Prenatal Screening Methods

Guide To Prenatal Genetic Testing And Screening First trimester screening tests can begin as early as 10 weeks. these usually involve blood tests and an ultrasound. they test your baby’s overall development and check to see if your baby is at. The two main types of testing for genetic conditions during pregnancy are: screening tests. prenatal screening tests can find out whether your baby is more or less likely to have certain genetic conditions. most often, these screening tests are offered during the first or second trimester of pregnancy. they include blood tests and ultrasound.
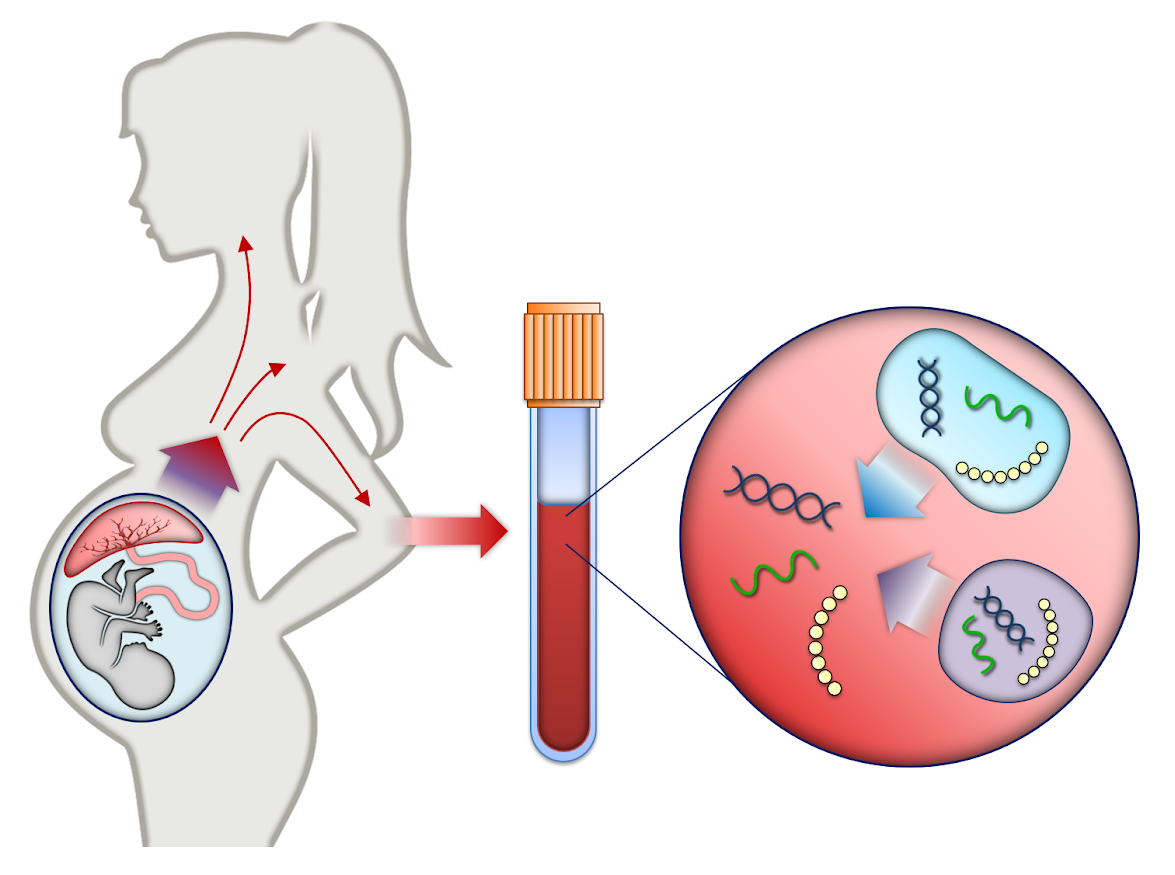
Nipt Test Non Invasive Prenatal Screening Geneton Carrier screening: a test done on a person without signs or symptoms to find out whether he or she carries a gene for a genetic disorder. cell free dna: dna from the placenta that moves freely in a pregnant woman’s blood. analysis of this dna can be done as a noninvasive prenatal screening test. cells: the smallest units of a structure in the. First trimester screen (nuchal translucency, hcg, and papp a): this test is usually performed during weeks 11 13 of pregnancy. it's a noninvasive evaluation combining a mother's blood screening with an ultrasound of the fetus. the test includes nuchal translucency, a portion that can help discover other potential abnormalities, including heart. Second trimester prenatal screening tests. second trimester prenatal screening may include several blood tests called multiple markers. these markers provide information about your potential risk of having a baby with certain genetic conditions or birth defects. screening is usually done by taking a sample of your blood between 15 and 20 weeks. Diagnostic prenatal testing can be performed by invasive or non invasive methods. an invasive method involves probes or needles being inserted into the uterus , e.g. amniocentesis , which can be done from about 14 weeks gestation, and usually up to about 20 weeks, and chorionic villus sampling , which can be done earlier (between 9.5 and 12.5.

Comments are closed.