Solved The Tangential Velocity Component Linear The Surface Chegg

Solved 2 5 The Tangential Velocity Component Of Air At The Chegg Here’s the best way to solve it. first, start by applying bernoulli's equation to the flow around the cylinder to relate the pressure distribution to the given tangential velocity component. the tangential velocity component linear the surface of a cylinder of radius a is given by: u theta = 2u sin theta gamma 2pi a assuming that there are. The linear (tangential) velocity of a point on a rotating body will always be to the radial direction along the body. a) perpendicular b) parallel c) equal d) greater than there are 2 steps to solve this one.

Solved 3 Tangential Component 50 Points The Illustration Chegg Theorem 12.5.2: tangential and normal components of acceleration. let ⇀ r(t) be a vector valued function that denotes the position of an object as a function of time. then ⇀ a(t) = ⇀ r′ ′(t) is the acceleration vector. the tangential and normal components of acceleration a ⇀ t and a ⇀ n are given by the formulas. Directly below the axle, where the tire touches the road, the tire tread moves backward with respect to the axle with tangential velocity v = r ω v = r ω, where r is the tire radius. because the road is stationary with respect to this point of the tire, the car must move forward at the linear velocity v. a larger angular velocity for the tire. Its tangential component of acceleration is a) positive. b) negative. c) zero. d) constant. 2. the normal component of acceleration represents a) the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. b) the time rate of change in the direction of the velocity. c) magnitude of the velocity. d) direction of the total acceleration. Integrated by justin marshall. 2.6: tangential and normal components of acceleration is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. this section breaks down acceleration into two components called the tangential and normal components. similar to how we break down all vectors into \ (\hat {\textbf.

Solved Tangential Velocity п їv Tan Vtan п ї Of The Black Chegg Its tangential component of acceleration is a) positive. b) negative. c) zero. d) constant. 2. the normal component of acceleration represents a) the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. b) the time rate of change in the direction of the velocity. c) magnitude of the velocity. d) direction of the total acceleration. Integrated by justin marshall. 2.6: tangential and normal components of acceleration is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. this section breaks down acceleration into two components called the tangential and normal components. similar to how we break down all vectors into \ (\hat {\textbf. R = 0.30 m. angular velocity, ω = 40radpers. tangential velocity formula is as given: vt = r × ω. = 0.30 × 40. = 12 m s. thus tangential velocity will be 12 meters per sec. q.2: if a wheel is turning with a speed of 12 m per sec, and its angular velocity is 6 radians per sec. then find out its radius. The linear component of angular velocity is the linear velocity. when the linear velocity is generalized to any point along the circular curve, the new velocity is called the tangential velocity .
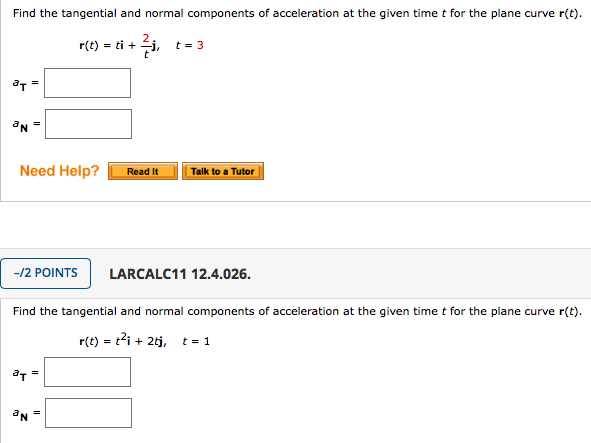
Solved Find The Tangential And Normal Components Of Chegg R = 0.30 m. angular velocity, ω = 40radpers. tangential velocity formula is as given: vt = r × ω. = 0.30 × 40. = 12 m s. thus tangential velocity will be 12 meters per sec. q.2: if a wheel is turning with a speed of 12 m per sec, and its angular velocity is 6 radians per sec. then find out its radius. The linear component of angular velocity is the linear velocity. when the linear velocity is generalized to any point along the circular curve, the new velocity is called the tangential velocity .

Comments are closed.