Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Ener

Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Ene Vibrational energy and entropy general chemistry: chapter 19. 19 4 criteria for spontaneous change:the second law of thermodynamics. Δstotal = Δsuniverse = Δssystem Δssurroundings the second law of thermodynamics: Δsuniverse = Δssystem Δssurroundings > 0 all spontaneous processes produce an increase in the entropy of the universe. 8 general chemistry: chapter 19 chemistry 140 fall 2002 trouton’s rule a useful generalization known as trouton s rule states that for many liquids at their normal boiling points, the standard molar entropy of vaporization has a value of about 87 j mol 1 k 1 Δs = Δhvap tbp ~ 87 kj mol 1 k 1 instances in which trouton s rule fails are also understandable.
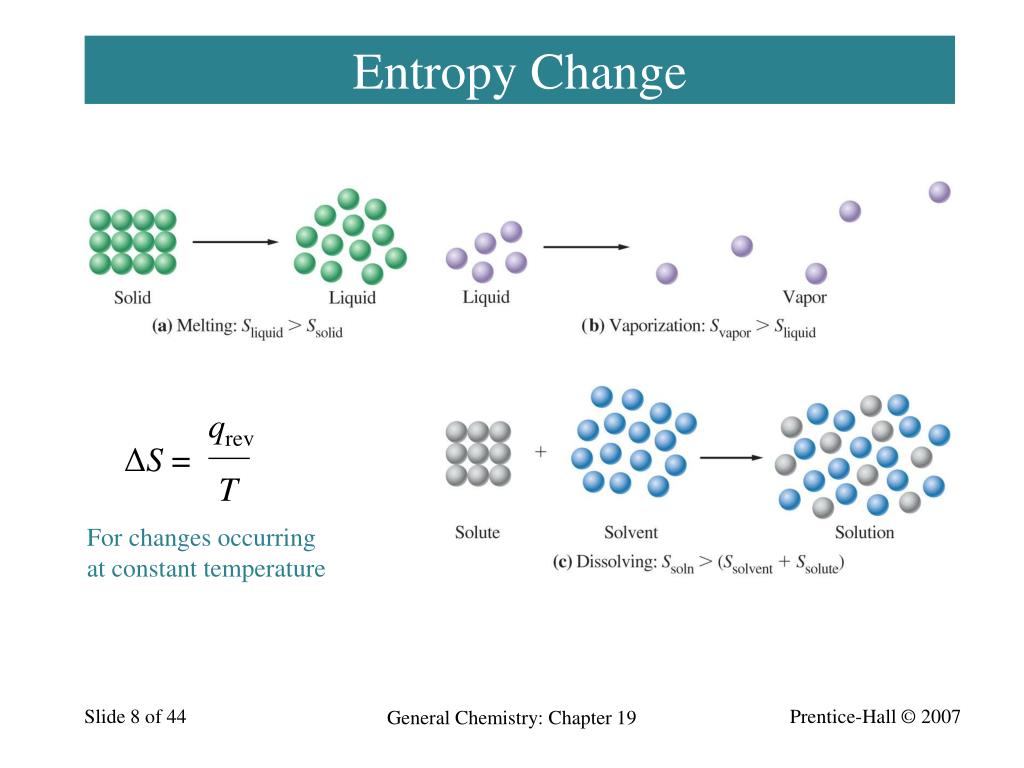
Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Ener Download ppt "chapter 19 spontaneous change: entropy and free energy dr. peter warburton" similar presentations thermodynamics:entropy, free energy, and equilibrium. Entropy • entropy (from greek, meaning • “in transformation”) • is a thermodynamic property • that relates • the distribution of the total energy of the system • to the available energy levels of the particles. entropy • a general way to envision entropy is • “differing ways to move” • consider mountain climbers on a. 23 slide 23 of 44 the entropy change for the decomposition of ozone forming diatomic oxygen, 1.is positive because two moles of gas are forming three moles of gas. 2.is close to zero because there are the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. 3.is negative because energy is released as the reaction proceeds. 4.is close to zero because both ozone and oxygen are in the gas phase. 5. A spontaneous process may proceed very slowly. spontaneity there are three factors that combine to predict spontaneity. they are: 1. energy change 2. temperature 3. entropy change entropy a measure of randomness or disorder entropy entropy, s, is a measure of randomness or disorder.

Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Ener 23 slide 23 of 44 the entropy change for the decomposition of ozone forming diatomic oxygen, 1.is positive because two moles of gas are forming three moles of gas. 2.is close to zero because there are the same number of atoms on each side of the equation. 3.is negative because energy is released as the reaction proceeds. 4.is close to zero because both ozone and oxygen are in the gas phase. 5. A spontaneous process may proceed very slowly. spontaneity there are three factors that combine to predict spontaneity. they are: 1. energy change 2. temperature 3. entropy change entropy a measure of randomness or disorder entropy entropy, s, is a measure of randomness or disorder. Chapter 19 spontaneous processes and entropy thermodynamics lets us predict whether a process will occur but gives no information about the amount of time required for the process. a spontaneous process is one that occurs without outside intervention. entropy the driving force for a spontaneous process is an increase in the entropy of the universe. Law of thermodynamics: 1st law: energy in conserved (neither created nor destroyed in any process) 2nd law: the total entropy of the universe increases in any spontaneous process. 3rd law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (s =0) understanding entropy. is a state function so that Δs = sfinal sinitial.
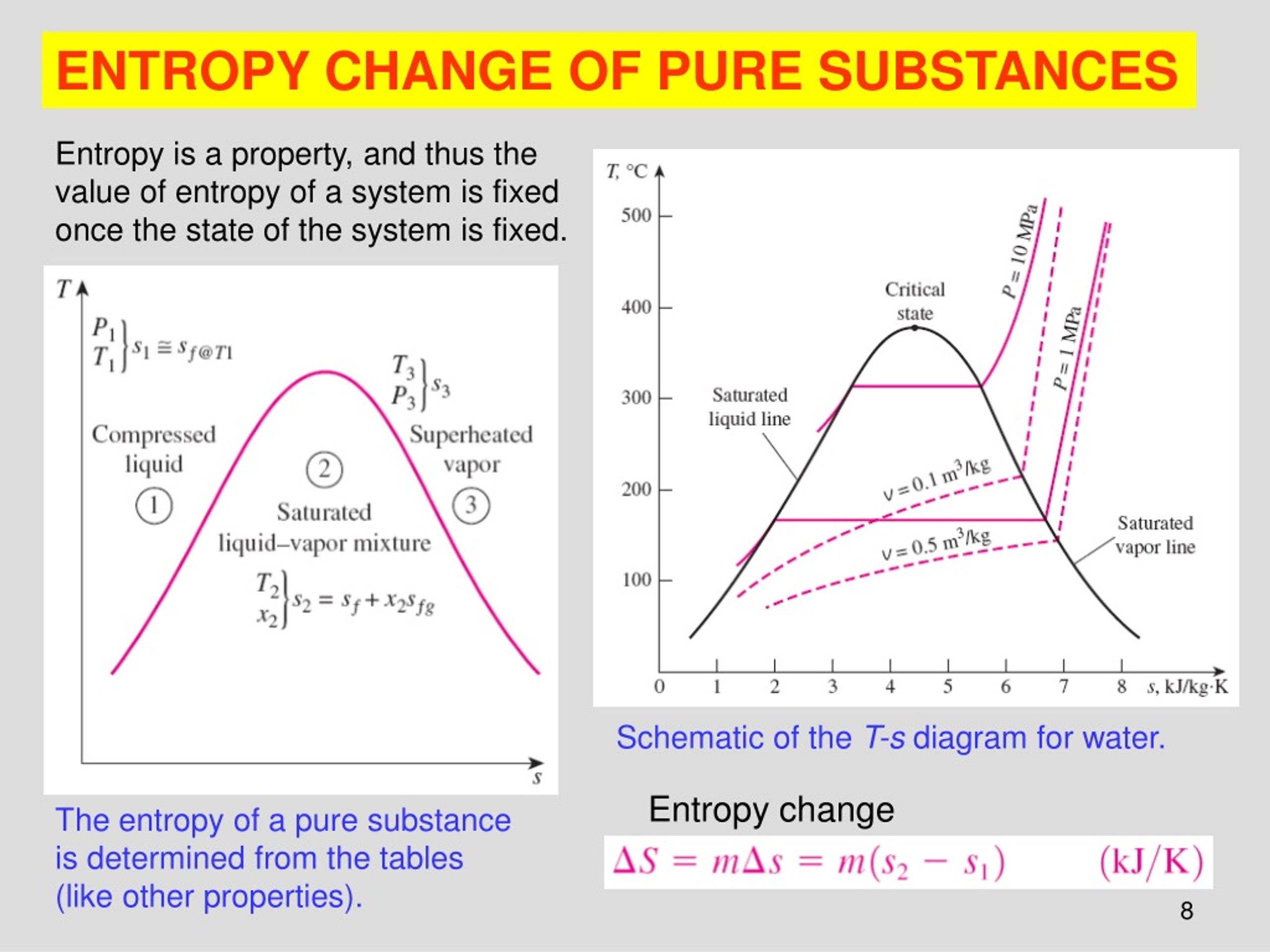
Ppt Chapter 19 Spontaneous Change Entropy And Free Ener Chapter 19 spontaneous processes and entropy thermodynamics lets us predict whether a process will occur but gives no information about the amount of time required for the process. a spontaneous process is one that occurs without outside intervention. entropy the driving force for a spontaneous process is an increase in the entropy of the universe. Law of thermodynamics: 1st law: energy in conserved (neither created nor destroyed in any process) 2nd law: the total entropy of the universe increases in any spontaneous process. 3rd law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (s =0) understanding entropy. is a state function so that Δs = sfinal sinitial.

Comments are closed.