Producers Consumers And Decomposers Overview
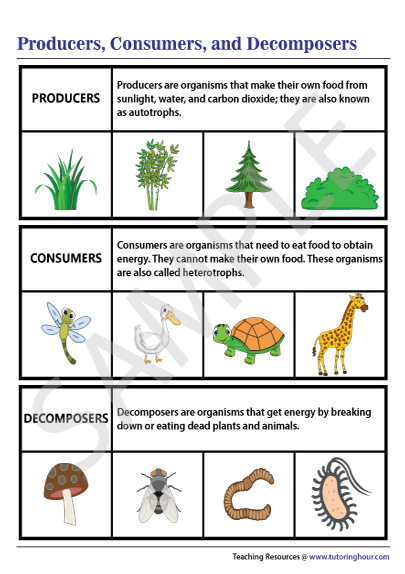
Producers Consumers And Decomposers Chart Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. This short video gives elementary students an introduction to some basic food web vocabulary: producers, consumers, and decomposers. students will learn the.
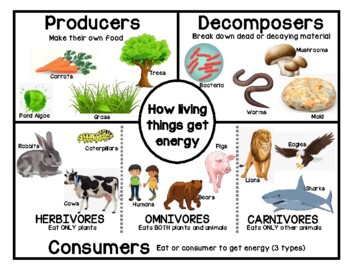
Producers Consumers Decomposers Anchor Chart By Deborah Tomoff Welcome to producers, consumers, and decomposers with mr. j! need help with what producers, consumers, and decomposers are? you're in the right place!whether. Summary. ecosystems require constant inputs of energy from sunlight or chemicals. producers use energy and inorganic molecules to make food. consumers take in food by eating producers or other living things. decomposers break down dead organisms and other organic wastes and release inorganic molecules back to the environment. Post and review the following directions: 1. as a group, read and look at the picture cards. 2. as a group, categorize the organisms on the picture cards as producers, primary consumers, or secondary consumers. 3. individually record your findings in the three column chart in your student science notebook. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.

Food Chain Producers Consumers Decomposers Food Chain In Pond Post and review the following directions: 1. as a group, read and look at the picture cards. 2. as a group, categorize the organisms on the picture cards as producers, primary consumers, or secondary consumers. 3. individually record your findings in the three column chart in your student science notebook. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Today, we're going to delve into the intricate world of ecosystems – those complex webs where life and the environment coexist. we'll explore the roles and r. Roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain. autotrophs are usually plants or one celled organisms.

Components Of Ecosystem Biotic And Abiotic Teachoo Concepts Today, we're going to delve into the intricate world of ecosystems – those complex webs where life and the environment coexist. we'll explore the roles and r. Roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. they make up the first level of every food chain. autotrophs are usually plants or one celled organisms.

Producers Consumers And Decomposers Science Quizizz

Comments are closed.