The Boutonniere Breakdown A Therapist S Guide To Evaluation Treatment

The Boutonniere Breakdown A Therapist S Guide To Evaluation Treatment A boutonniere deformity usually results from trauma directly to the digit or a rheumatic condition. the extensor tendon is the chief tissue of concern. the lateral portions of the extensor tendon will split, allowing the phalangeal head to protrude through the new opening created by the disrupted tendon. evaluation of boutonniere deformity. In the thumb, boutonnière deformity (bd) occurs at the metacarpophalangeal (mcp) joint, whereas in the remaining fingers bd occurs at the proximal interphalangeal (pip) joint. area(s) of specialty: hand therapy, orthopedic rehabilitation. description: a rupture of the central slip causing a deformity characterized by flexion of the pip joint.
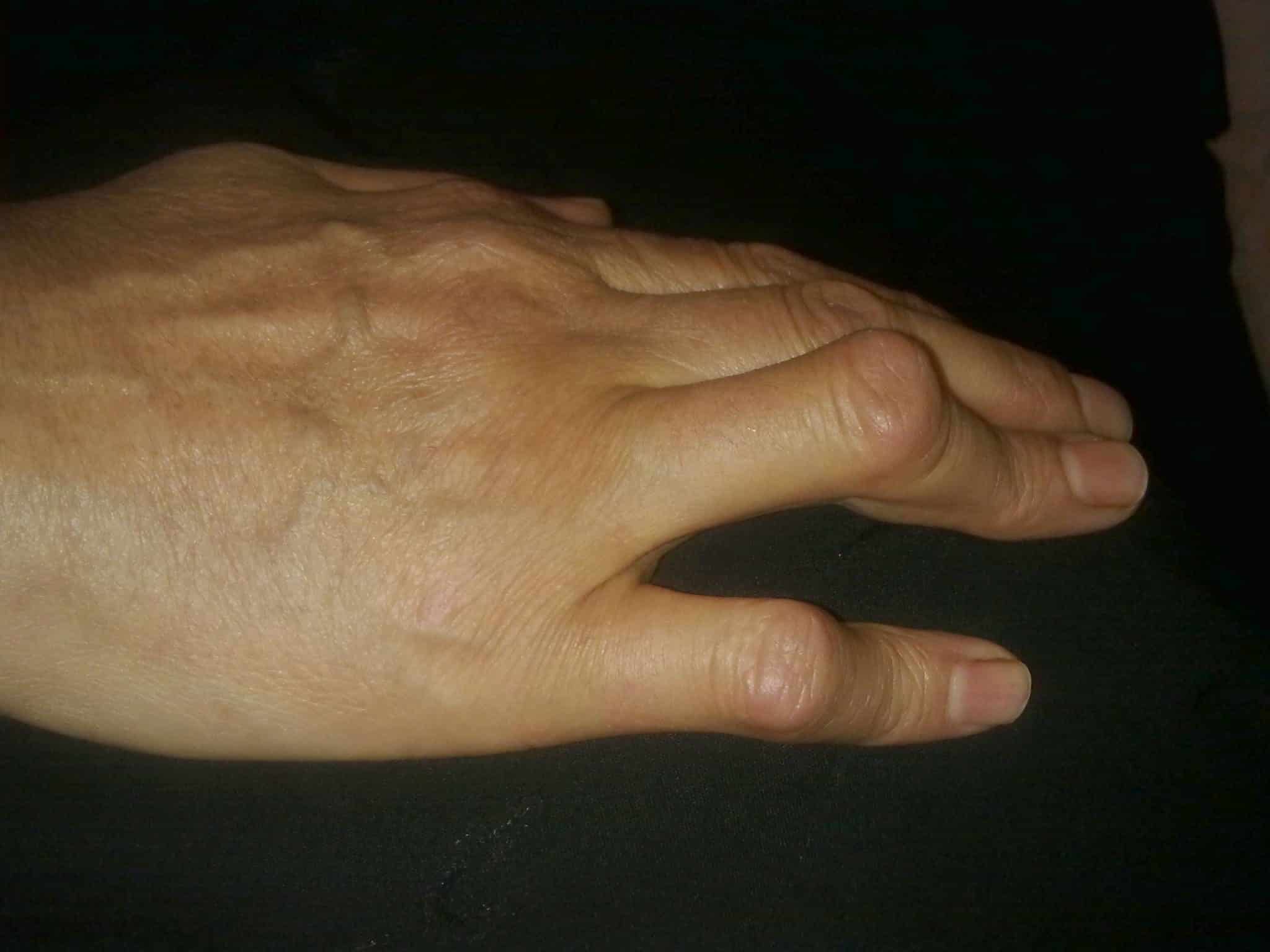
The Boutonniere Breakdown A Therapist S Guide To Evaluation Treatment Boutonniere deformity. boutonniere deformities are zone iii extensor tendon injuries characterized by pip flexion and dip extension. diagnosis is made clinically with pip flexion and dip extension of a digit with presence of a positive elson test. treatment of acute injuries involves splinting of the pip joint with operative management reserved. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what boutonnière deformity is, its causes and risk factors, how to recognize its symptoms, the diagnostic process, available treatment options, rehabilitation and physical therapy, prevention strategies, coping and support, as well as the latest research and advancements in the field. Boutonniere deformity describes a medical condition in which the finger is flexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint (pip) and hyperextended at the distal interphalangeal joint (dip). this is usually a result of trauma in the acute setting and is caused by a rupture of the pip central slip. this results in damage to the extensor function of the affected digit. a boutonniere deformity can. The full course of treatment of a bd should be discussed at the initiation of therapy. patients will often wear a static splint maintaining full pip extension after an operation to allow for healing. thereafter, patients will proceed to intermittent splinting and undergo passive stretching exercises.
The Boutonniere Breakdown A Therapist S Guide To Evaluation Treatment Boutonniere deformity describes a medical condition in which the finger is flexed at the proximal interphalangeal joint (pip) and hyperextended at the distal interphalangeal joint (dip). this is usually a result of trauma in the acute setting and is caused by a rupture of the pip central slip. this results in damage to the extensor function of the affected digit. a boutonniere deformity can. The full course of treatment of a bd should be discussed at the initiation of therapy. patients will often wear a static splint maintaining full pip extension after an operation to allow for healing. thereafter, patients will proceed to intermittent splinting and undergo passive stretching exercises. Management of boutonniere deformities. a boutonniere deformity in the finger is due to a disruption of the central slip, which is a key component of the extensor mechanism at the proximal interphalangeal joint (pipj). 1. the balance between the extensor mechanism over the pipj and the flexors is disrupted. as the deformity progresses, the pipj. The diagnosis and management of boutonniere deformity is complex and requires an interprofessional team that includes a primary care provider, nurse practitioner, physical therapist, hand surgeon, and orthopedic surgeon. the goal of treatment is to regain full range of motion of the affected finger.
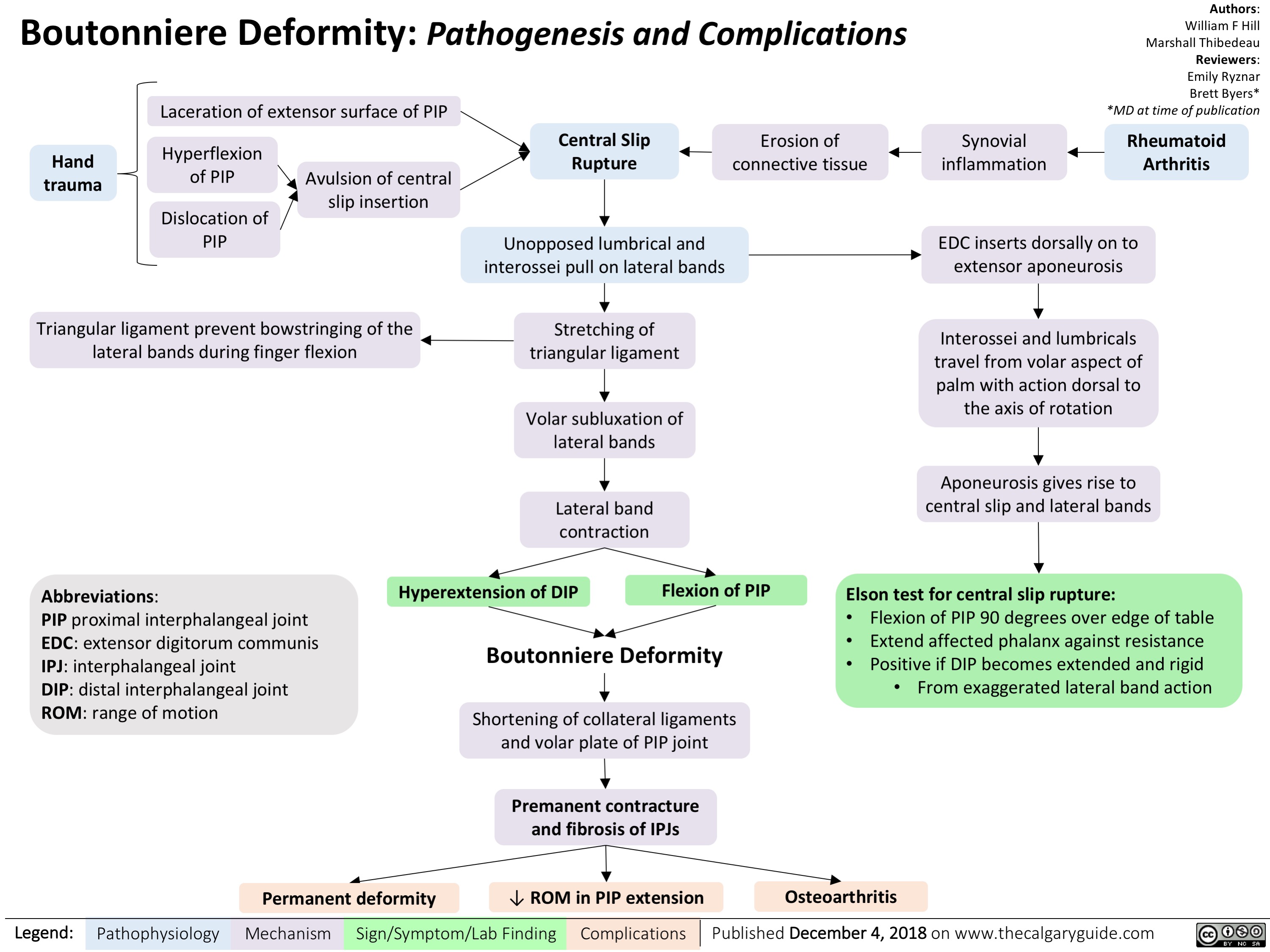
Boutonniere Deformity Pathogenesis And Complications Calgary Guide Management of boutonniere deformities. a boutonniere deformity in the finger is due to a disruption of the central slip, which is a key component of the extensor mechanism at the proximal interphalangeal joint (pipj). 1. the balance between the extensor mechanism over the pipj and the flexors is disrupted. as the deformity progresses, the pipj. The diagnosis and management of boutonniere deformity is complex and requires an interprofessional team that includes a primary care provider, nurse practitioner, physical therapist, hand surgeon, and orthopedic surgeon. the goal of treatment is to regain full range of motion of the affected finger.

Comments are closed.