The Functionalist Theory Of Society For A Level Sociology вђ Revision

The Functionalist Theory Of Society For A Level Sociology вђ Revisi Functionalism as a structural systems theory – it focuses on the needs of the social system as a whole; it is a consensus theory – it sees society as based on shared values; it is also a modernist theory – it believes that research can find the truth and lead to progress. functionalism is closely related to the new right and modernisation. The key ideas of functionalist perspective are as follows. there is such a thing as a social structure that exists independently from individuals. this social structure consists of norms values passed on through institutions which shape the individual. we should study society scientifically and at the macro level – looking for the general.
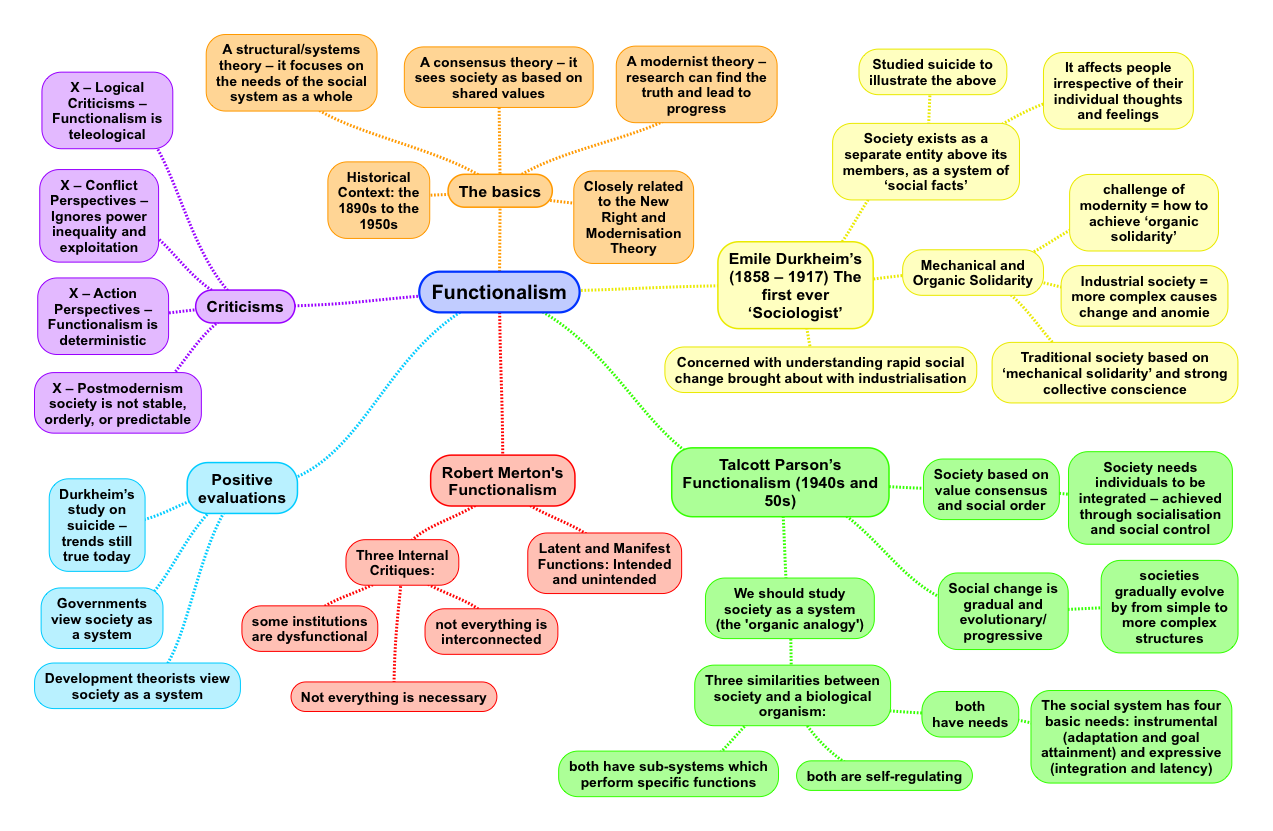
The Functionalist Theory Of Society For A Level Sociology вђ Revisi Functionalists davis and moore argue that education selects the most appropriate people to do particular jobs, yet other factors aside from qualifications, such as social contacts (who you know) also influence the labour market. functionalists believe that education equips people to perform different functional roles in society. Functionalism is a ‘structural consensus theory’. the ‘ structural bit’ means that functionalists argue there is a social structure that shapes individual behaviour through the process of socialisation. the ‘ consensus bit’ means that functionalists believe that a successful society is based on ‘value consensus’ – people agree. The main purpose of these notes is to provide a basic overview of different sociological perspectives. each set of notes is organised around three basic themes: 1. a brief overview of the perspective. 2. an outline of the “basic principles” on which each perspective is based. 3. a brief evaluation of the perspective. The functionalist perspective. the family meets the needs of society by socialising children into shared norms and values, that is, a value consensus leading to social harmony and stability. the family provides security for conception, birth and nurture of new members of society.

Comments are closed.