Supply And Demand Plot
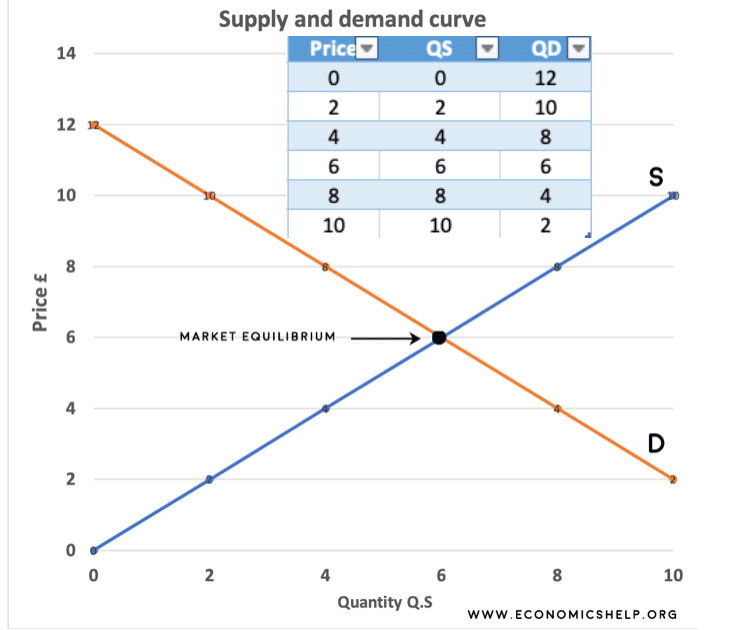
Example Of Plotting Demand And Supply Curve Graph Economics Help Calculus: fundamental theorem of calculus. example. explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Create supply & demand graphs in minutes. customize supply and demand graphs with easy to use drag and drop tools. purpose built shapes for grids, graphs, charts and 50 more diagram types. link survey, market research, and sales data in one place with integrated notes. multiple pre made supply and demand graph templates to get a quick start.
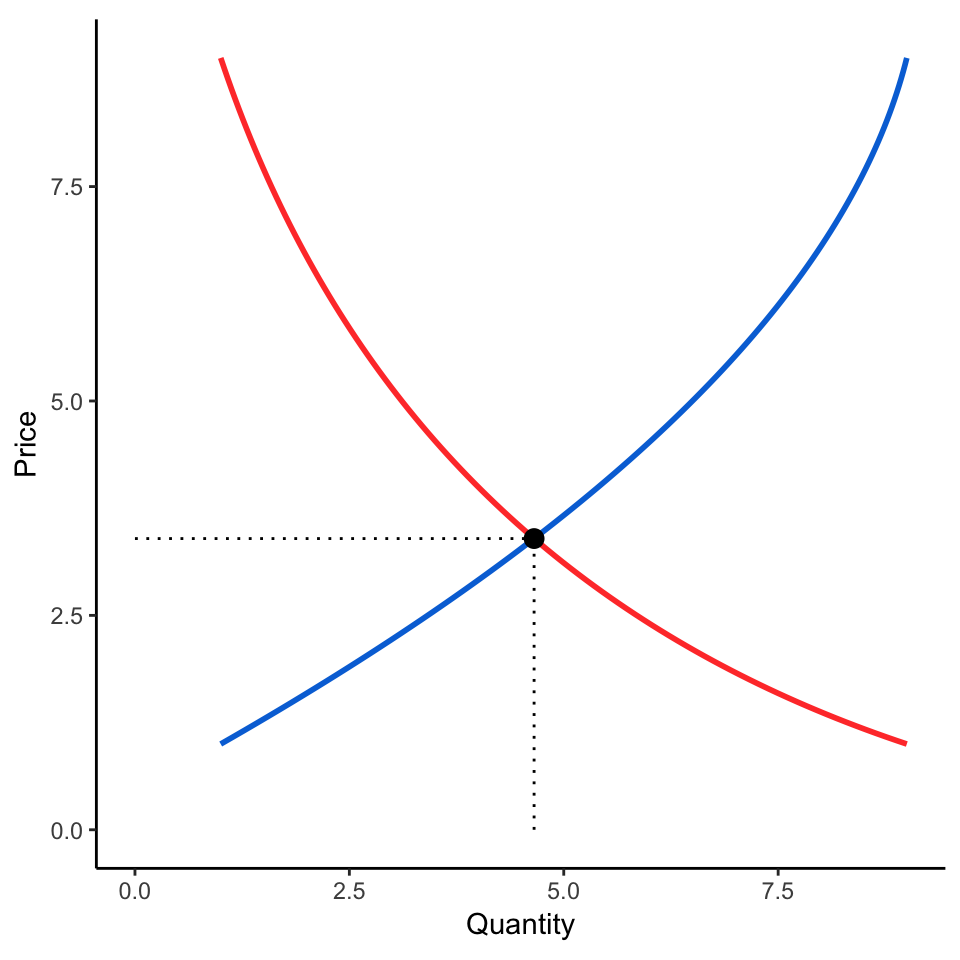
Create Supply And Demand Economics Curves With Ggplot2 Andrew Heiss David murphy, karl lew, wilson cheung, harrison caudill, and kyle moore. i’ve drawn inspiration and support from the community nicky case has built up around explorable explanations, including amit patel, chris walker, hamish todd, andy matuschak, and many others. the econgraphs logo was generously contributed by jørgen veisdal. Part 7.1 drawing supply and demand diagrams. the data is in natural logs: for example, the numbers in the price column are the logs of the prices of watermelons in each year, rather than the prices in dollars. before plotting supply and demand curves, we will first practise converting natural logarithms to numbers. Supply and demand shift right. in this diagram, supply and demand have shifted to the right. this has led an increase in quantity (q1 to q2) but price has stayed the same. it is possible, that if there is an increase in demand (d1 to d2) this encourages firms to produce more and so supply increases as well. To make a supply and demand graph with data, you need to plot the data points on a graph. the x axis will represent the quantity of the item, and the y axis will represent the item's price. then, draw a line connecting the data points to show the supply and demand curves.

Example Of Plotting Demand And Supply Curve Graph Economics Help Supply and demand shift right. in this diagram, supply and demand have shifted to the right. this has led an increase in quantity (q1 to q2) but price has stayed the same. it is possible, that if there is an increase in demand (d1 to d2) this encourages firms to produce more and so supply increases as well. To make a supply and demand graph with data, you need to plot the data points on a graph. the x axis will represent the quantity of the item, and the y axis will represent the item's price. then, draw a line connecting the data points to show the supply and demand curves. 2. add your starting supply and demand curves. plot your supply curve according to the law of supply. the law of supply states that when the market price of a unit goes up, firms will produce more of that unit since it represents a greater potential profit. choose two prices, and forecast how many units you would produce at each one. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage.
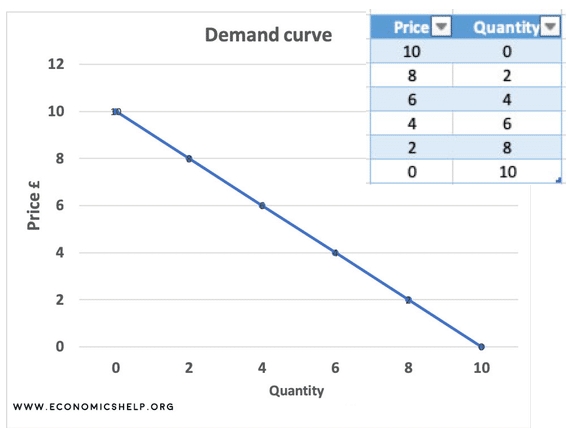
Example Of Plotting Demand And Supply Curve Graph Economics Help 2. add your starting supply and demand curves. plot your supply curve according to the law of supply. the law of supply states that when the market price of a unit goes up, firms will produce more of that unit since it represents a greater potential profit. choose two prices, and forecast how many units you would produce at each one. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage.

Comments are closed.