Signal Theory Signals And Systems Introduction
Classification Of Signals Signals Systems Engineerstutor Signals and systems (pdf) 2 discrete time (dt) systems (pdf) 3 feedback, poles, and fundamental modes (pdf) 4 continuous time (ct) systems (pdf) 5 z transform (pdf) 6 laplace transform (pdf) 7 discrete approximation of continuous time systems (pdf) 8 convolution (pdf 2.0mb) 9 frequency response (pdf 1.6mb) 10 feedback and control (pdf 1. While only a short time ago signal processing systems were predominantly analog, integrated circuit technology has made digital signal processing often preferable and more cost effective. this course is an introduction to the basic concepts and theory of analog and digital signal processing.
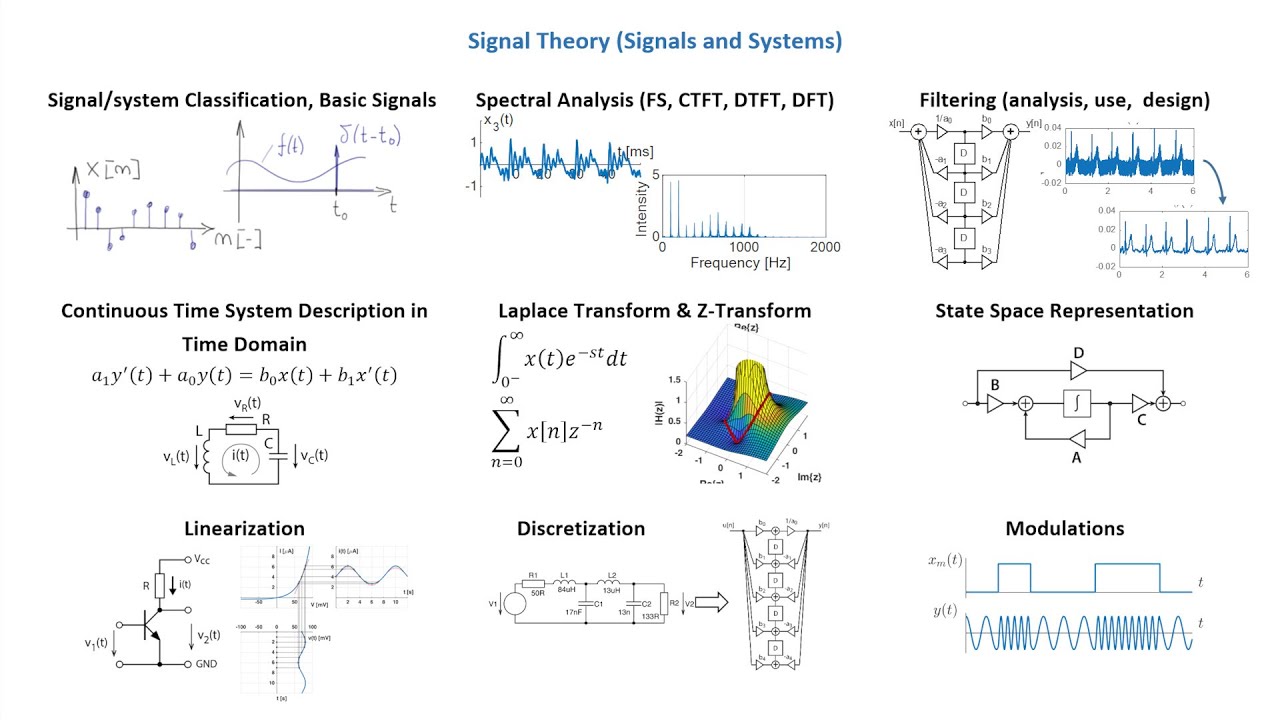
Signal Theory Signals And Systems Introduction Youtube 6.003 covers the fundamentals of signal and system analysis, focusing on representations of discrete time and continuous time signals (singularity functions, complex exponentials and geometrics, fourier representations, laplace and z transforms, sampling) and representations of linear, time invariant systems (difference and differential equations, block diagrams, system functions, poles and. This module will begin our study of signals and systems by laying out some of the fundamentals of signal classification. it is essentially an introduction to the important definitions and properties that are fundamental to the discussion of signals and systems, with a brief discussion of each. 1.2: signal size and norms. Systems act on signals (inputs and outputs) mathematically, they are similar. a signal can be represented by a function. a system can be represented by a function (the domain is the space of input signals). we focus on 1 dimensional signals. our systems are not random. cu (lecture 1) ele 301: signals and systems fall 2011 12 19 45. 2.5: introduction to systems. signals are manipulated by systems. a system's input is analogous to an independent variable and its output the dependent variable. for the mathematically inclined, a system is a functional: a function of a function (signals are functions). simple systems can be connected together one system's output becomes.

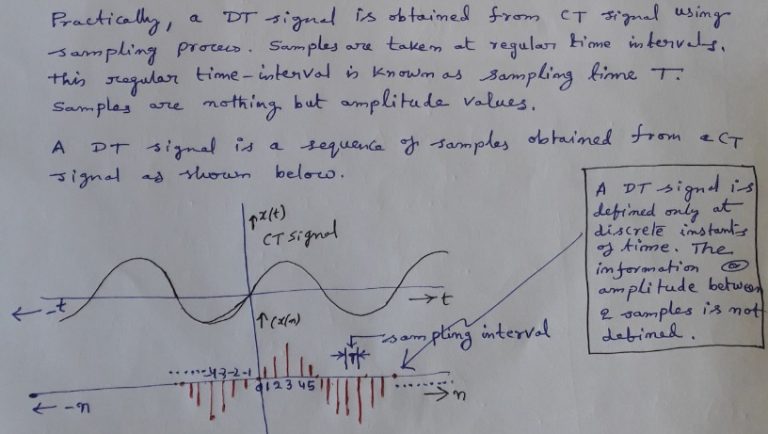
Signals And Systems Theory And Applications 9781607854869 Fawwaz Systems act on signals (inputs and outputs) mathematically, they are similar. a signal can be represented by a function. a system can be represented by a function (the domain is the space of input signals). we focus on 1 dimensional signals. our systems are not random. cu (lecture 1) ele 301: signals and systems fall 2011 12 19 45. 2.5: introduction to systems. signals are manipulated by systems. a system's input is analogous to an independent variable and its output the dependent variable. for the mathematically inclined, a system is a functional: a function of a function (signals are functions). simple systems can be connected together one system's output becomes. The theory of sampled signals is introduced in this chapter. the analog signal is first interfaced to a digital computer via analog to digital converter (adc). adc consists of a sampler and a quantizer. we will mainly discuss the sampler in this chapter. the analog signal, when sampled, gets converted to discrete time (dt) signal. These notes are about the mathematical representation of signals and systems. the most important representations we introduce involve the frequency domain – a different way of looking at signals and systems, and a complement to the time domain viewpoint. indeed engineers and.
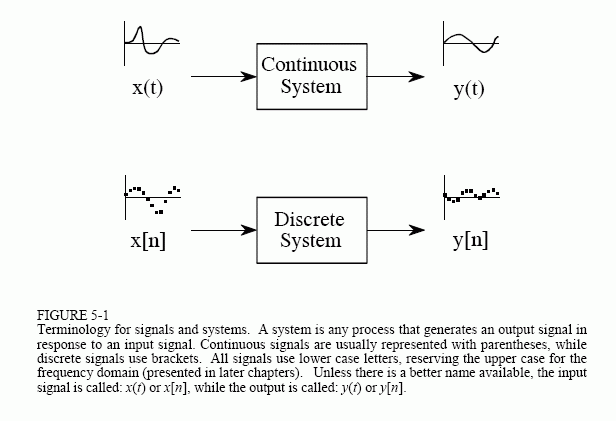
Signals And Systems The theory of sampled signals is introduced in this chapter. the analog signal is first interfaced to a digital computer via analog to digital converter (adc). adc consists of a sampler and a quantizer. we will mainly discuss the sampler in this chapter. the analog signal, when sampled, gets converted to discrete time (dt) signal. These notes are about the mathematical representation of signals and systems. the most important representations we introduce involve the frequency domain – a different way of looking at signals and systems, and a complement to the time domain viewpoint. indeed engineers and.

Comments are closed.