Solved Euler S Formula Relates The Complex Exponential Chegg
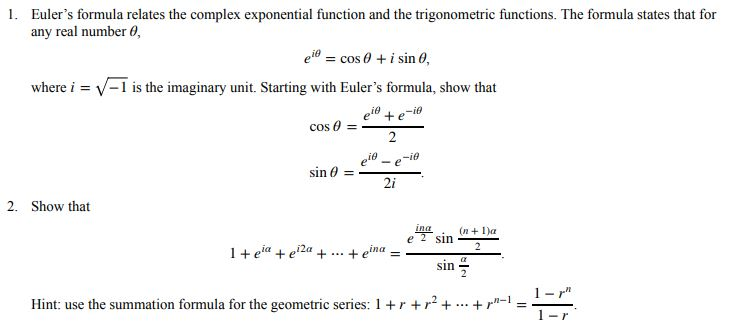
Solved Euler S Formula Relates The Complex Exponential Chegg Euler's formula relates the complex exponential e i θ to the unit circle. use the formula. e i θ = c o s (θ) i s i n (θ) to represent the following exponentials in the form a i b. show your work and simplify as much as possible, using the unit circle to evaluate s i n (π 4), c o s (2 π 3), etc. if needed. e) , e i 2 π. Question: euler's formula relates the complex exponential function and the trigonometric functions. the formula states that for any real number θ, 1. eie cos θ i sin θ, where i v i is the imaginary unit. starting with euler's formula, show that 2i 2.
Solved Euler S Formula Relates The Complex Exponential Eiо Euler’s (pronounced ‘oilers’) formula connects complex exponentials, polar coordinates, and sines and cosines. it turns messy trig identities into tidy rules for exponentials. we will use it a lot. the formula is the following: eiθ = cos(θ) isin(θ). there are many ways to approach euler’s formula. V. t. e. euler's formula, named after leonhard euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. euler's formula states that, for any real number x, one has where e is the base of the natural logarithm, i is the imaginary. The complex logarithm using polar coordinates and euler’s formula allows us to define the complex exponential as ex iy = ex eiy (11) which can be reversed for any non zero complex number written in polar form as ‰ei` by inspection: x = ln(‰); y = ` to which we can also add any integer multiplying 2… to y for another solution! 4. One of the most fundamental equations used in complex theory is euler's formula, which relates the exponent of an imaginary number, e^ {i\theta}, eiθ, to the two parametric equations we saw above for the unit circle in the complex plane: x = cos θ. x = \cos \theta x = cosθ. y = sin θ. y = \sin \theta. y = sinθ.

Comments are closed.