Solved If The Vacancy Formation Energy Is 2 1 Ev Atom For Elemen
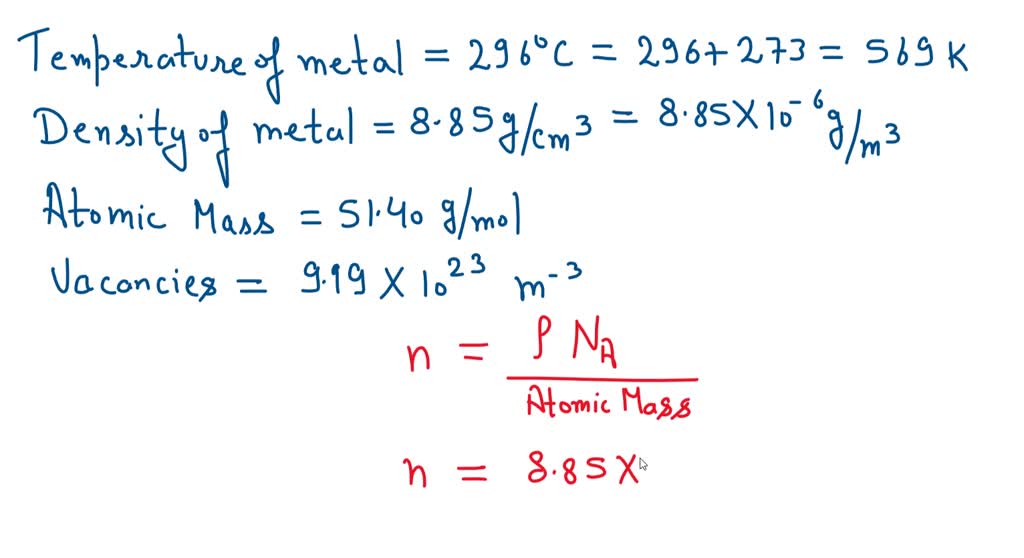
Solved If The Vacancy Formation Energy Is 2 1 Ev Atomођ If the vacancy formation energy is 2.1 ev atom for element a, determine the equilibrium of the number of vacancies at a unit volume, at 77 0c. the atomic weight and the density of element a are 113 g mol and 21 g cm3, respectively. Correction on vacancy formation energy calculation. as the first approximation, treat the vacancy as an interior surface: ∆ e. 2. c = 4 π r ∆ σ. where r is the radius of the “hole”. the corrected vacancy formation energy: ∆ e corrected =∆ e f ∆ e c. f.

Solved If The Vacancy Formation Energy Is 2 1 Ev Atomођ Box. the vacancy formation energy is independent of the position of a vacancy. energy per atom at most stable state. for example, ecoh in lennard jones(lj) potential between 2 atoms is shown as fig.3. we assume that the total potential energy, e1 in the perfect crystalhas been reached to the cohesive state and so does the energy, e2 in the. Question: calculate the energy (in ev atom) for vacancy formation in some metal, m, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 312°c is4.91×1023m 3. the density and atomic weight at 312°c ) for this metal are 19.1gcm3 and 84.10gmol, respectively.qv=ev2, etom. 4. 9 1 × 1 0 2 3 m 3. This relation for vacancies comes from, and 2) you’ll need to know about arrhenius for other topics so good to lay the groundwork here. remember that n is the number of possible vacancy sites (that’s just the number of atoms!) and nv is the number of vacancies. ev is the vacancy formation energy: per mole use r, per atom use k. b. 1 4. find step by step engineering solutions and the answer to the textbook question a. calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper (cu) at its melting temperature of 1084°c (1357 k). assume an energy for vacancy formation of 0.90 ev atom. b. repeat this calculation at room temperature (298 k).

Solved Calculate The Energy In Ev Atom For Vacancy Chegg This relation for vacancies comes from, and 2) you’ll need to know about arrhenius for other topics so good to lay the groundwork here. remember that n is the number of possible vacancy sites (that’s just the number of atoms!) and nv is the number of vacancies. ev is the vacancy formation energy: per mole use r, per atom use k. b. 1 4. find step by step engineering solutions and the answer to the textbook question a. calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper (cu) at its melting temperature of 1084°c (1357 k). assume an energy for vacancy formation of 0.90 ev atom. b. repeat this calculation at room temperature (298 k). Calculate the energy (in e v atom) for vacancy formation in some metal, m , given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 3 8 1 ° c is. 4. 2 8 × 1 0 2 3 m 3. the density and atomic weight (at 3 8 1 ° c ) for this metal are 1 3. 4 g c m 3 and 8 5. 4 0 g m o l, respectively. q v =. Calculate the energy (in ev atom) for vacancy formation in some metal, m, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 375°c is 7.00 x 1023 m 3. the density and atomic weight (at 375°c) for this metal are 4.10 g cm3 and 173.1 g mol, respectively. qv = .539 ev atom.

Comments are closed.