Sum Of Arithmetic Sequence Formula Derivation Examples

Sum Of Arithmetic Sequence Formula Derivation Examples The sum of the arithmetic sequence can be derived using the general term of an arithmetic sequence, a n = a 1 (n – 1)d. step 1: find the first term. step 2: check for the number of terms. step 3: generalize the formula for the first term, that is a 1 and thus successive terms will be a 1 d, a 1 2d. Arithmetic progression (also called arithmetic sequence), is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. each term therefore in an arithmetic progression will increase or decrease at a constant value called the common difference, d. d = a2 − a1 = a3 − a2 = a4 − a3 d = a 2 − a 1 = a 3 −.
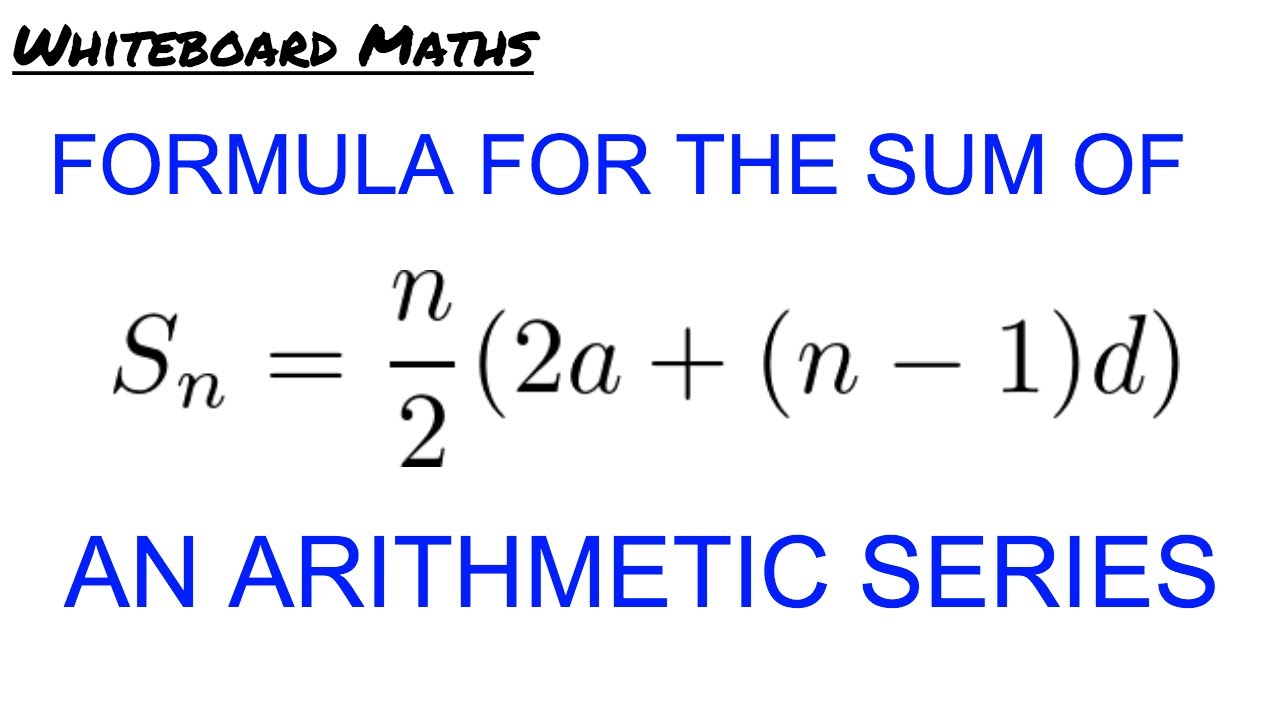
Derivation Of The Formula For The Sum Of An Arithmetic Series Youtube Derivation of the arithmetic series formula. this is a good way to appreciate why the formula works. let’s add the terms in reverse or descending order. here’s the “trick”. now, we sum up the two arithmetic series above – the ones with ascending and descending terms. notice that the sum of each column is always. Definition 1: a mathematical sequence in which the difference between two consecutive terms is always a constant and it is abbreviated as ap. definition 2: an arithmetic sequence or progression is defined as a sequence of numbers in which for every pair of consecutive terms, the second number is obtained by adding a fixed number to the first one. Arithmetic sequences are sequences in which their terms are formed from the previous term by adding a certain number called the common difference. the sum of the first n n terms of an arithmetic sequence can be found with the following formula. s {n}=\frac {n} {2} (a l) s n = 2n(a l) where, a. a a is the first term of the sequence. Examples of applying the arithmetic series formula. example 1: find the sum of the first [latex]100[ latex] natural numbers. this is an easy problem. the purpose of this problem is to serve as an introductory example. this should help you get familiar quickly with the arithmetic series formula.

Sum Of Numbers In Arithmetic Sequence Arithmetic sequences are sequences in which their terms are formed from the previous term by adding a certain number called the common difference. the sum of the first n n terms of an arithmetic sequence can be found with the following formula. s {n}=\frac {n} {2} (a l) s n = 2n(a l) where, a. a a is the first term of the sequence. Examples of applying the arithmetic series formula. example 1: find the sum of the first [latex]100[ latex] natural numbers. this is an easy problem. the purpose of this problem is to serve as an introductory example. this should help you get familiar quickly with the arithmetic series formula. This video explains how to derive the formula that gives you the sum of an arithmetic series. this video also explains the difference between an arithmetic. Derivation – sum of arithmetic series. arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which every term after the first is obtained by adding a constant, called the common difference (d). to find the nth term of a an arithmetic sequence, we know an = a1 (n – 1)d. the first term is a1, second term is a1 d, third term is a1 2d, etc.

Sum Of The First N Terms Of An Arithmetic Progression A Plus Topper This video explains how to derive the formula that gives you the sum of an arithmetic series. this video also explains the difference between an arithmetic. Derivation – sum of arithmetic series. arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which every term after the first is obtained by adding a constant, called the common difference (d). to find the nth term of a an arithmetic sequence, we know an = a1 (n – 1)d. the first term is a1, second term is a1 d, third term is a1 2d, etc.

Comments are closed.