Route Of Blood Flow Through The Heart
Cardiovascular System Anatomy And Physiology Study Guide For Nurses Blood flows through your heart, lungs and body in a series of steps. after delivering oxygen and nutrients to all your organs and tissues, your blood enters your heart and flows to your lungs to gain oxygen and get rid of waste. it then flows back to your heart, which pumps the refreshed blood out through your aorta to nourish your body again. The path of blood flow through the heart and lungs is pulmonary circulation, while the blood supply to the heart itself is coronary circulation. pulmonary circulation: purpose: pulmonary circulation is responsible for oxygenating the blood. it involves the movement of deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and then.

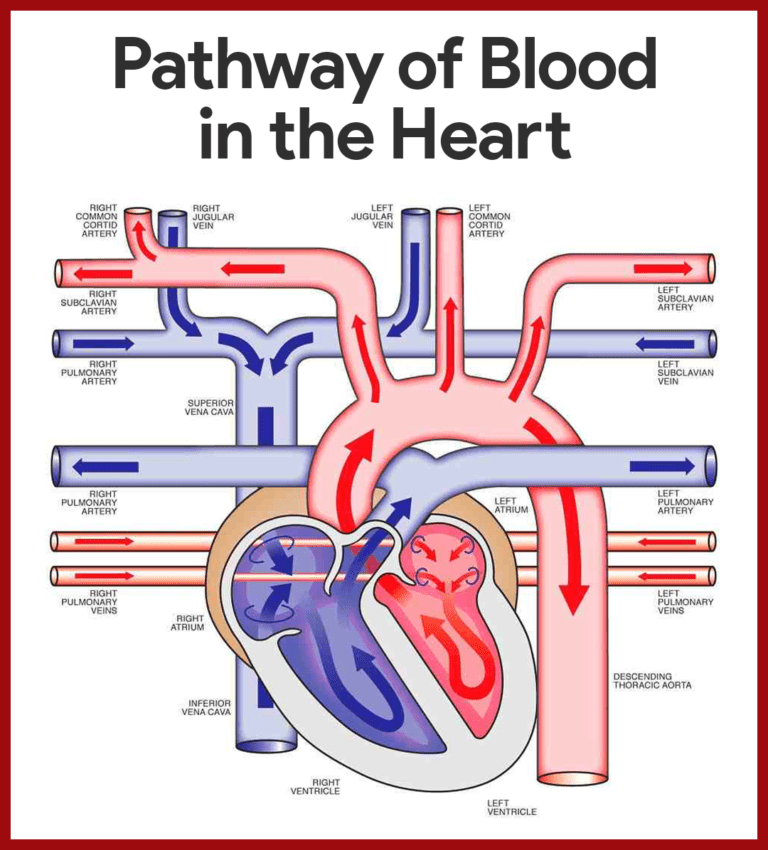
Blood Flow Through Heart Diagrams 101 Diagrams Oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart gets pumped out of the aorta. from there, blood flows through arteries, arterioles, and then capillaries (tiny blood vessels that transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen to cells). deoxygenated blood from the capillaries then flows back to the heart through venules, veins, and ultimately through. Pathway of blood through the heart. in this educational lesson, we learn about the blood flow order through the human heart in 14 easy steps, from the superior and inferior vena cava to the atria and ventricles. come also learn with us the heart’s anatomy, including where deoxygenated and oxygenated blood flow, in the superior vena cava. Learn how your heart valves, arteries, veins, and lungs work together to circulate blood through your body. see animations and diagrams of the heart's chambers, coronary arteries, and pulmonary system. Pulmonary circulation facilitates the process of external respiration: deoxygenated blood flows into the lungs. it absorbs oxygen from tiny air sacs (the alveoli) and releases carbon dioxide to be exhaled. systemic circulation facilitates internal respiration: oxygenated blood flows into capillaries through the rest of the body. the blood.

Comments are closed.