Patterns Of Inheritance Anatomy And Physiology Ii
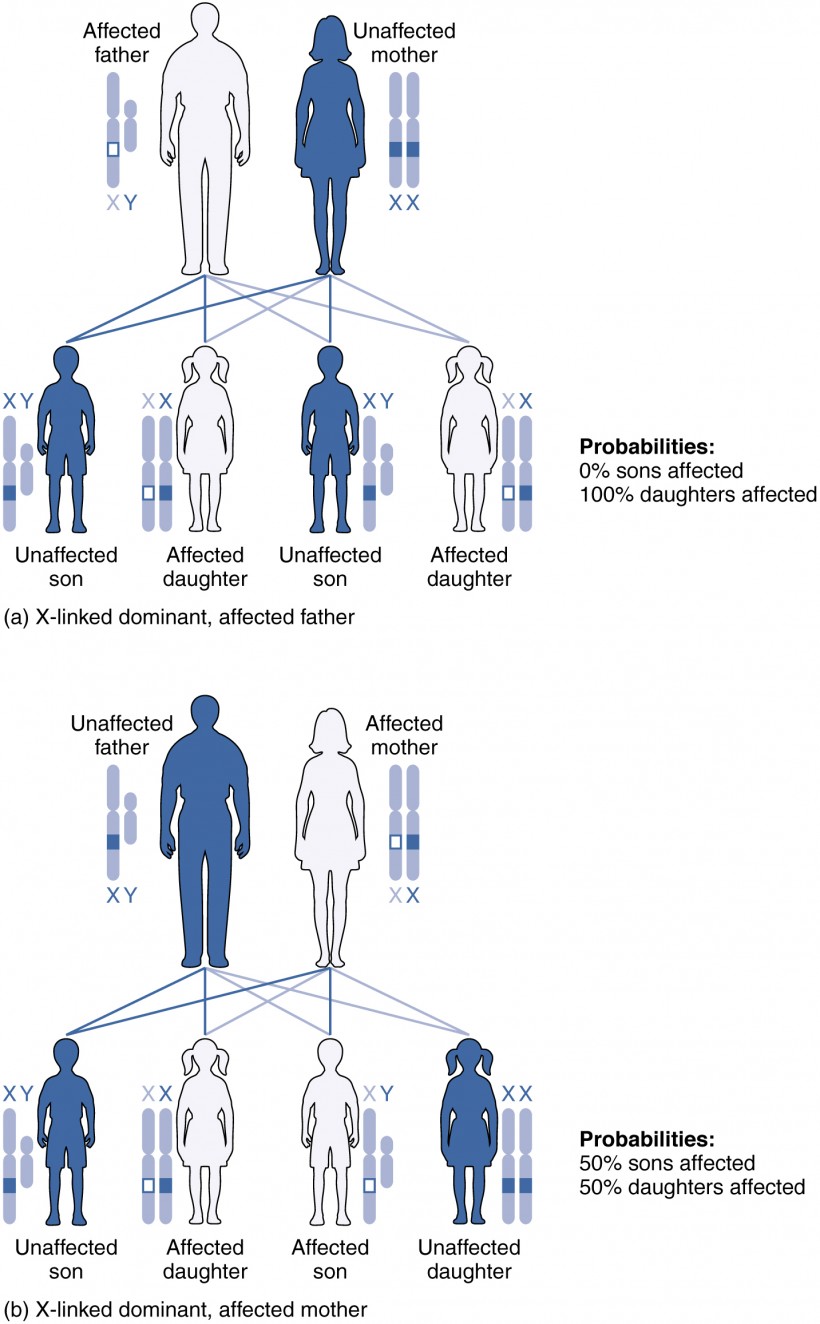
Patterns Of Inheritance Anatomy And Physiology Ii You inherit one chromosome in each pair—a full complement of 23—from each parent. this occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. homologous chromosomes—those that make up a complementary pair—have genes for the same characteristics in the same location on the chromosome. Figure 28.26 autosomal dominant inheritance inheritance pattern of an autosomal dominant disorder, such as neurofibromatosis, is shown in a punnett square. other genetic diseases that are inherited in this pattern are achondroplastic dwarfism, marfan syndrome, and huntington’s disease.
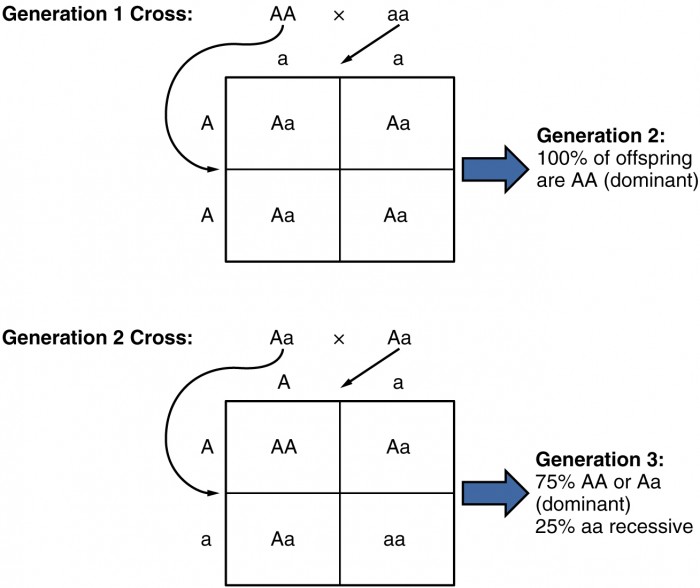
Patterns Of Inheritance Anatomy And Physiology Ii This inheritance pattern is shown in figure 28.7.3, in a form called a punnett square, named after its creator, the british geneticist reginald punnett. figure 28.7.3 – autosomal dominant inheritance: inheritance pattern of an autosomal dominant disorder, such as neurofibromatosis, is shown in a punnett square. Classify and describe the different patterns of inheritance figure 1. a single fertilized egg develops over the span of nine months into an infant consisting of trillions of cells and capable of surviving outside the womb. You inherit one chromosome in each pair—a full complement of 23—from each parent. this occurs when the sperm and oocyte combine at the moment of your conception. homologous chromosomes—those that make up a complementary pair—have genes for the same characteristics in the same location on the chromosome. The dramatic changes of fertilization, embryonic development, and fetal development are followed by remarkable adaptations of the newborn to life outside the womb. an offspring’s normal development depends upon the appropriate synthesis of structural and functional proteins. this, in turn, is governed by the genetic material inherited from.

Comments are closed.