flow of ii in the left anterior descending (lad) and left circumflex (lcx) branches) and major adverse cardiac events (mace) encompassing all cause death, new onset myocardial infarction, target lesion. Ostial left anterior descending artery (lad) acute myocardial infarction (ami) is associated with high morbidity and mortality owing to a broad ischemic area. 1 involvement of the left main trunk (lmt) bifurcation makes it challenging treatment wise; hence, several studies recommend stenting for complete plaque coverage from ostial lad to lmt.
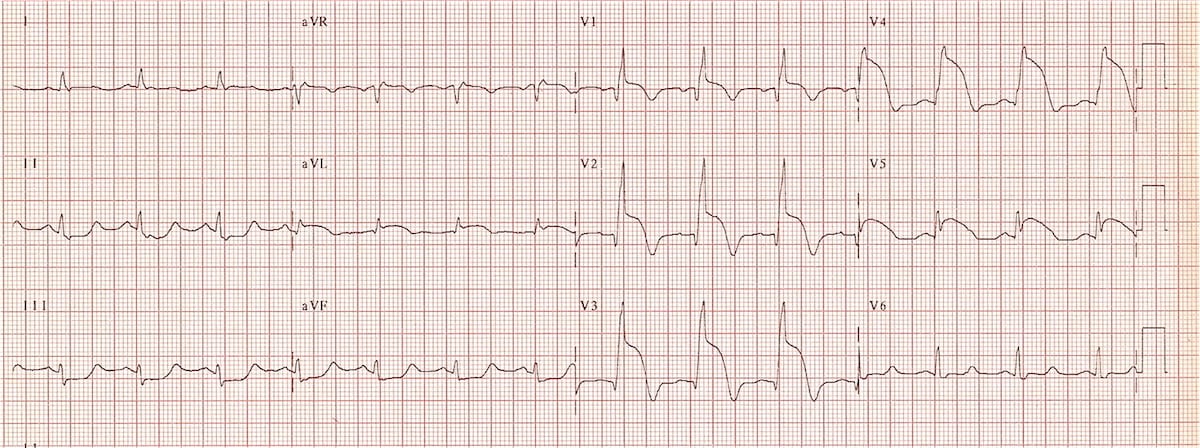
Anterior Myocardial Infarction вђў Litfl вђў Ecg Library Diagnosis Procedural success (defined as successful implantation of an lm stent and restoration of at least a thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (timi) flow of ii in the left anterior descending (lad) and left circumflex (lcx) branches) and major adverse cardiac events (mace) encompassing all cause death, new onset myocardial infarction, target lesion. Ostial left anterior descending artery (lad) acute myocardial infarction (ami) is associated with high morbidity and mortality owing to a broad ischemic area. 1 involvement of the left main trunk (lmt) bifurcation makes it challenging treatment wise; hence, several studies recommend stenting for complete plaque coverage from ostial lad to lmt. Distal lm bifurcation pci can be optimized by using ivus to ensure optimal stent expansion at both the ostial lad, ostial lcx and the distal lm. 24 angiographic in stent restenosis is predicted with ivus minimal stent area of 8.2 mm2 for the proximal lm above the polygon of confluence, 7.2 mm2 for the polygon of confluence, 6.3 mm2 for the lad. The higher incidence of acute lcx intervention in the crossover arm may be mitigated by routine fkbi, although the long term implication of this remains unclear. several determinants of success in the treatment of ostial lad disease remain unexplored, leaving unfilled gaps in the overall management algorithm.

Pathophysiology Of Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Vrogue Co Distal lm bifurcation pci can be optimized by using ivus to ensure optimal stent expansion at both the ostial lad, ostial lcx and the distal lm. 24 angiographic in stent restenosis is predicted with ivus minimal stent area of 8.2 mm2 for the proximal lm above the polygon of confluence, 7.2 mm2 for the polygon of confluence, 6.3 mm2 for the lad. The higher incidence of acute lcx intervention in the crossover arm may be mitigated by routine fkbi, although the long term implication of this remains unclear. several determinants of success in the treatment of ostial lad disease remain unexplored, leaving unfilled gaps in the overall management algorithm.

Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarc

Comments are closed.