Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy 3b5
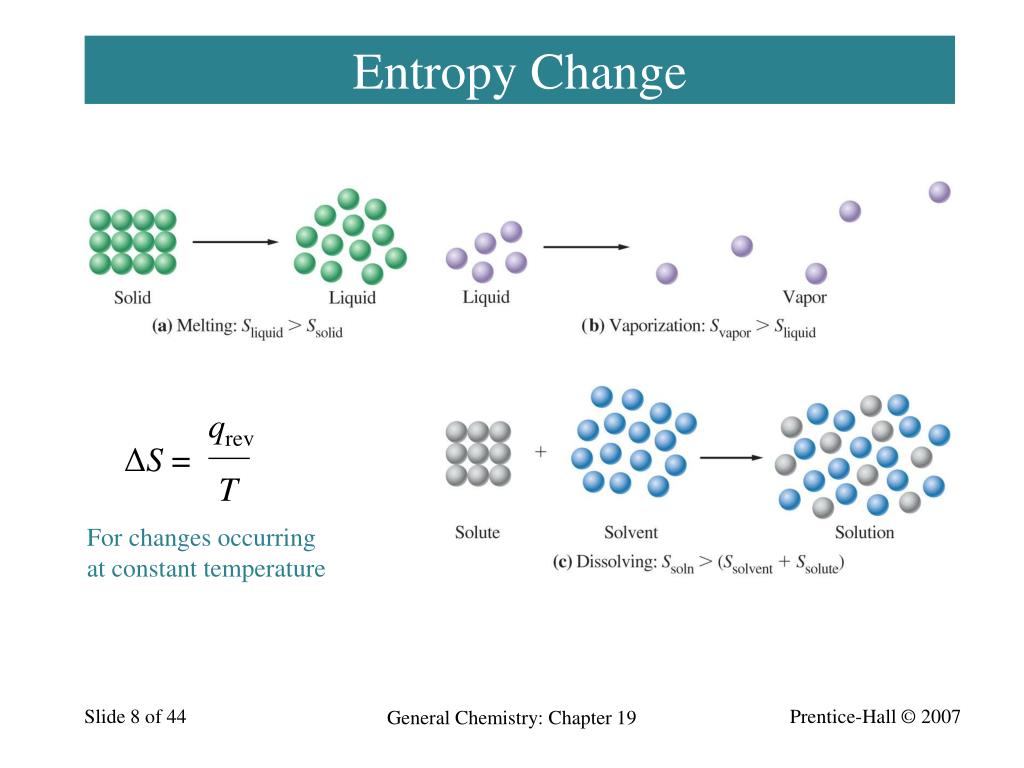
Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy 3b5 Vibrational energy and entropy general chemistry: chapter 19. 19 4 criteria for spontaneous change:the second law of thermodynamics. Δstotal = Δsuniverse = Δssystem Δssurroundings the second law of thermodynamics: Δsuniverse = Δssystem Δssurroundings > 0 all spontaneous processes produce an increase in the entropy of the universe. A process that is spontaneous in one direction is non spontaneous in the reverse direction. 19 2 the concept of entropy entropy is a thermodynamic property related to the distribution of a system’ s energy among the available microscopic energy levels. entropy usually refers to the idea that everything in the universe eventually moves from.

Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy 3b5 Presentation on theme: "chapter 19 spontaneous change: entropy and free energy dr. peter warburton"— presentation transcript:. Entropy • entropy (from greek, meaning • “in transformation”) • is a thermodynamic property • that relates • the distribution of the total energy of the system • to the available energy levels of the particles. entropy • a general way to envision entropy is • “differing ways to move” • consider mountain climbers on a. Table of contents (17.1) spontaneous processes and entropy (17.2) entropy and the second law of thermodynamics (17.3) the effect of temperature on spontaneity (17.4) free energy (17.5) entropy changes in chemical reactions (17.6) free energy and chemical reactions (17.7) the dependence of free energy on pressure (17.8) free energy and equilibrium (17.9) free energy and work. Chapter 19 spontaneous processes and entropy thermodynamics lets us predict whether a process will occur but gives no information about the amount of time required for the process. a spontaneous process is one that occurs without outside intervention. entropy the driving force for a spontaneous process is an increase in the entropy of the universe.

Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy 3b5 Table of contents (17.1) spontaneous processes and entropy (17.2) entropy and the second law of thermodynamics (17.3) the effect of temperature on spontaneity (17.4) free energy (17.5) entropy changes in chemical reactions (17.6) free energy and chemical reactions (17.7) the dependence of free energy on pressure (17.8) free energy and equilibrium (17.9) free energy and work. Chapter 19 spontaneous processes and entropy thermodynamics lets us predict whether a process will occur but gives no information about the amount of time required for the process. a spontaneous process is one that occurs without outside intervention. entropy the driving force for a spontaneous process is an increase in the entropy of the universe. A spontaneous process may proceed very slowly. spontaneity there are three factors that combine to predict spontaneity. they are: 1. energy change 2. temperature 3. entropy change entropy a measure of randomness or disorder entropy entropy, s, is a measure of randomness or disorder. 3) entropy is a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system. it increases for spontaneous processes according to the second law of thermodynamics. 4) the gibbs free energy, Δg, can be used to determine whether a process is spontaneous, with a negative Δg corresponding to a spontaneous process. spontaneity entropy and free energy.ppt.
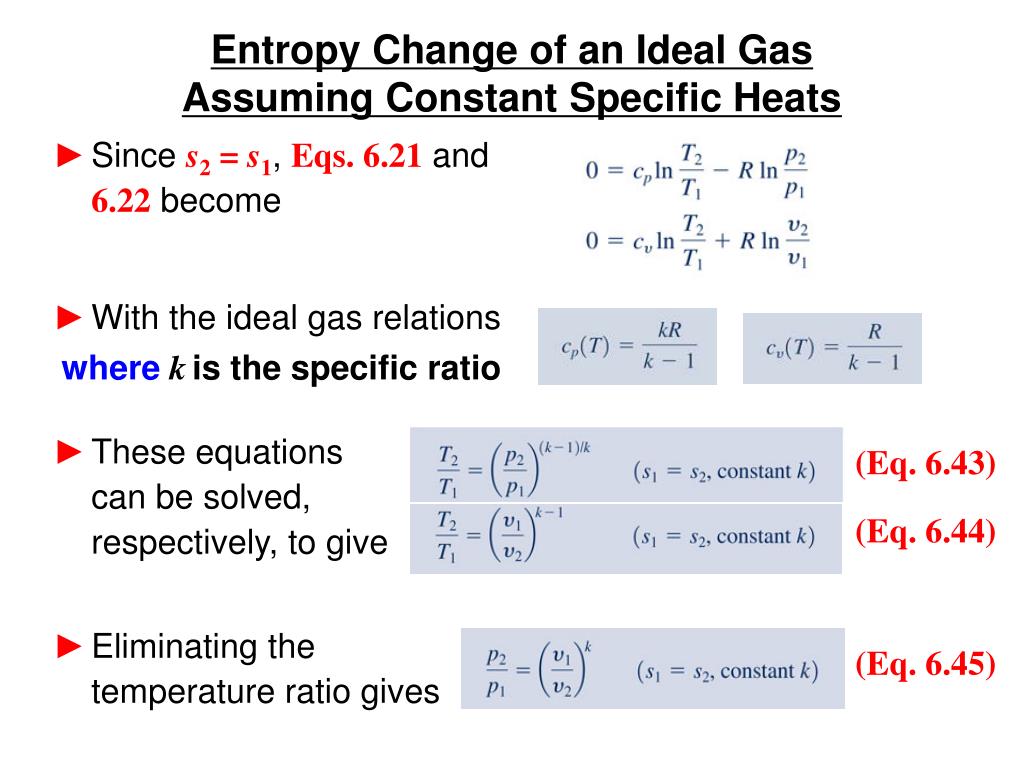
Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Energy 3b5 A spontaneous process may proceed very slowly. spontaneity there are three factors that combine to predict spontaneity. they are: 1. energy change 2. temperature 3. entropy change entropy a measure of randomness or disorder entropy entropy, s, is a measure of randomness or disorder. 3) entropy is a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system. it increases for spontaneous processes according to the second law of thermodynamics. 4) the gibbs free energy, Δg, can be used to determine whether a process is spontaneous, with a negative Δg corresponding to a spontaneous process. spontaneity entropy and free energy.ppt.

Comments are closed.