Perovskite Solar Cells Department Of Energy
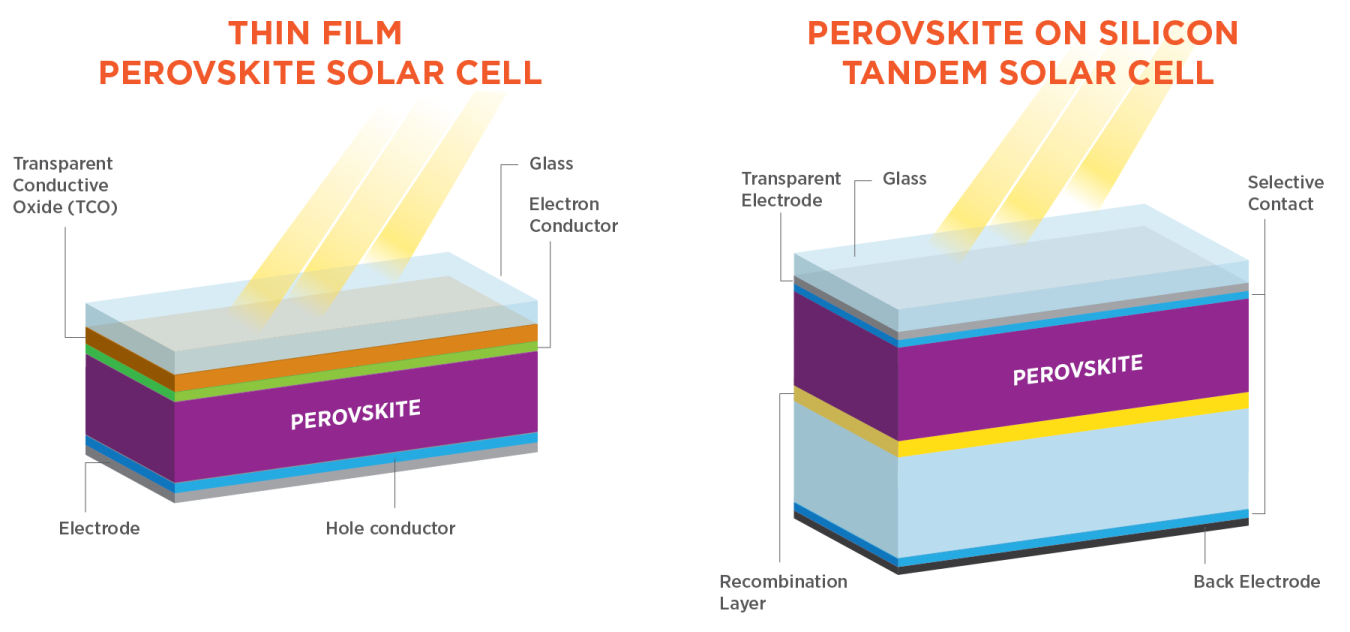
Perovskite Solar Cells Department Of Energy The name “perovskite” comes from the nickname for their crystal structure, although other types of non halide perovskites (such as oxides and nitrides) are utilized in other energy technologies, such as fuel cells and catalysts. perovskite solar cells have shown remarkable progress in recent years with rapid increases in efficiency, from. The perovskite startup prize is part of the american made challenges and is administered by the national renewable energy laboratory. the perovskite startup prize is a two stage, $3 million prize competition designed to accelerate the development and manufacturing of perovskite solar cells by moving world class research out of the lab and into.
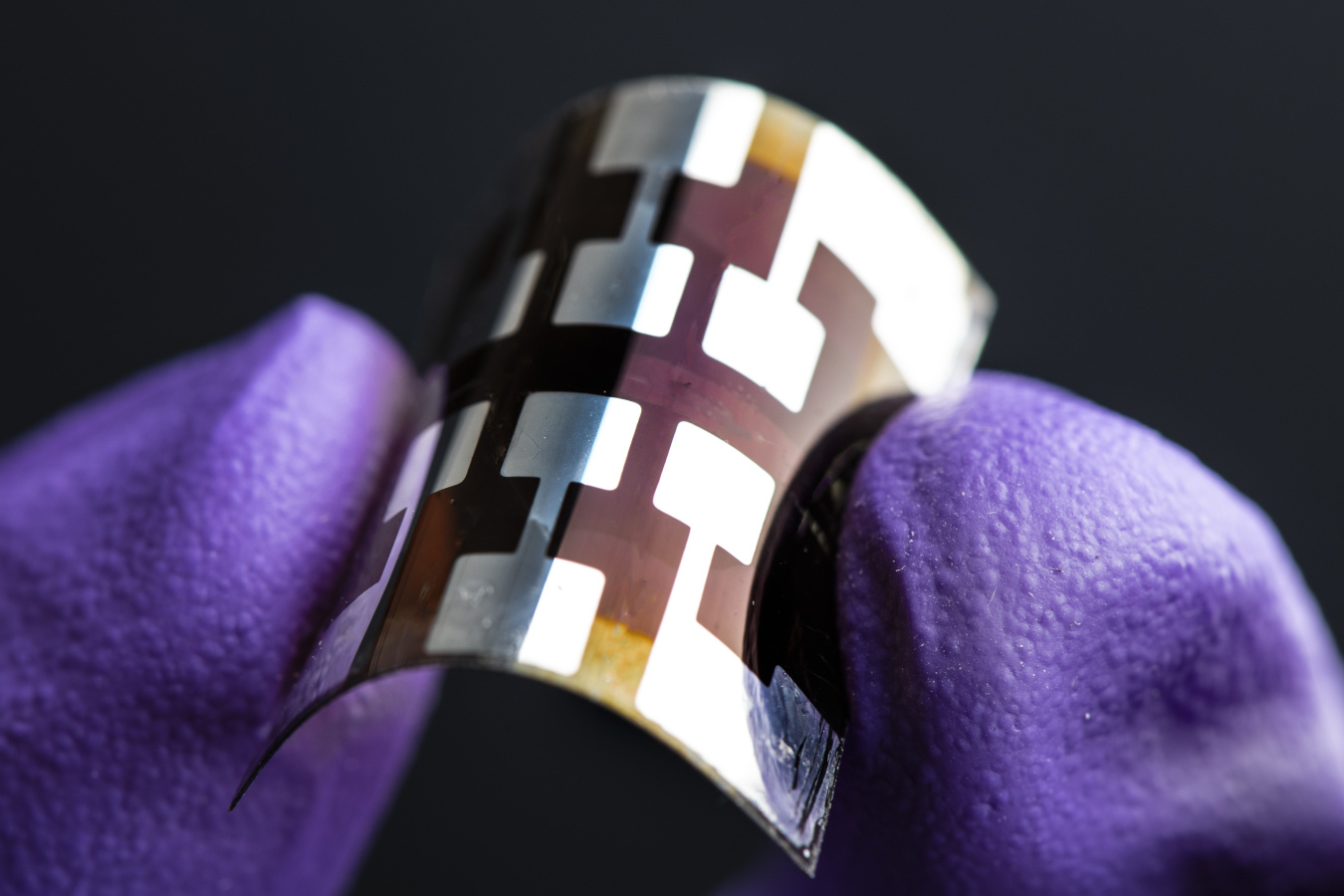

Perovskite Solar Cells Department Of Energy Washington, d.c. – today, the u.s. department of energy (doe) announced $20 million in funding to advance perovskite solar photovoltaic technologies. perovskites are a family of materials with a specific crystal structure, named after the mineral with that structure. A bifacial perovskite solar cell, which allows sunlight to reach both sides of the device, holds the potential to produce higher energy yields at lower overall costs, according to scientists at the u.s. department of energy’s national renewable energy laboratory (nrel). the dual nature of a bifacial solar cell enables the capture of direct. “we’re grateful to the department of energy for supporting this powerful new model and excited to get to work.” adam lorenz, cto of solar energy technology company cubicpv, stresses the importance of thinking about scale, alongside quality and efficiency, to accelerate the perovskite effort into the commercial environment. Researchers at nrel made a technological breakthrough and constructed a perovskite solar cell with the dual benefits of being both highly efficient and highly stable. the work was done in collaboration with scientists from the university of toledo, the university of colorado–boulder, and the university of california–san diego.

Comments are closed.