Sum Of Arithmetic Progression Arithmetic Progression Assignment
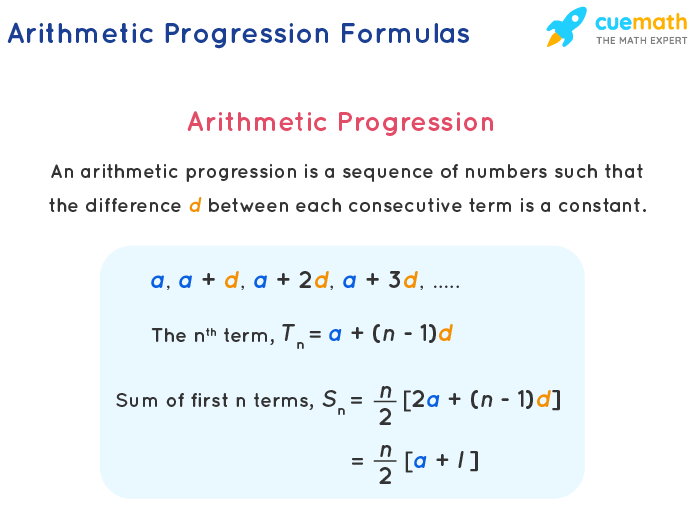
Arithmetic Progression Formula Sum Examples Ap Formula Arithmetic progression. an arithmetic progression (ap) is a sequence where the differences between every two consecutive terms are the same. for example, the sequence 2, 6, 10, 14, … is an arithmetic progression (ap) because it follows a pattern where each number is obtained by adding 4 to the previous term. 2sn = n(a1 an) dividing both sides by 2 leads us the formula for the n th partial sum of an arithmetic sequence17: sn = n(a1 an) 2. use this formula to calculate the sum of the first 100 terms of the sequence defined by an = 2n − 1. here a1 = 1 and a100 = 199. s100 = 100(a1 a100) 2 = 100(1 199) 2 = 10, 000.
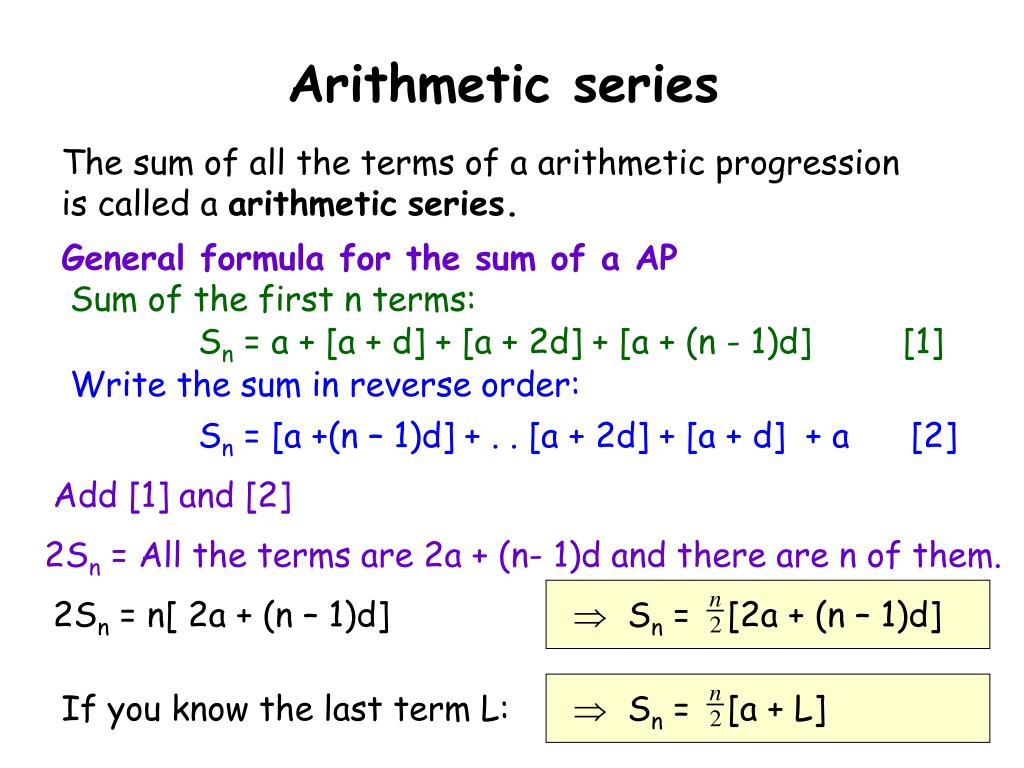
Sum Of Arithmetic Progression Arithmetic Progression Assignment Definition 1: a mathematical sequence in which the difference between two consecutive terms is always a constant and it is abbreviated as ap. definition 2: an arithmetic sequence or progression is defined as a sequence of numbers in which for every pair of consecutive terms, the second number is obtained by adding a fixed number to the first one. Problem: given the n th term of an arithmetic progression t n = 2 n 3, find the sum of the first n terms, s n, using the relationships p = 2 p and q = q − p derived from the general form of an arithmetic progression sum s n = p n 2 q n. solution: step 1: identify p and q from t n. from t n = 2 n 3, we identify:. The arithmetic series formula and the arithmetic sequence formula (nth term formula) because they go hand in hand when solving many problems. \large { {s n} = n\left ( { { { {a 1} \, {a n}} \over 2}} \right)} before we start working with examples, you may recall me mentioning that the arithmetic sequence formula is embedded in the arithmetic. Arithmetic progression (also called arithmetic sequence), is a sequence of numbers such that the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. each term therefore in an arithmetic progression will increase or decrease at a constant value called the common difference, d. d = a2 − a1 = a3 − a2 = a4 − a3 d = a 2 − a 1 = a 3 −.

Comments are closed.