The Coeliac Trunk Branches Anastomoses Teachmeanatomy
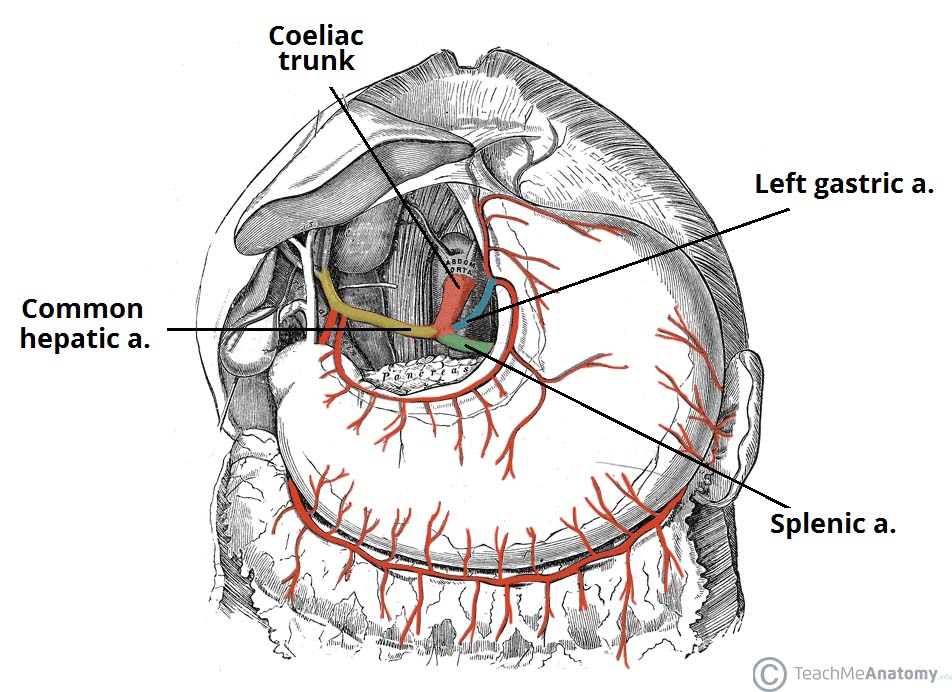
The Coeliac Trunk Branches Anastomoses Teachmeanatomy The stomach is the only organ to receive arterial supply from the three branches of the coeliac trunk (left gastric, splenic and common hepatic arteries). this is achieved through a system of anastomoses along the greater (gastroepiploic arteries) and lesser (gastric arteries) curvatures of the stomach. pancreas. Anatomical position. the superior mesenteric artery is the second of the three major anterior branches of the abdominal aorta (the other two are the coeliac trunk and inferior mesenteric artery). it arises anteriorly from the abdominal aorta at the level of the l1 vertebrae, immediately inferior to the origin of the coeliac trunk.

The Coeliac Trunk Branches Anastomoses Teachmeanatomy The inferior mesenteric artery is the last of the three major anterior branches of the abdominal aorta (the other two are the coeliac trunk and superior mesenteric artery). it arises at l3, near the inferior border of the duodenum, 3 4 cm above where the aorta bifurcates into the common iliac arteries. as the artery arises from the aorta, it. The celiac trunk (or coeliac trunk) is a major artery that supplies the foregut of the gastrointestinal tract. it arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebrae. it gives off three major branches, the left gastric, common hepatic and splenic arteries. the gastrointestinal tract extends from mouth to the rectum. The abdominal aorta's first major branch, the celiac trunk, arises anteriorly at approximately the t12 vertebral level. this short artery is the primary blood supply of the foregut and foregut derived organs in the superior abdominal cavity. the celiac trunk is an important blood vessel that may vary in form and branching pattern. pancreatic dysfunction, liver failure, and hemorrhage are some. These branches unite inferiorly to form the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery, which is given off by the superior mesenteric artery. that’s the branches of the celiac trunk. i really hope that's cleared things up. 3d video anatomy tutorial on the branches of the celiac artery trunk. clear audio visual description on the anatomy of the.

Celiac Artery And Branches Anatomy 1 Proper Hepatic Grepmed The abdominal aorta's first major branch, the celiac trunk, arises anteriorly at approximately the t12 vertebral level. this short artery is the primary blood supply of the foregut and foregut derived organs in the superior abdominal cavity. the celiac trunk is an important blood vessel that may vary in form and branching pattern. pancreatic dysfunction, liver failure, and hemorrhage are some. These branches unite inferiorly to form the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery, which is given off by the superior mesenteric artery. that’s the branches of the celiac trunk. i really hope that's cleared things up. 3d video anatomy tutorial on the branches of the celiac artery trunk. clear audio visual description on the anatomy of the. The anatomical variations of the coeliac trunk are due to developmental changes in the ventral segmental arteries. primitive segmental branches arise from the dorsal aorta and form the celiac trunk and the superior mesenteric artery. these branches are connected to the ventral longitudinal anastomotic channel. Observations on clinically important variations of the coeliac trunk were noted. results: the patterns of branching of the coeliac trunk were observed to vary from classical trifurcation to abnormal trifurcation, bifurcation, quadrifurcation, pentafurcation and even hexafurcation of the trunk. the additional branches of the trunk included the.

Comments are closed.