Results Of Uniformity Coefficients Cu And Curvature Coefficients Cc

Results Of Uniformity Coefficients Cu And Curvature Coefficients Cc The uniformity coefficient (cu) is defined as the ratio of d60 to d10. a value of cu greater than 4 to 6 classifies the soil as well graded. when cu is less than 4, it is classified as poorly graded or uniformly graded soil. uniformly graded soil has identical particles with cu value approximately equal to 1. a uniformity coefficient value of 2. A uniformity coefficient value of 2 or 3 classifies the soil as poorly graded. beach sand comes under this category. a higher value of cu indicates that the soil mass consists of soil particles with different size ranges. coefficient of curvature (cc) coefficient of curvature is given by the formula: for the soil to be well graded, the value of.
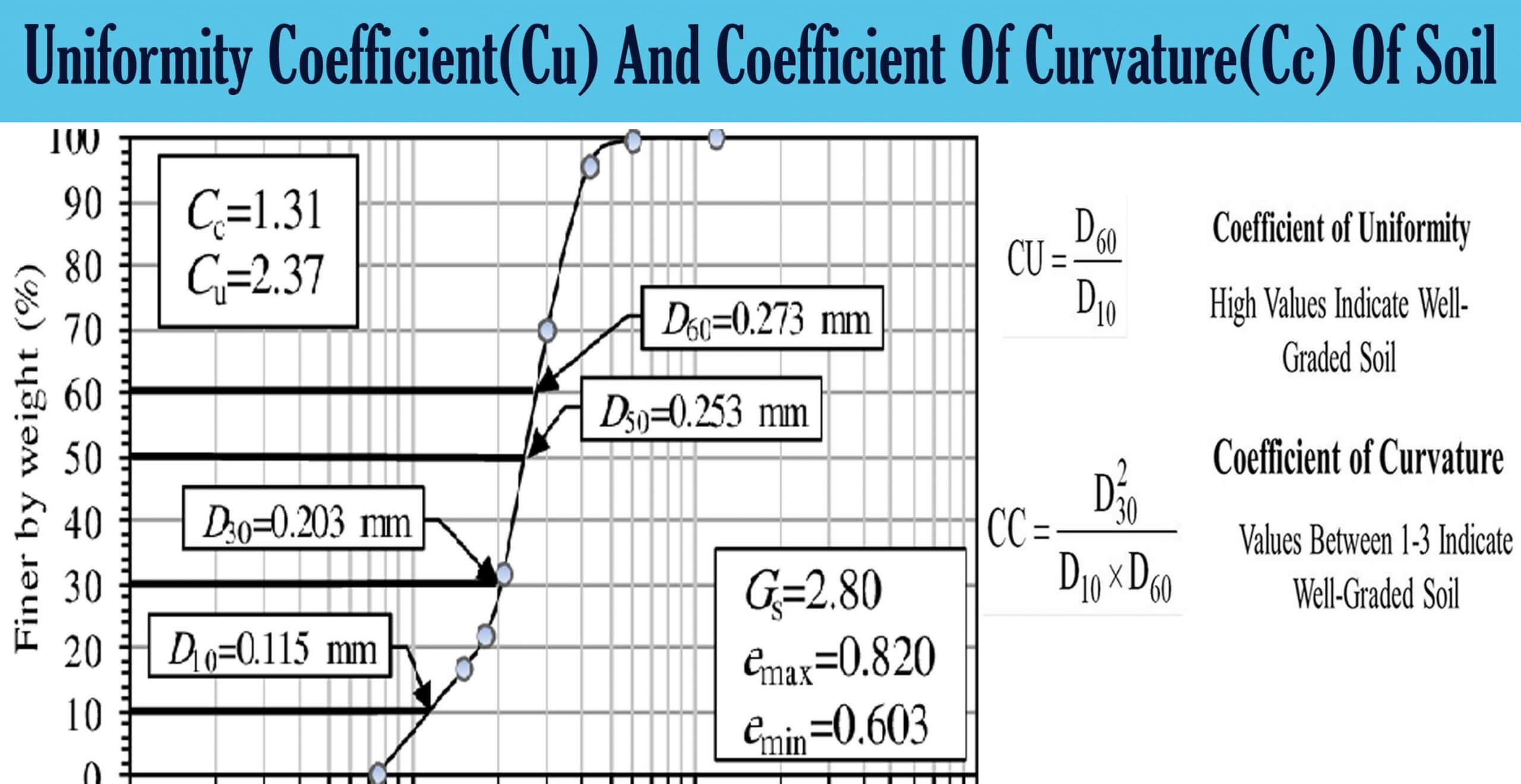
Uniformity Coefficient Cu And Coefficient Of Curvature Cc Of Soi The coefficient of uniformity is a crude shape parameter and the coefficient of curvature is a shape parameter. once these coefficients have been calculated, they are compared to published gradation criteria. soil gradation is essential in geotechnical engineering, as the gradation of in situ or on site soil often controls the design and ground. The most important criteria for grading any soil are its coefficient of uniformity (cu) and coefficient of curvature (cc). uniformity coefficient (cu): it is the ratio between the sieve size which will pass 60% of the sand by weight (d60) to the effective size (d10). cu = d60 d10. a higher cu value indicates a wider range of particle sizes and. The uniformity coefficient (c u) the uniformity coefficient (c u ) expresses the variety in particle sizes of soil and is defined as the ratio of d 60 to d 10 ( figure 1 ). the value d 60 is the grain diameter at which 60% of soil particles are finer and 40% of soil particles are coarser, while d 10 is the grain diameter at which 10% of. The values of the uniformity coefficient c u and the coefficient of gradation c c can be calculated using the following equations: the values of c u and c c are used to classify whether the soil is well graded or not. sand isconsidered well graded, if c u is greater than 6 and c c is between 1 and 3.
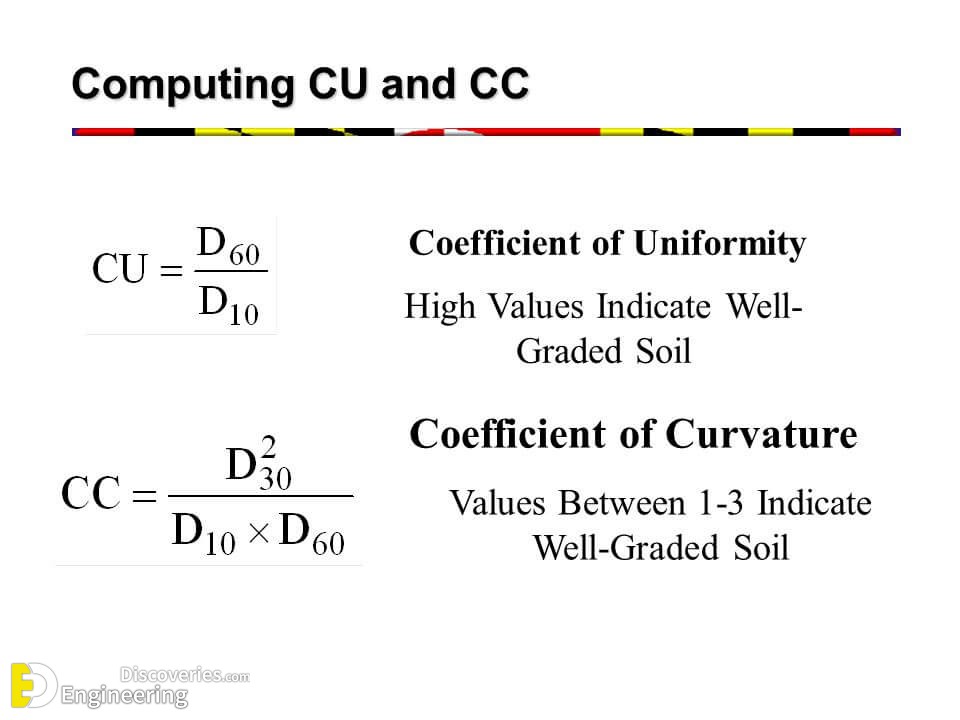
Uniformity Coefficient Cu And Coefficient Of Curvature Cc Of Soi The uniformity coefficient (c u) the uniformity coefficient (c u ) expresses the variety in particle sizes of soil and is defined as the ratio of d 60 to d 10 ( figure 1 ). the value d 60 is the grain diameter at which 60% of soil particles are finer and 40% of soil particles are coarser, while d 10 is the grain diameter at which 10% of. The values of the uniformity coefficient c u and the coefficient of gradation c c can be calculated using the following equations: the values of c u and c c are used to classify whether the soil is well graded or not. sand isconsidered well graded, if c u is greater than 6 and c c is between 1 and 3. The coefficient of gradation may he expressed as: where cc is the coefficient of gradation and d30 diameter corresponding to 30% finer. for the particle size distribution curve of soil b shown in figure 2, the values of d10 d30 and d60 are 0.096 mm, 0.16 mm and 0.24 mm, respectively. the uniformity coefficient and coefficient of gradation are:. 1) the uniformity coefficient: c u = d 60 d 10 soils with cu <= 4 are considered to be "poorly graded" or uniform. 2) the coefficient of gradation: c c = (d 30)2 (d 60 *d 10) for well−graded soils, c c ~ 1 3) the sorting coefficient: s o = (d 75 d25) 1 2 this measure tends to be used more by geologists than engineers. the larger s o.

Coefficients Of Uniformity Cu And Coefficient Of Curvature Cc The coefficient of gradation may he expressed as: where cc is the coefficient of gradation and d30 diameter corresponding to 30% finer. for the particle size distribution curve of soil b shown in figure 2, the values of d10 d30 and d60 are 0.096 mm, 0.16 mm and 0.24 mm, respectively. the uniformity coefficient and coefficient of gradation are:. 1) the uniformity coefficient: c u = d 60 d 10 soils with cu <= 4 are considered to be "poorly graded" or uniform. 2) the coefficient of gradation: c c = (d 30)2 (d 60 *d 10) for well−graded soils, c c ~ 1 3) the sorting coefficient: s o = (d 75 d25) 1 2 this measure tends to be used more by geologists than engineers. the larger s o.

Comments are closed.