Producer Consumer Surplus Graph
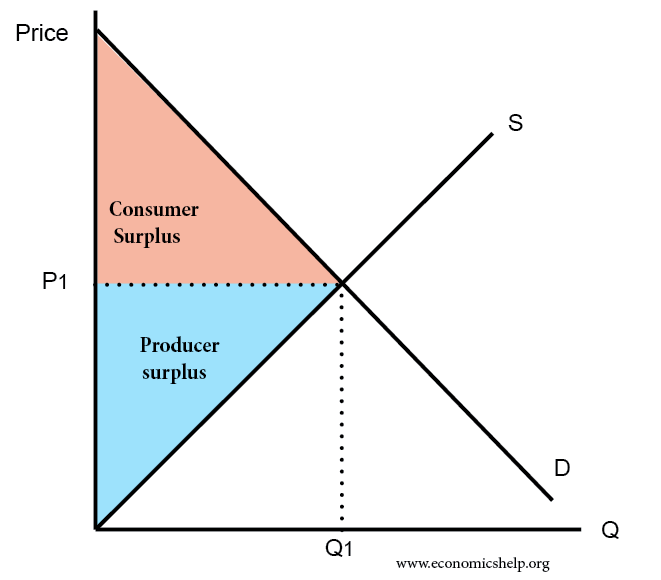
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Economics Help Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. In the context of welfare economics, consumer surplus and producer surplus measure the amount of value that a market creates for consumers and producers, respectively. . consumer surplus is defined as the difference between consumers' willingness to pay for an item (i.e. their valuation, or the maximum they are willing to pay) and the actual price that they pay, while producer surplus is.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Graphical-CSPS-5-57eec9385f9b586c3581f1fa.png)
Finding Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Graphically From figure 1 the following formula can be derived for consumer and producer surplus: consumer surplus = (qe x (p2 – pe)) ÷ 2. producer surplus = (qe x (pe – p1)) ÷ 2. where: qe is the equilibrium price. pe is the equilibrium price. p2 is the y intercept of the demand curve. p1 is the y intercept of the supply curve. The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers. Understanding consumer surplus and producer surplus. when discussing consumer and producer surplus, it is important to understand some base concepts used by economists to explain the inter relationship. both consumer and producer surplus can be graphed to display either a demand curve or marginal benefit curve (mb) and a supply curve or. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber.

Producer Surplus Definition And Meaning Capital Understanding consumer surplus and producer surplus. when discussing consumer and producer surplus, it is important to understand some base concepts used by economists to explain the inter relationship. both consumer and producer surplus can be graphed to display either a demand curve or marginal benefit curve (mb) and a supply curve or. Description. this lecture covers supply and demand curves, consumer surplus, and producer surplus. see handout 9 for relevant graphs for this lecture instructor: prof. jonathan gruber. The producer's surplus is the total revenue minus the total variable cost. it's maximized when mc = p. p =. p = p =. \begin {aligned}\\ tb (q) &= 42.00 \\ tc (q) &= 15.00 \\ p \times q &= 24.00\\ \\ ps &= p \times q tc (q) = 9.00\\ cs &= tb (q) p \times q = 18.00\\ \\ & \text {total welfare }= 27.00\end {aligned} t b(q) t c (q) p ×q p s c. Consumer surplus is t u, and producer surplus is v w x. a price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800.
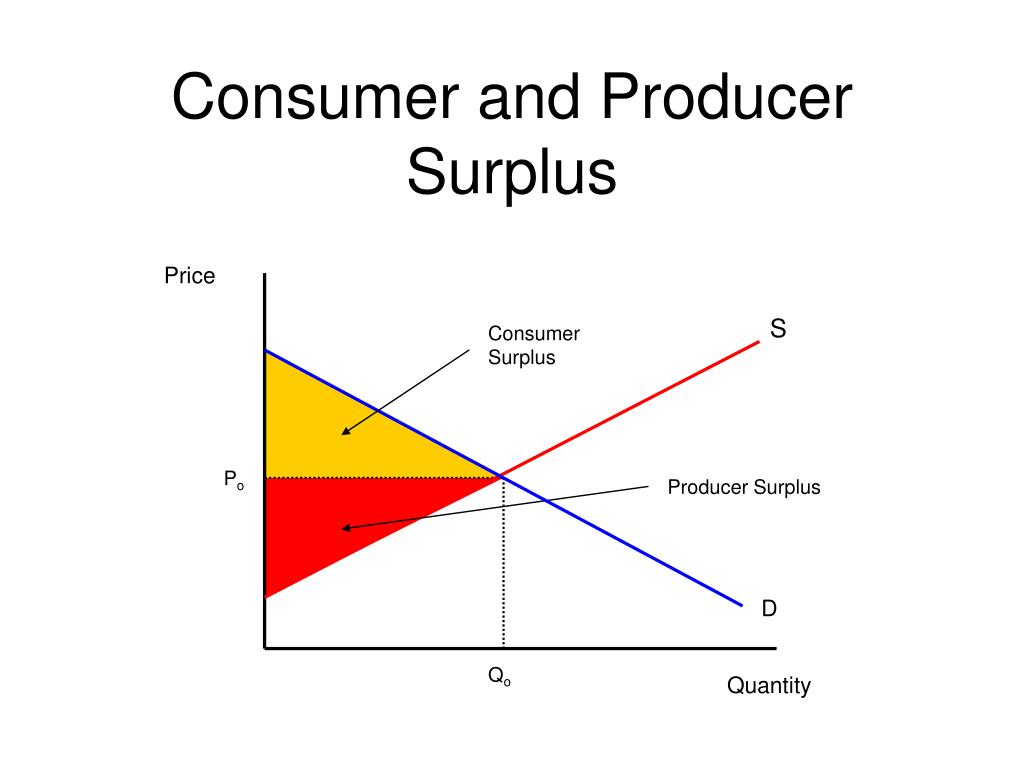
Consumer Producer Surplus Graph The producer's surplus is the total revenue minus the total variable cost. it's maximized when mc = p. p =. p = p =. \begin {aligned}\\ tb (q) &= 42.00 \\ tc (q) &= 15.00 \\ p \times q &= 24.00\\ \\ ps &= p \times q tc (q) = 9.00\\ cs &= tb (q) p \times q = 18.00\\ \\ & \text {total welfare }= 27.00\end {aligned} t b(q) t c (q) p ×q p s c. Consumer surplus is t u, and producer surplus is v w x. a price ceiling is imposed at $400, so firms in the market now produce only a quantity of 15,000. as a result, the new consumer surplus is t v, while the new producer surplus is x. (b) the original equilibrium is $8 at a quantity of 1,800.

Producer Surplus Economics Tutor2u

Comments are closed.