Solved If Two Bodies Are Pressed Against Each Other Compressive
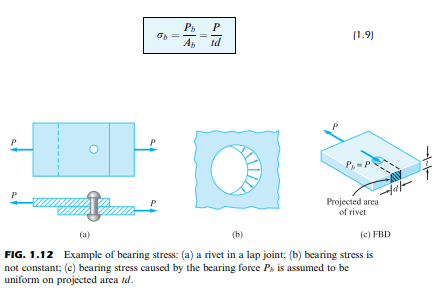
Solved If Two Bodies Are Pressed Against Each Other Compressive If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet or bolt and the side of the hole it is in. If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet or bolt and the side of the hole it is in.

Lesson 2 3 2 4 Pdf Strength Of Materials Topic 2 3 Bearing Stress 1. represent compressive stresses developed from surface pressures between two curved bodies pressed together; 2. possess an area of contact. the initial point contact (spheres) or line contact (cylinders) become area contacts, as a result of the force pressing the bodies against each other; 3. When two bodies with rough surfaces are pressed against each other, the true contact area formed between the two bodies, , is much smaller than the apparent or nominal contact area . the mechanics of contacting rough surfaces are discussed in terms of normal contact mechanics and static frictional interactions. [ 29 ]. If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet and the side of its hole. If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet and the side of its hole.

Solved 2 Two Bodies Connected By String Are Moving As Shown In The If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet and the side of its hole. If two bodies are pressed against each other, compressive forces are developed on the area of contact. the pressure caused by these surface loads is called bearing stress. examples of bearing stress are the soil pressure beneath a pier and the contact pressure between a rivet and the side of its hole. Tensile or compressive stress, strain, and young’s modulus. tension or compression occurs when two antiparallel forces of equal magnitude act on an object along only one of its dimensions, in such a way that the object does not move. one way to envision such a situation is illustrated in figure 12.18. a rod segment is either stretched or. A 10 ft diameter spherical tank has wall thickness of. 1.) a stress of 20 mpa is developed in a circular section of 10 mm in diameter. find the applied force in the body. a.) 1000 pi n. b.)2000 pi n. c.) 500 pi n. d.) 250 pi n. 2.) calculate the sheared area if the shear stress is 20 mpa and the applied force is 20kn.

Solved Two Bodies With Masses M1 And M2 And Velocities V1 And V2 Tensile or compressive stress, strain, and young’s modulus. tension or compression occurs when two antiparallel forces of equal magnitude act on an object along only one of its dimensions, in such a way that the object does not move. one way to envision such a situation is illustrated in figure 12.18. a rod segment is either stretched or. A 10 ft diameter spherical tank has wall thickness of. 1.) a stress of 20 mpa is developed in a circular section of 10 mm in diameter. find the applied force in the body. a.) 1000 pi n. b.)2000 pi n. c.) 500 pi n. d.) 250 pi n. 2.) calculate the sheared area if the shear stress is 20 mpa and the applied force is 20kn.

Solved Two Rigid Bodies 2 And 3 Are Connected By Three Chegg

Comments are closed.