Standard Normal Distribution Tables Z Scores Probability Empirical Rule Stats
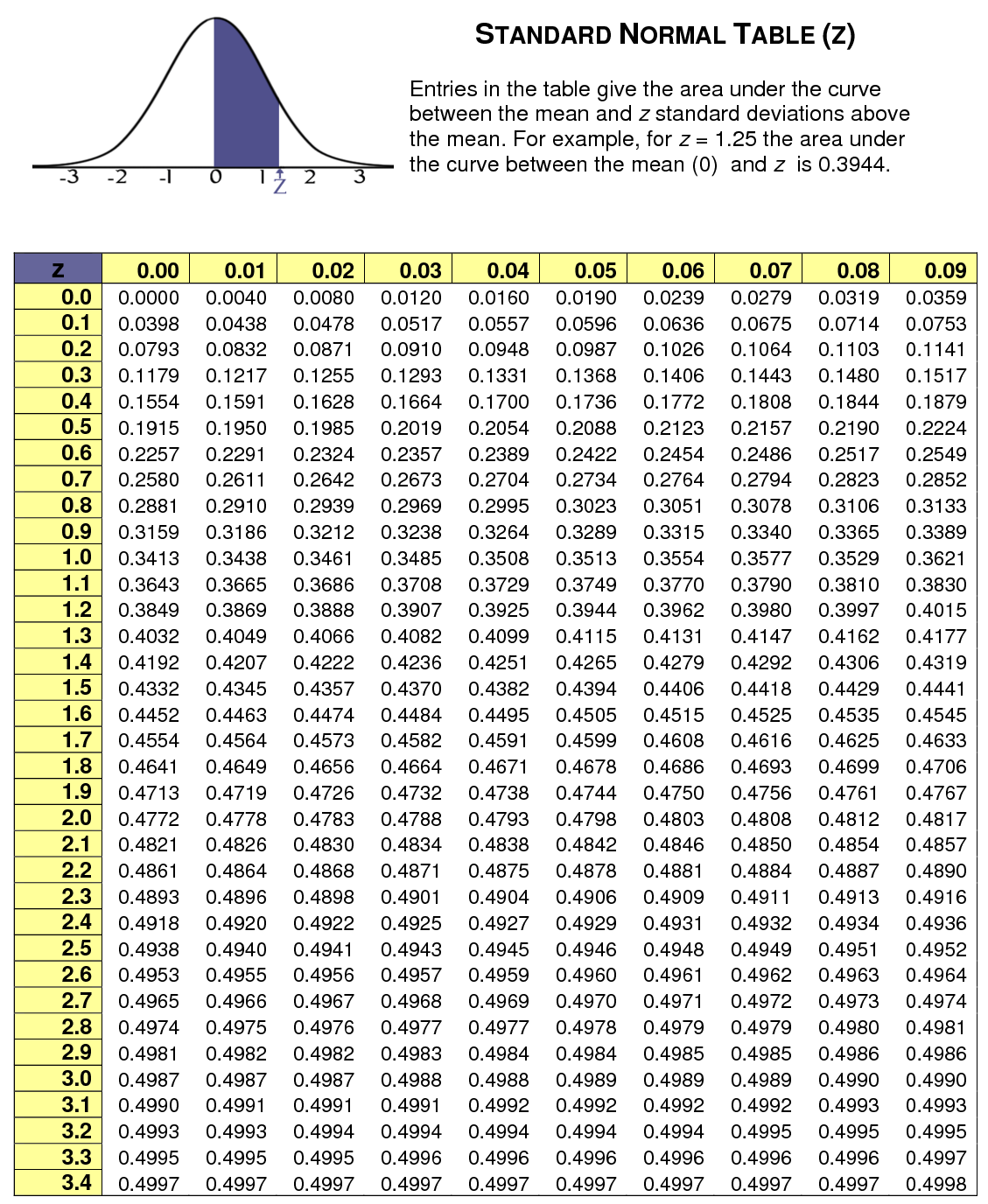
Z Score Table Standard Normal Distribution Statcalculators This statistics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into standard normal distributions. it explains how to find the z score given a value of x as w. X – m = 1380 − 1150 = 230. step 2: divide the difference by the standard deviation. sd = 150. z = 230 ÷ 150 = 1.53. the z score for a value of 1380 is 1.53. that means 1380 is 1.53 standard deviations from the mean of your distribution. next, we can find the probability of this score using a z table.

Free Course Standard Normal Distribution Tables Z Scores Prob 2.2.7 the empirical rule. a normal distribution is symmetrical and bell shaped. the empirical rule is a statement about normal distributions. your textbook uses an abbreviated form of this, known as the 95% rule, because 95% is the most commonly used interval. the 95% rule states that approximately 95% of observations fall within two standard. What is the maximum time a skater can post if he wants to skate faster than. normal distributions follow the empirical rule, also called the 68 95 99.7 rule. the rule tells us that, for a normal distribution, there’s a 68% chance a data point falls within 1 standard deviation of the mean, there’s a 95% chance a data point falls within 2. The empirical rule is a rule telling us about where an observation lies in a normal distribution. the empirical rule states that approximately 68% of data will be within one standard deviation of the mean, about 95% will be within two standard deviations of the mean, and about 99.7% will be within three standard deviations of the mean. The empirical rule in statistics, also known as the 68 95 99 rule, states that for normal distributions, 68% of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean, 95% will fall within two standard deviations, and 99.7% will occur within three standard deviations. thanks to the empirical rule, the mean and standard.

Itec Fayoum 39 Standard Normal Distribution Tables Z Scores The empirical rule is a rule telling us about where an observation lies in a normal distribution. the empirical rule states that approximately 68% of data will be within one standard deviation of the mean, about 95% will be within two standard deviations of the mean, and about 99.7% will be within three standard deviations of the mean. The empirical rule in statistics, also known as the 68 95 99 rule, states that for normal distributions, 68% of observed data points will lie inside one standard deviation of the mean, 95% will fall within two standard deviations, and 99.7% will occur within three standard deviations. thanks to the empirical rule, the mean and standard. Dive into a comprehensive 51 minute statistics tutorial covering standard normal distributions, z scores, probability, and the empirical rule. learn how to calculate z scores from given values, determine probabilities using the empirical rule and z tables, and find areas under the curve. C. z = y − μ σ y − μ σ = 4 − 2 1 4 − 2 1 = 2, where µ = 2 and σ = 1. the z score for y = 4 is z = 2. this means that four is z = 2 standard deviations to the right of the mean. . therefore, x = 17 and y = 4 are both two of their own standard deviations to the right of their respective.
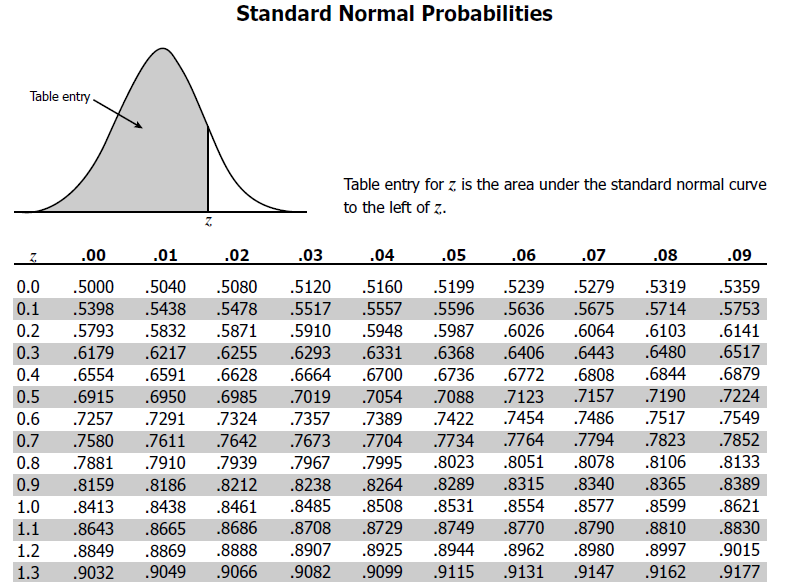
Z Score Table Standard Normal Table Negative Z Scoresођ Dive into a comprehensive 51 minute statistics tutorial covering standard normal distributions, z scores, probability, and the empirical rule. learn how to calculate z scores from given values, determine probabilities using the empirical rule and z tables, and find areas under the curve. C. z = y − μ σ y − μ σ = 4 − 2 1 4 − 2 1 = 2, where µ = 2 and σ = 1. the z score for y = 4 is z = 2. this means that four is z = 2 standard deviations to the right of the mean. . therefore, x = 17 and y = 4 are both two of their own standard deviations to the right of their respective.

Comments are closed.