Secondary Consumers In Grasslands

Ppt Grasslands Powerpoint Presentation Id 2209806 Learn how grass is the producer and insects are the primary consumers in a grassland food chain. see how frogs, snakes, coyotes, vultures and hawks are the secondary and tertiary consumers in this ecosystem. Learn how grasses, herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers form interconnected food chains in grassland ecosystems. discover the role of insects, birds, reptiles, and mutualistic plants in the grassland food web.
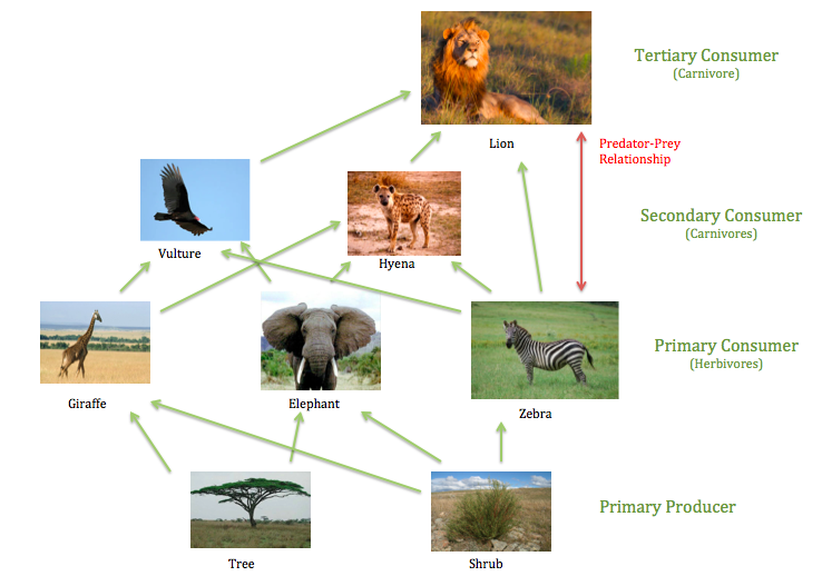
Food Chain Food Web Tropical Grasslands Savannas Learn how energy flows through the grassland ecosystem in a linear food chain or a complex food web. see examples of producers, consumers, and decomposers in the grasslands. The flesh eating animal species (carnivores & omnivores) are known as secondary consumers of the grassland ecosystem. these animals get energy from primary consumers. the carnivores are the secondary consumers of the grassland ecosystem that mostly include big cats, whereas omnivores include animals like hyenas, wild dogs, snakes, etc. scavengers. Secondary consumer responses to altered rainfall alterations occurring in the abundance and diversity of primary consumers can flow up through the food chain to affect populations of predators and parasitoids ( suttle et al., 2007 ; lee et al., 2014 ), which may themselves be more sensitive to climatic change ( voigt et al., 2003 ). The food chain in a grassland is producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, scavengers and detrivores. each part in this food chain is an important part of life in this harsh environment. in a grassland, the producers include grass, shrubs and trees, which are designated as plants that make their own food, also called autotrophs. the.
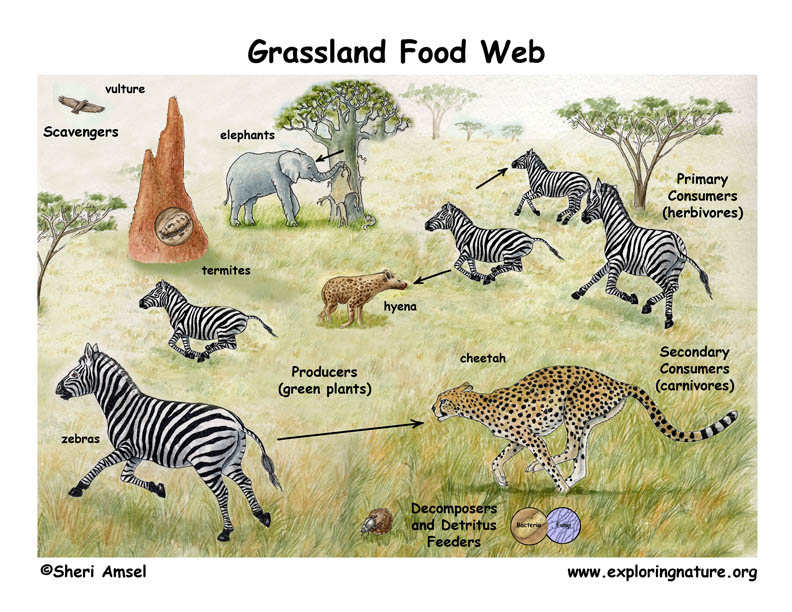
African Grassland Savanna Food Web Secondary consumer responses to altered rainfall alterations occurring in the abundance and diversity of primary consumers can flow up through the food chain to affect populations of predators and parasitoids ( suttle et al., 2007 ; lee et al., 2014 ), which may themselves be more sensitive to climatic change ( voigt et al., 2003 ). The food chain in a grassland is producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, scavengers and detrivores. each part in this food chain is an important part of life in this harsh environment. in a grassland, the producers include grass, shrubs and trees, which are designated as plants that make their own food, also called autotrophs. the. There may be more levels of consumers before a chain finally reaches its top predator. top predators, also called apex predators, eat other consumers. higher level consumers (i.e., secondary, tertiary, and above) can be carnivores (animals that eat other animals) or omnivores (animals that eat both plants and animals). omnivores, like people. Secondary consumer responses to altered rainfall alterations occurring in the abundance and diversity of primary consumers can flow up through the food chain to affect populations of predators and parasitoids ( suttle et al., 2007 ; lee et al., 2014 ), which may themselves be more sensitive to climatic change ( voigt et al., 2003 ).

Comments are closed.