Plate Layers Convection Distribution Movement
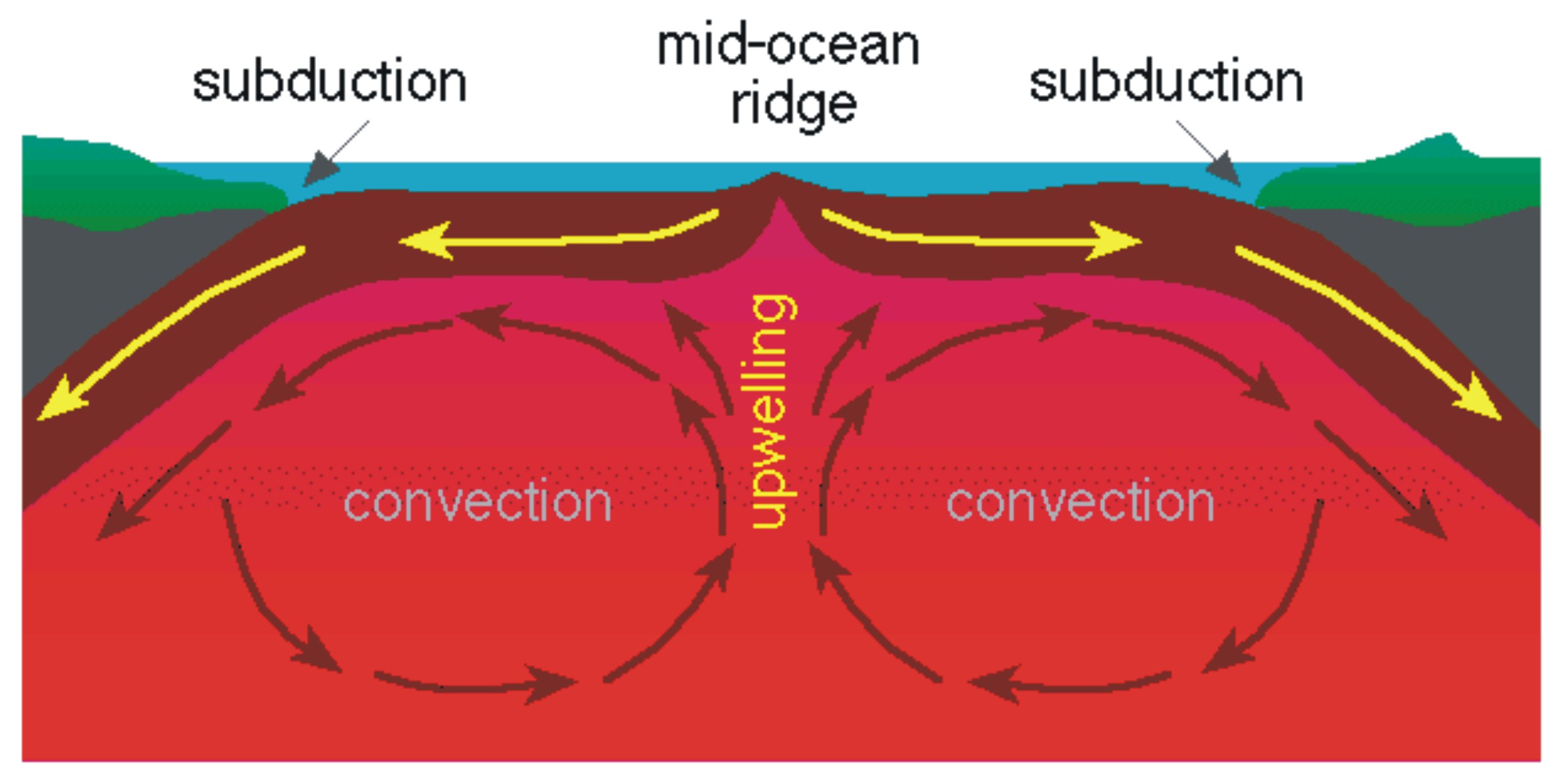
A Shift To Plate Tectonics The Emergence And Evolution Of Plate Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that explains how major landforms are created as a result of earth’s subterranean movements. the theory, which solidified in the 1960s, transformed the earth sciences by explaining many phenomena, including mountain building events, volcanoes, and earthquakes. in plate tectonics, earth’s outermost. The initial explanation for the movement of tectonic plates was convection currents in the mantle. the theory suggests these convection currents are created by heat from within the earth – much of which is generated by radioactive decay in the core. the idea is that the outer core, which is hotter than the mantle, drives convection currents.

Convection Earth's lithosphere and upper mantle a cross section of earth's outer layers, from the crust through the lower mantle. in essence, plate tectonic theory is elegantly simple. earth ’s surface layer, 50 to 100 km (30 to 60 miles) thick, is rigid and is composed of a set of large and small plates. together, these plates constitute the. Plate tectonics (from latin tectonicus, from ancient greek τεκτονικός (tektonikós) 'pertaining to building') [ 1 ] is the scientific theory that earth 's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. [ 2 ][ 3 ][ 4 ] the model builds on the concept of continental. Plate tectonics. plate tectonics refers to the process of plate formation, movement, and destruction. it finds its foundations in two theories, continental drift and sea floor spreading. continental drift describes the movements of continents over the earth's surface. sea floor spreading refers to the creation new oceanic plate material and. Plate tectonics shapes global landforms and environments through the rock cycle, mountain building, volcanism, and the distribution of continents and oceans. these phenomena, ultimately driven by earth’s internal heat, have far reaching effects on other parts of the earth system, including the sea level experienced along coastlines.
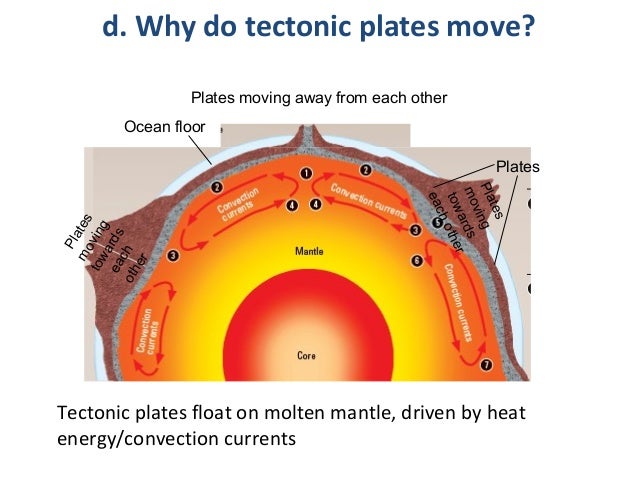
Plate Layers Convection Distribution Movement Plate tectonics. plate tectonics refers to the process of plate formation, movement, and destruction. it finds its foundations in two theories, continental drift and sea floor spreading. continental drift describes the movements of continents over the earth's surface. sea floor spreading refers to the creation new oceanic plate material and. Plate tectonics shapes global landforms and environments through the rock cycle, mountain building, volcanism, and the distribution of continents and oceans. these phenomena, ultimately driven by earth’s internal heat, have far reaching effects on other parts of the earth system, including the sea level experienced along coastlines. Frp = 3.24x1012n m. this page titled 4.1: the forces driving plate motions is shared under a cc by sa license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by magali billen. the motion of tectonic plates is driven by one simple principle, convection. convection is the idea that dense, cold things sink, and buoyant, warm things rise. Earthquakes,volcanic activity, mountain building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. the lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually. tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust.

Plate Layers Convection Distribution Movement Ppt Frp = 3.24x1012n m. this page titled 4.1: the forces driving plate motions is shared under a cc by sa license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by magali billen. the motion of tectonic plates is driven by one simple principle, convection. convection is the idea that dense, cold things sink, and buoyant, warm things rise. Earthquakes,volcanic activity, mountain building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. the lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually. tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust.
Theory Of Plate Tectonics Ck 12 Foundation

Comments are closed.