Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostics Nursing Immunosuppressants Osteoarthritis

Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostics Nursing Immunosuppressants Head to simplenursing’s official website here: bit.ly 48nwtlxsimplenursing memberships have 1,200 animated videos, 900 colorful study guides, 3,000. Rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions of individuals worldwide, causing joint inflammation, pain, and potential disability. as nurses, our role in the care of patients with ra is paramount. this article aims to shed light on the crucial nursing interventions, patient education, and holistic support.
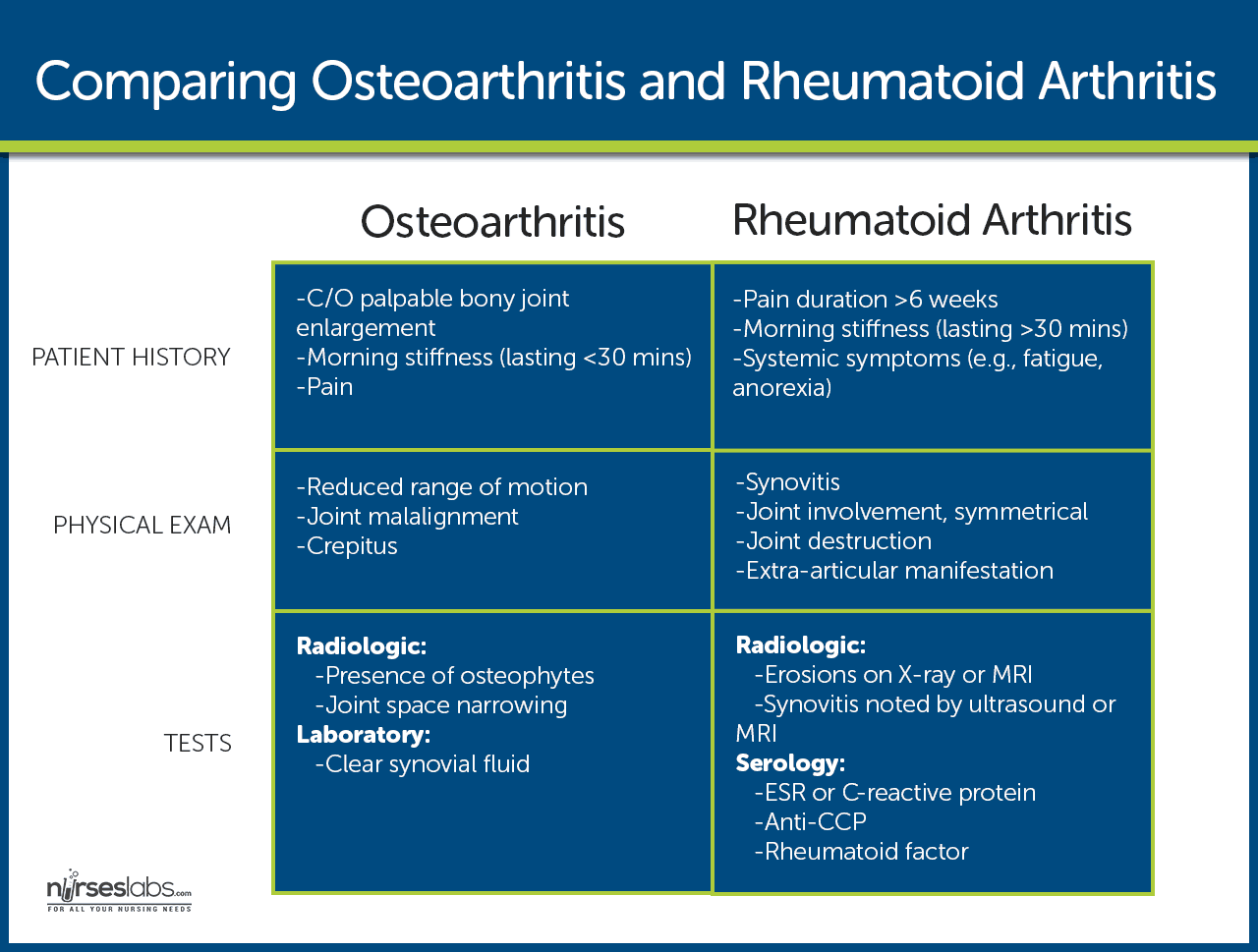
Osteoarthritis Nursing Care And Management Study Guide For Nurses Nursing interventions and actions. therapeutic interventions and nursing actions for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (ra) may include: 1. managing pain relief. patients with rheumatoid arthritis may experience acute pain due to injury, which can be caused by several factors. Figure. rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is an autoimmune illness caused by inflammation of the tendon and synovium (tenosynovitis), resulting in cartilage destruction, bone erosion, joint swelling, stiffness, and pain. 1,2 ra typically begins in the peripheral joints, moves proximally, is usually bilateral and symmetrical, and has multiorgan manifestations. 1,2 it's important for nurses to be aware. Rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a symmetric, inflammatory, peripheral polyarthritis of unknown etiology. it typically leads to joint destruction through the erosion of cartilage and bone. untreated, it will lead to loss of physical function, inability to carry out daily tasks of living, and difficulties in maintaining employment. Abstract. rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease of unknown etiology, primarily affecting the joints, then extra articular manifestations can occur. due to its complexity, which is based on an incompletely elucidated pathophysiological mechanism, good ra management requires a multidisciplinary approach.
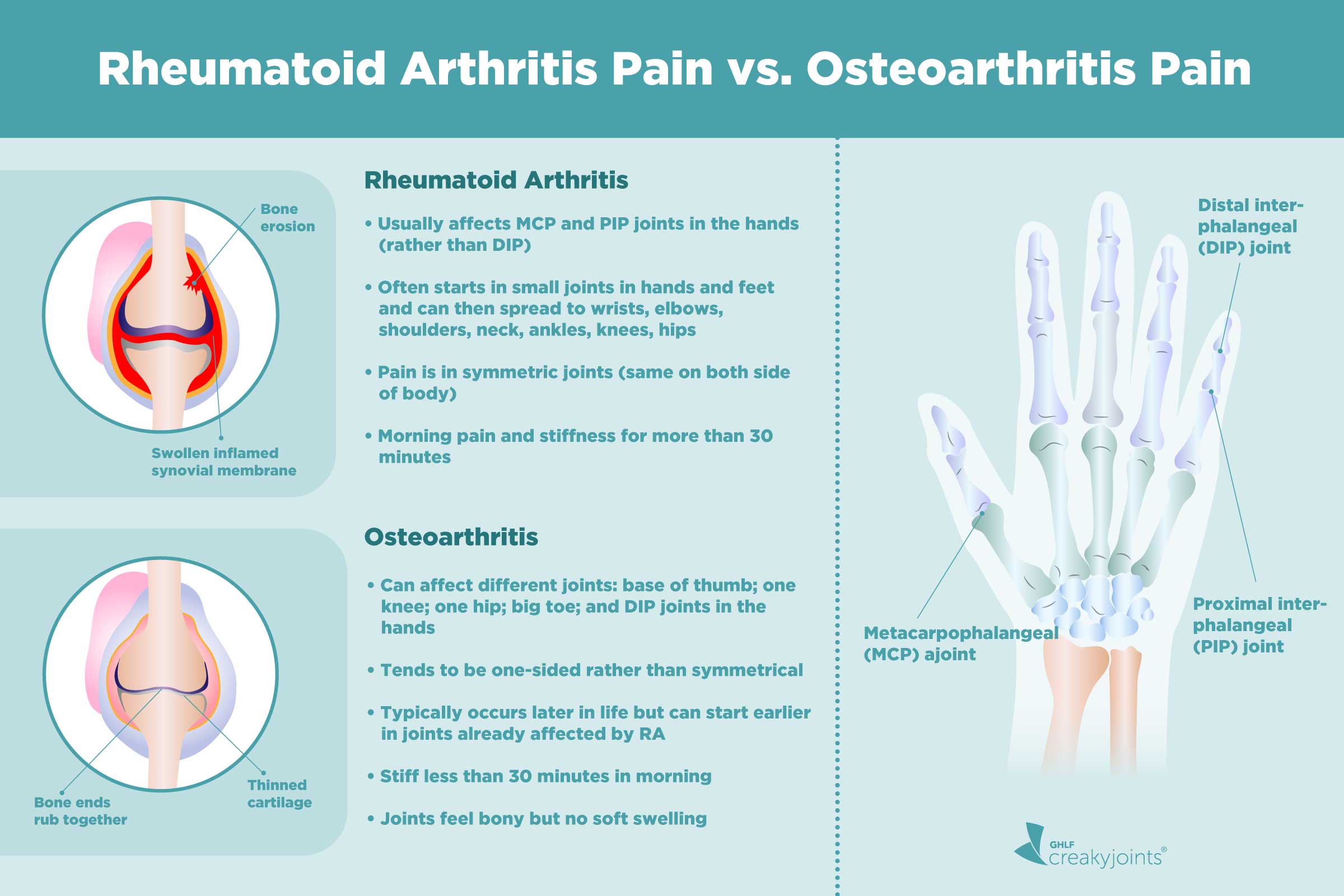
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs Osteoarthritis Blood Test At Tom Shaw Blog Rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a symmetric, inflammatory, peripheral polyarthritis of unknown etiology. it typically leads to joint destruction through the erosion of cartilage and bone. untreated, it will lead to loss of physical function, inability to carry out daily tasks of living, and difficulties in maintaining employment. Abstract. rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a multifactorial autoimmune disease of unknown etiology, primarily affecting the joints, then extra articular manifestations can occur. due to its complexity, which is based on an incompletely elucidated pathophysiological mechanism, good ra management requires a multidisciplinary approach. Rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is the most common inflammatory arthritis, with a lifetime prevalence of up to 1 percent worldwide. 1 onset can occur at any age, but peaks between 30 and 50 years. 2. Rheumatoid arthritis (ra) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammatory arthritis and extra articular involvement. it is a chronic inflammatory disorder caused in many cases by the interaction between genes and environmental factors, including tobacco, that primarily involves synovial joints.[1] it typically starts in small peripheral joints, is usually symmetric, and.

Comments are closed.