Structural Chemical Formula Of Caffeine Molecule With Roasted Coffee
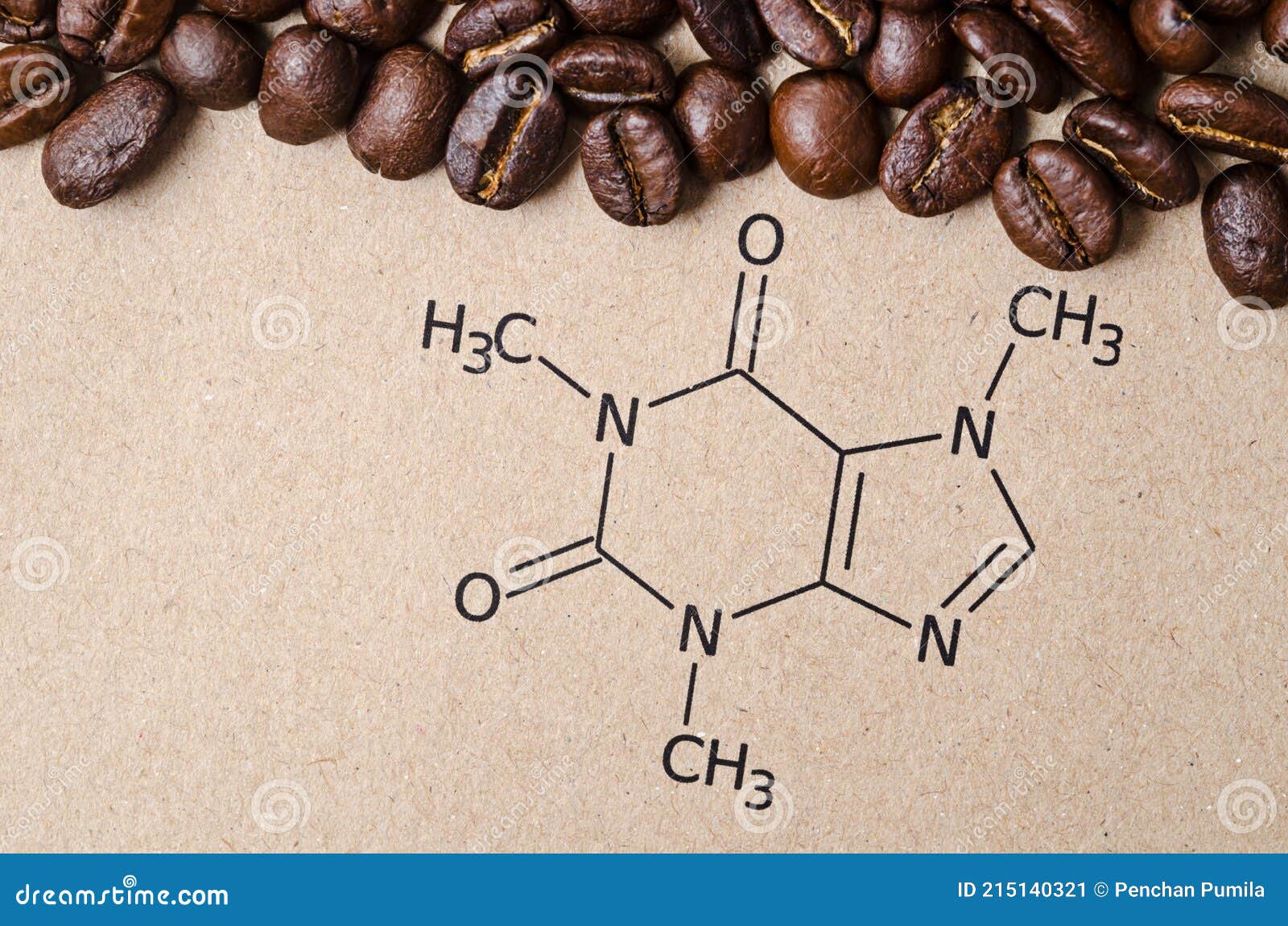
Structural Chemical Formula Of Caffeine Molecule With Roasted Coffee Lipids (oils and fats): coffee has oils and fats that enhance its texture and fragrance. these lipids can trap certain volatile aromatic compounds, releasing them as you savor those fragrant sips. water: the water content in green coffee should fall within 10.5% to 11.5% of its total weight. Caffeine is a drug of the methylxanthine class used for a variety of purposes, including certain respiratory conditions of the premature newborn, pain relief, and to combat drowsiness. caffeine is similar in chemical structure to [theophylline] and [theobromine]. it can be sourced from coffee beans, but also occurs naturally in various teas and.

Structural Chemical Formula Of Caffeine Molecule With Roasted Coffee Caffeine. formula: c 8 h 10 n 4 o 2; molecular weight: chemical structure: this structure is also available as a 2d mol file or as a computed 3d sd file. Chemical constituents. the main constituents of coffee are caffeine, tannin, fixed oil, carbohydrates, and proteins. it contains 2–3% caffeine, 3–5% tannins, 13% proteins, and 10–15% fixed oils. in the seeds, caffeine is present as a salt of chlorogenic acid (cga). also it contains oil and wax [2]. The chemical formula for caffeine is c 8 h 10 n 4 o 2 and chemical structure is shown in figure 1. pure caffeine occurs as odorless, white powder. view in full text. Its chemical formula is c8h10n4o2, meaning it contains 8 carbon (c) atoms, 10 hydrogen (h) atoms, 4 nitrogen (n) atoms, and 2 oxygen (o) atoms. the structure of a caffeine molecule can be visualized as a combination of several organic functional groups. it consists of three fused rings: two six membered rings (hexagons) and one five membered.
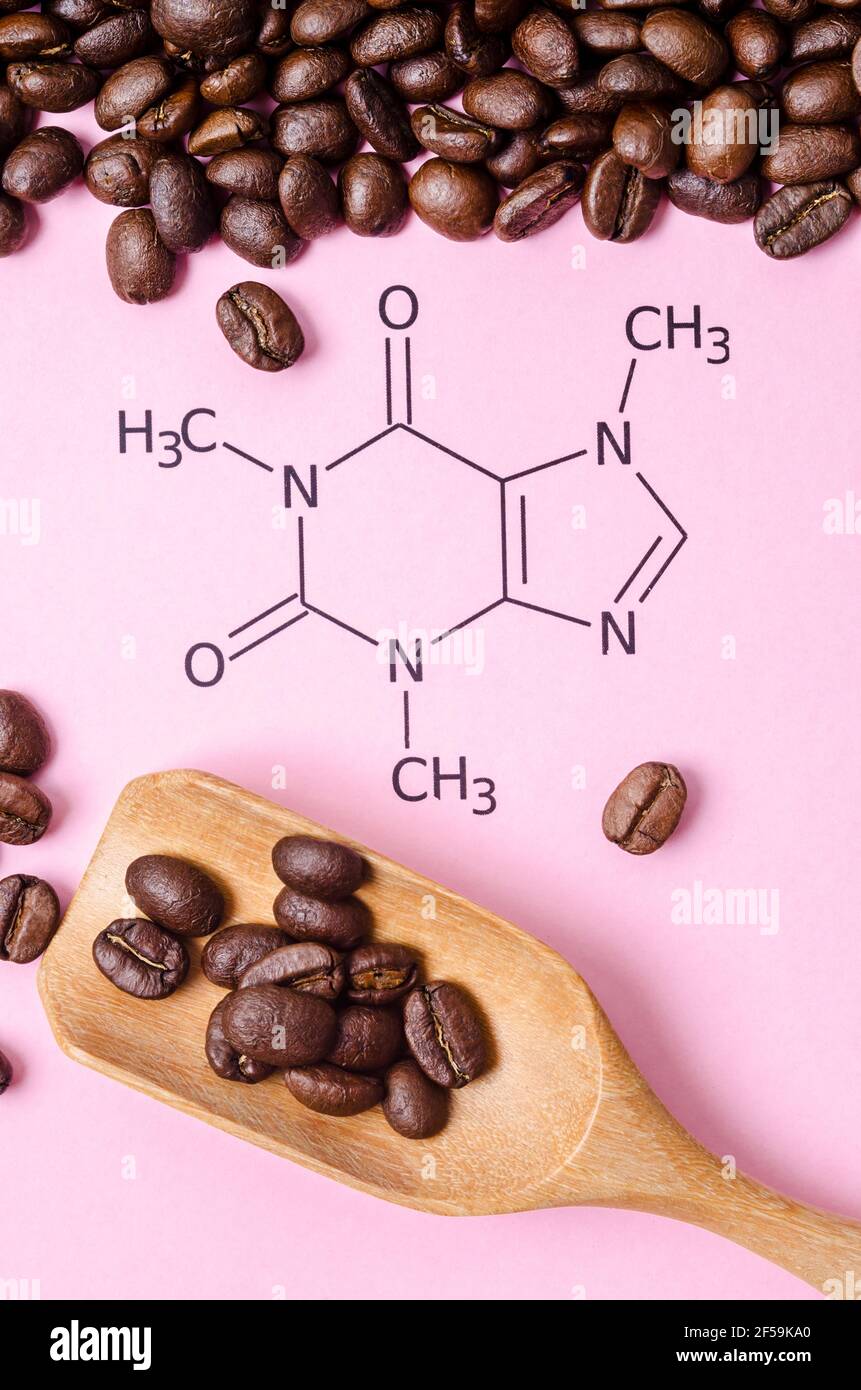
Structural Chemical Formula Of Caffeine Molecule With Roasted Coffee The chemical formula for caffeine is c 8 h 10 n 4 o 2 and chemical structure is shown in figure 1. pure caffeine occurs as odorless, white powder. view in full text. Its chemical formula is c8h10n4o2, meaning it contains 8 carbon (c) atoms, 10 hydrogen (h) atoms, 4 nitrogen (n) atoms, and 2 oxygen (o) atoms. the structure of a caffeine molecule can be visualized as a combination of several organic functional groups. it consists of three fused rings: two six membered rings (hexagons) and one five membered. Chemspider record containing structure, synonyms, properties, vendors and database links for caffeine, 58 08 2, guaranine. molecular formula: c 8 h 10 n 4 o 2:. Chemical structure of caffeine. caffeine, one of the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive substances, is a naturally occurring compound that belongs to a class of alkaloids called methylxanthines. with a molecular formula of c8h10n4o2 and a molar mass of 194.194 g mol, caffeine is made up of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms.

Structural Chemical Formula Of Caffeine Molecule With Roasted Coffee Chemspider record containing structure, synonyms, properties, vendors and database links for caffeine, 58 08 2, guaranine. molecular formula: c 8 h 10 n 4 o 2:. Chemical structure of caffeine. caffeine, one of the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive substances, is a naturally occurring compound that belongs to a class of alkaloids called methylxanthines. with a molecular formula of c8h10n4o2 and a molar mass of 194.194 g mol, caffeine is made up of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms.

Comments are closed.