Tertiary Consumer In Coral Reef

Coral Reef On Emaze Similarly, a single organism can serve more than one role in a food web. for example, a queen conch can be both a consumer and a detritivore, or decomposer. food webs consist of different organism groupings called trophic levels. in this example of a coral reef, there are producers, consumers, and decomposers. producers make up the first. Coral polyps, jellyfish, fan worm, and blue chromis are also abundant on the coral reef that feeds on smaller fishes, crustaceans, and zooplanktons. sometimes, corals also act as secondary consumers based on the food chain in which they participate. 4. tertiary consumers: these predators feed on secondary consumers. these predators are often.
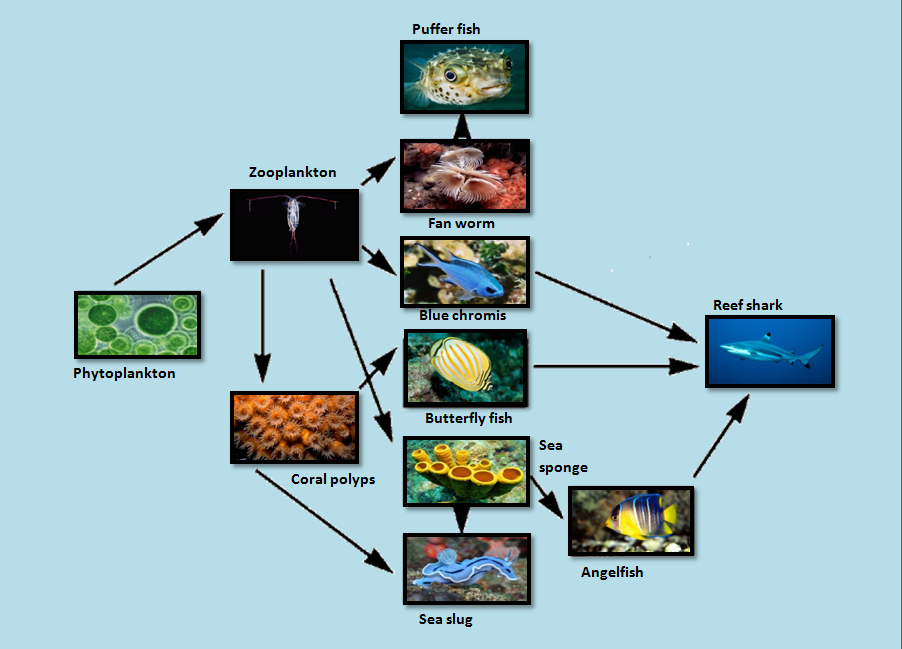
Food Web The Coral Reef Secondary consumers in coral reef food webs include marine animals such as fan worms, blue chromis, sea sponges, and coral polyps. tertiary consumers such as puffer fish, sea slugs, angelfish, and reef sharks feed on these secondary consumers. the delicate balance of the coral reef food web is crucial for the ecosystem’s health and survival. In general, for coral reef food webs it is somewhat simpler to consider only these three basic trophic levels. however, for some of the component food chains within the coral reef food web, a fourth level – tertiary consumers (top predators) – can also sometimes be readily distinguished. Resource. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. pictures represent the organisms. Tertiary consumers eat both primary and secondary consumers and keep the food web in balance. coral reefs are hot spots of biodiversity. coastal reefs, like the great barrier reef , exist in warm.

Food Chain Great Barrier Reef At Francis Wall Blog Resource. feeding relationships are often shown as simple food chains – in reality, these relationships are much more complex, and the term ‘food web’ more accurately shows the links between producers, consumers and decomposers. a food web diagram illustrates ‘what eats what’ in a particular habitat. pictures represent the organisms. Tertiary consumers eat both primary and secondary consumers and keep the food web in balance. coral reefs are hot spots of biodiversity. coastal reefs, like the great barrier reef , exist in warm. This is a coral reef food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface. the primary consumers – the coral, sea turtle, and fish. the secondary consumers – the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea. A coral reef is a diverse environment that encompasses a wide ranging food web. trophic levels in a coral reef describe the feeding position of the plants and animals that make up that ecosystem. plants, which are able to create their own energy, are primary producers. herbivores, creatures that eat primary producers, make up the second level.

Ppt Life In A Coral Reef Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id This is a coral reef food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface. the primary consumers – the coral, sea turtle, and fish. the secondary consumers – the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea. A coral reef is a diverse environment that encompasses a wide ranging food web. trophic levels in a coral reef describe the feeding position of the plants and animals that make up that ecosystem. plants, which are able to create their own energy, are primary producers. herbivores, creatures that eat primary producers, make up the second level.

Coral Reef Food Web Diagram

Comments are closed.