Signal Theory Signals And Systems Lecture 13 Modulations Am Qam

Signal Theory Signals And Systems Lecture 13 Modulations Am Qam Corona virus edition of our signal theory (signals and systems) class. lecture 13.it is highly recommended to take notes during the presentation. this helps. The tms320c6713 dsk. your transmitter should use a symbol rate of 1000 baud and bit rates of 2000 and 4000 bits per second for full duplex transmission. full duplex means that one modem transmits to a second and the second transmits to the first simultaneously, and the transmissions in both directions are independent.
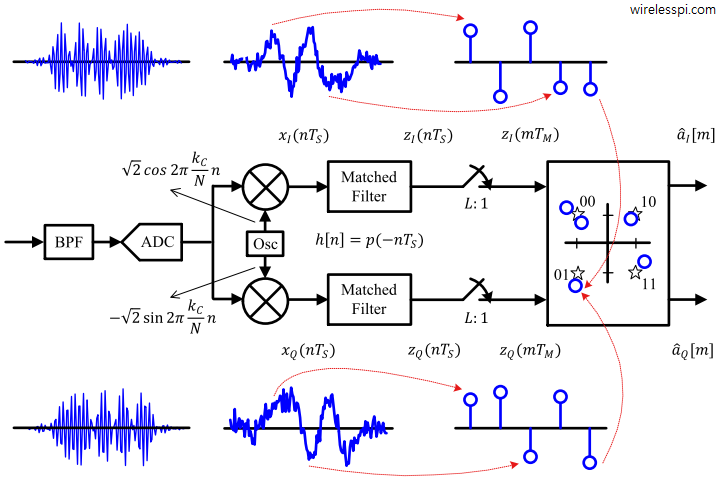
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Qam Wireless Pi Qam (quadrature amplitude modulation) is defined as a modulation technique that combines phase and amplitude modulation in a single channel. it transmits information by changing both the amplitude and phase of a carrier wave, doubling the effective bandwidth. qam is also known as quadrature carrier multiplexing. Qam, or quadrature amplitude modulation, is a way to compress vast amounts of digital information onto an rf analog carrier capable of transmitting this information wirelessly, without consuming more bandwidth in the modulation process. more specifically, qam encodes digital data on two carrier waves that are 90⁰ out of phase (also commonly. Digital pulse amplitude modulation (pam) modulates digital information onto amplitude of pulse and may be later modulated by sinusoid. digital quadrature amplitude modulation (qam) is two dimensional extension of digital pam that requires sinusoidal modulation. digital qam modulates digital information onto pulses that are modulated onto. In chapter 2, we discussed the discrete time processing of continuous time signals, and in that context reviewed and discussed d c conversion for reconstructing a continuous time signal from a discrete time sequence. another common context in which it is useful and important to generate a continuous time signal from a.

Comments are closed.