The Knowledge Economy A 4 Minute Introduction

What Is Knowledge Economy Teachfloor Blog The broad label ”knowledge economy” covers a wide array of activities and interpretations. at least three lines of research fall under this umbrella. the oldest approach, with its origins dating back to the early 1960s, focuses on the rise of new science based industries and their role in social and economic change. The knowledge economy, which is the primary economy among developed nations, is an economy dependent on human capital and intangible assets, such as proprietary technology. the knowledge economy has placed the it ict industries at the forefront of overall economic growth. skill sets that include data analysis, creating and working with.

The Four Pillars Of The Knowledge Economy 4 Download Scientific 4.1 introduction. the knowledge based economy, sometimes referred to as the economy of ideas, is a stage of the economy where the production of goods and services is mainly driven by knowledge and by the increased emphasis on intangible assets and intellectual capital (powell and snellman, 2004; barlow, 1994). As the u.s. economy resurges in the wake of covid 19, its recovery can – in part – be attributed to the knowledge economy. a knowledge based economy is more resilient and better equipped to respond to specific problems and economic challenges. in this article, we’ll explore the knowledge economy – let’s start with the definition. The knowledge economy, or knowledge based economy, is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is based principally on knowledge intensive activities that contribute to advancement in technical and scientific innovation. [1] the key element of value is the greater dependence on human capital and intellectual property as. W e define the knowledge economy as production and services based on. knowledge intensi ve activities that contribute to an accelerated pace of technical and. scientific adv ance, as well as.

The Four Pillar Framework Of The Knowledge Economy Download The knowledge economy, or knowledge based economy, is an economic system in which the production of goods and services is based principally on knowledge intensive activities that contribute to advancement in technical and scientific innovation. [1] the key element of value is the greater dependence on human capital and intellectual property as. W e define the knowledge economy as production and services based on. knowledge intensi ve activities that contribute to an accelerated pace of technical and. scientific adv ance, as well as. Abstract we define the knowledge economy as production and services based on knowledge intensive activities that contribute to an accelerated pace of technical and scientific advance, as well as rapid obsolescence. the key component of a knowledge economy is a greater reliance on intellectual capabilities than on physical inputs or natural. Abstract. universities face new challenges in the knowledge economy, due to two underlying transformations. one is that universities have increasingly developed from bodies of professorial self governance bodies towards a status as ‘complete’ organisational actors, able to develop and deploy organisation level strategies.
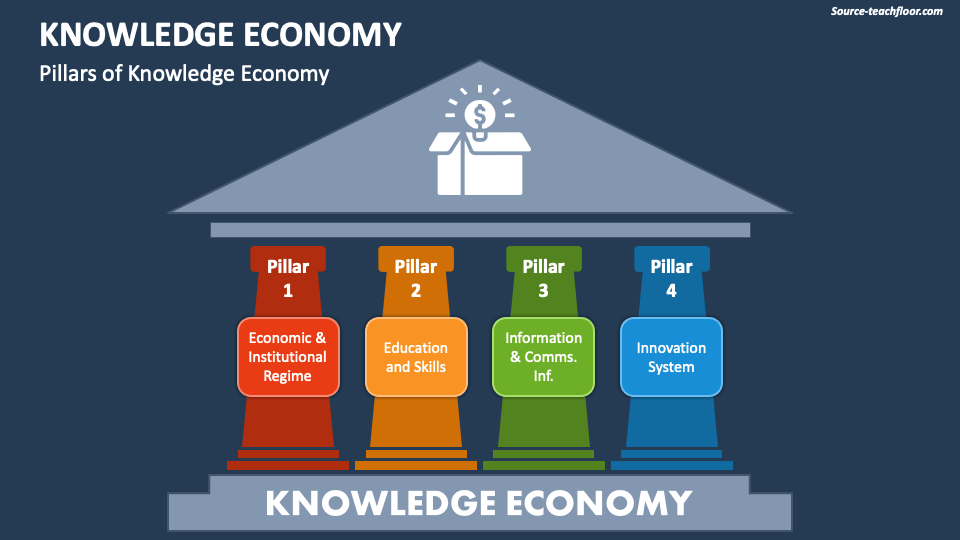
Knowledge Economy Powerpoint And Google Slides Template Ppt Slides Abstract we define the knowledge economy as production and services based on knowledge intensive activities that contribute to an accelerated pace of technical and scientific advance, as well as rapid obsolescence. the key component of a knowledge economy is a greater reliance on intellectual capabilities than on physical inputs or natural. Abstract. universities face new challenges in the knowledge economy, due to two underlying transformations. one is that universities have increasingly developed from bodies of professorial self governance bodies towards a status as ‘complete’ organisational actors, able to develop and deploy organisation level strategies.

Comments are closed.