Production Of Low Temperature 01 Principle Of Regenerative Cooling

Production Of Low Temperature 01 Principle Of Regenerative Cooling Abstract. regenerative heat exchange method internally recovers useful cooling and heating energy inside a closed loop cooling system. however, depending on the specific cooling mechanisms for various cooling technologies, the configurations and characteristics of regeneration methods diverge significantly. therefore, it is necessary to review. Coil. thus the cooler low pressure gas abstracts heat from the incoming stream. in the ideal gas, the temperature of the low pressure gas at f should be the same as that of the high pressure gas at the entrance e. thus, if the j t cooling can be used regeneratively, it ultimately leads to production of temperature low enough for liquefaction of.

Principle Of Regenerative Cooling Bsc Physics Mangalore University Principles of regenerative cooling. at its core, regenerative cooling is based on the principle of heat transfer. in this system, the coolant absorbs heat as it flows through channels surrounding the combustion chamber and nozzle. this heat absorption raises the temperature of the coolant, which is then utilized in the combustion process. The concept of regenerative cooling was first proposed by tsiolkovski in the early 20th century. to begin with, the fuel flows through the cooling channel manufactured in the combustion chamber wall, the temperature of the inner wall of the combustion chamber is cooled down by the forced convective heat transfer of the fuel and the heat conduction of the chamber wall. The high temperature, low field stabilized phase, phase 1 joule reported the temperature changes (0.01–1.5 k) regenerative multicaloric cooling processes. V. t. e. regenerative cooling is a method of cooling gases in which compressed gas is cooled by allowing it to expand and thereby take heat from the surroundings. the cooled expanded gas then passes through a heat exchanger where it cools the incoming compressed gas. [1].
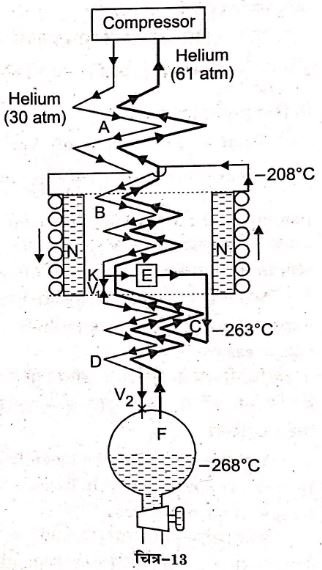
Explain The Principle Regenerative Cooling The high temperature, low field stabilized phase, phase 1 joule reported the temperature changes (0.01–1.5 k) regenerative multicaloric cooling processes. V. t. e. regenerative cooling is a method of cooling gases in which compressed gas is cooled by allowing it to expand and thereby take heat from the surroundings. the cooled expanded gas then passes through a heat exchanger where it cools the incoming compressed gas. [1]. In order to sustain the device development, an analytical model for regenerative cooling systems is presented in this work. it consists of a caloric material driven cyclically so that it exhibits harmonic temperature variations, whereas an oscillating fluid layer is exchanging heat with the caloric material, leading to a net heat flux along one. Here, we report a regenerative elastocaloric heat pump that exhibits a temperature span of 15.3 k on the water side with a corresponding specific heating power up to 800 w kg −1 and maximum cop.

Principle Of Regenerative Cooling Dr Nageswara Rao Asst Professor In order to sustain the device development, an analytical model for regenerative cooling systems is presented in this work. it consists of a caloric material driven cyclically so that it exhibits harmonic temperature variations, whereas an oscillating fluid layer is exchanging heat with the caloric material, leading to a net heat flux along one. Here, we report a regenerative elastocaloric heat pump that exhibits a temperature span of 15.3 k on the water side with a corresponding specific heating power up to 800 w kg −1 and maximum cop.
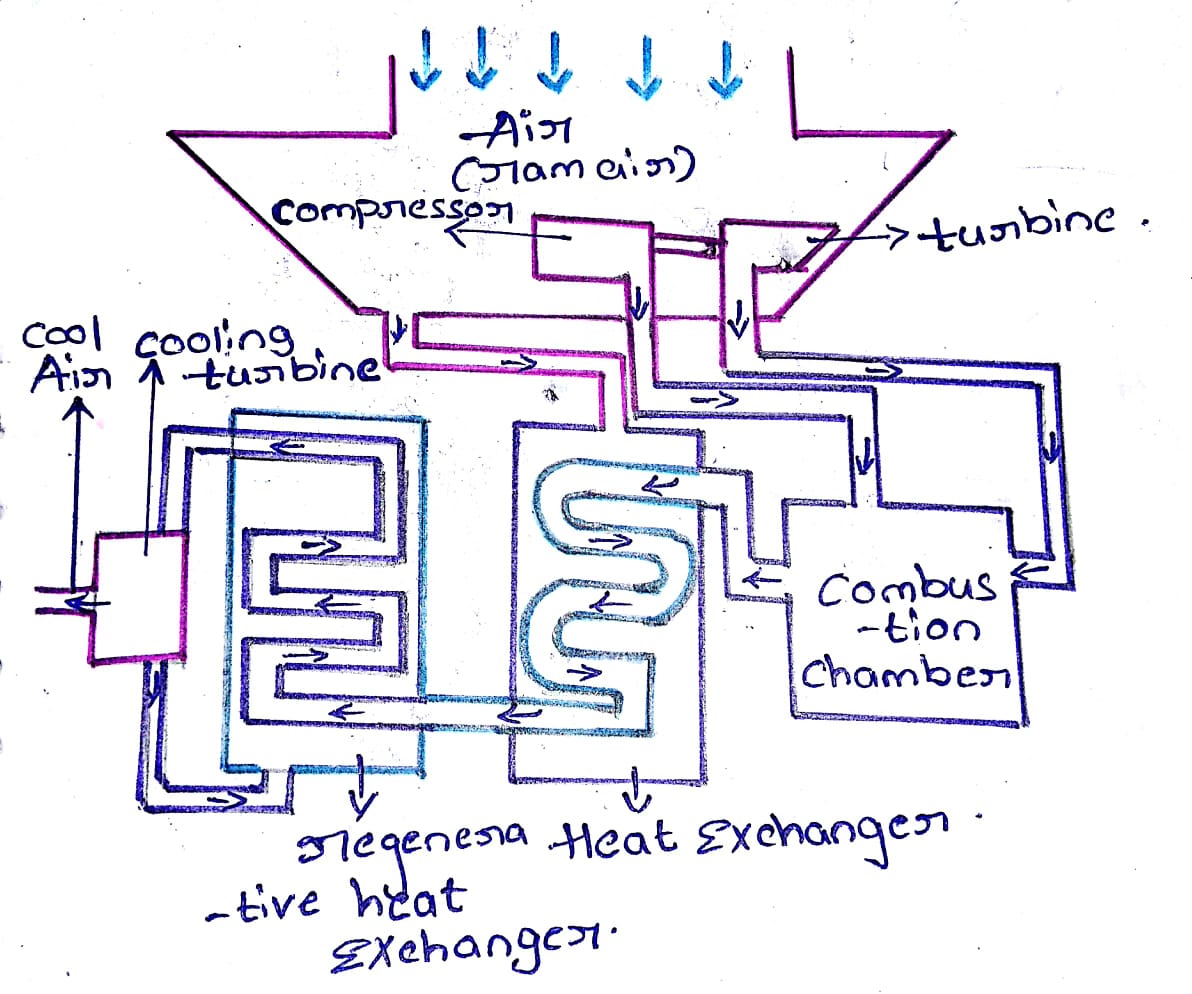
Regenerative Air Cooling System And Working Mechanical Education

Comments are closed.