Physical Properties Of Matter

Physical Property Of Matter Definition And Examples Learn what a physical property of matter is and how to observe and measure it without changing its chemical identity. find out the types and examples of physical properties, such as color, density, and temperature. Learn what matter is and how to distinguish it from other substances. explore the physical and chemical properties of matter, such as density, colour, reactivity, and flammability, with examples and videos.

Examples Of Chemical And Physical Properties All matter has physical and chemical properties. physical properties are characteristics that scientists can measure without changing the composition of the sample under study, such as mass, color, and volume (the amount of space occupied by a sample). Learn what physical properties are and how they differ from chemical properties. find out the types, examples, and applications of physical properties of matter. A physical change is a change in the state or properties of matter without any accompanying change in the chemical identities of the substances contained in the matter. physical changes are observed when wax melts, when sugar dissolves in coffee, and when steam condenses into liquid water (figure 1.18). other examples of physical changes. Learn the difference between physical and chemical properties and changes of matter, and how to measure and identify them. find examples of extensive and intensive properties, density, and common substances with their densities.

All The Properties Of Matter A physical change is a change in the state or properties of matter without any accompanying change in the chemical identities of the substances contained in the matter. physical changes are observed when wax melts, when sugar dissolves in coffee, and when steam condenses into liquid water (figure 1.18). other examples of physical changes. Learn the difference between physical and chemical properties and changes of matter, and how to measure and identify them. find examples of extensive and intensive properties, density, and common substances with their densities. Matter is the material substance that constitutes the observable universe and forms the basis of all objective phenomena. learn about the properties, states, and types of matter, as well as the history and modern theories of matter in physics. Learn what physical properties are and how they can be measured without changing the identity of a substance. find out the difference between intensive and extensive properties and see some examples of each type.
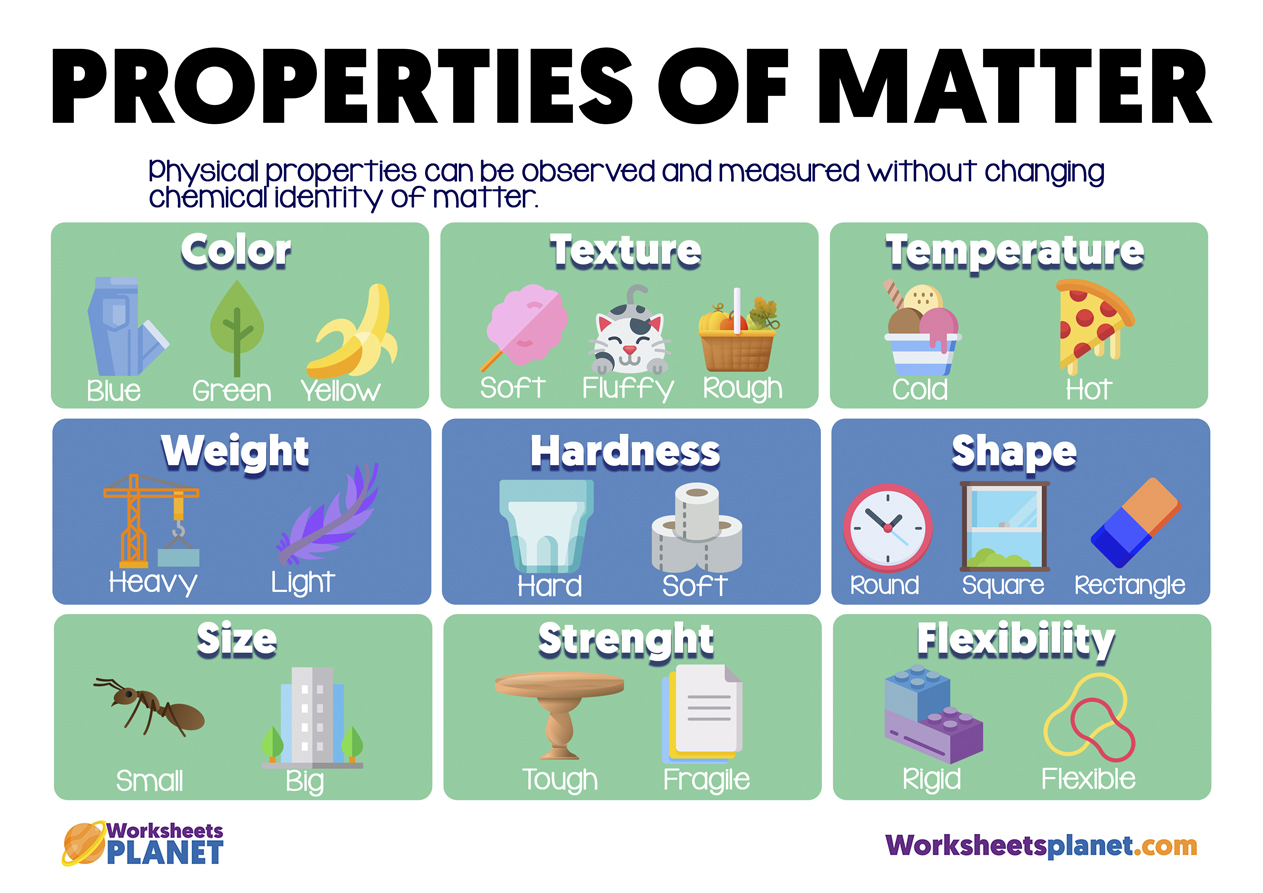
Properties Of Matter Matter is the material substance that constitutes the observable universe and forms the basis of all objective phenomena. learn about the properties, states, and types of matter, as well as the history and modern theories of matter in physics. Learn what physical properties are and how they can be measured without changing the identity of a substance. find out the difference between intensive and extensive properties and see some examples of each type.

Comments are closed.