Output Gap Topslenak

Output Gap Topslenak The output gap is useful for checking the health of the economy. potential output is an estimate of what the economy could produce. actual output is what the economy does produce. if actual output is below potential a negative output gap there is 'slack' in the economy. if actual output is above potential a positive output gap resources are fully employed, or perhaps overutilized. Output gap = actual output − potential output potential output × 100. a negative output gap indicates there’s slack in the economy as resources are being underutilized. the economy is performing below potential. a positive output gap means any slack has evaporated and resources are being fully employed, maybe even to the point of overcapacity.
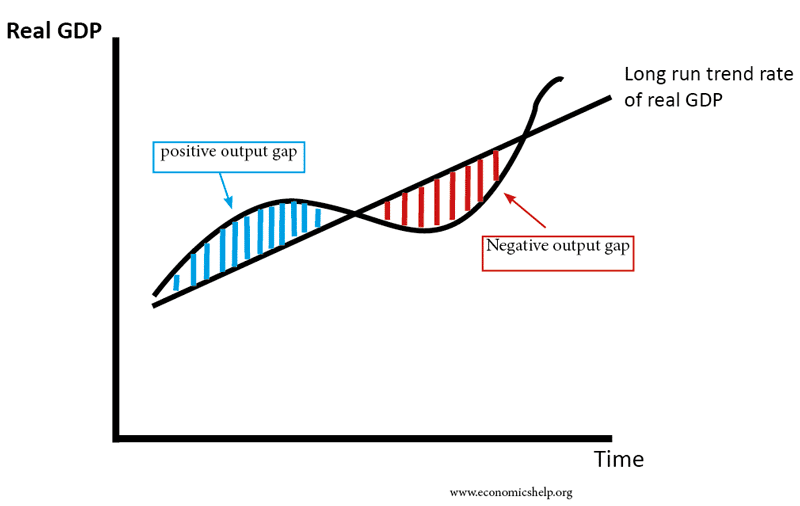
Output Gap Definition Economics Help Estimates of output gaps are subject to a significant margin of uncertainty. for a discussion of approaches to calculating potential output, see paula r. de masi, imf estimates of potential output: theory and practice, in staff studies for the world economic outlook (washington: imf, december 1997), pp. 40 46. The gdp gap formula (or output gap) is the percentage difference between aggregate output (actual gdp) and its potential level, the potential output. when output exceeds its potential level, there is a positive output gap, and the economy functions above its full capacity. employees tend to demand higher salaries, and firms are prone to use the. Imf estimates of the 2009 output gaps as % of gdp by country. the gdp gap or the output gap is the difference between actual gdp or actual output and potential gdp, in an attempt to identify the current economic position over the business cycle. the measure of output gap is largely used in macroeconomic policy (in particular in the context of. The level of certain latent variables (such the output gap, the natural rate of interest, the nairu, etc.) and in the changes that the crisis has brought about in nature of the cyclical uctuations in in ation and unemployment. unfortunately, while the profession agrees on the centrality of these.

Output Gaps In Macroeconomics Equilibrium Youtube Imf estimates of the 2009 output gaps as % of gdp by country. the gdp gap or the output gap is the difference between actual gdp or actual output and potential gdp, in an attempt to identify the current economic position over the business cycle. the measure of output gap is largely used in macroeconomic policy (in particular in the context of. The level of certain latent variables (such the output gap, the natural rate of interest, the nairu, etc.) and in the changes that the crisis has brought about in nature of the cyclical uctuations in in ation and unemployment. unfortunately, while the profession agrees on the centrality of these. Basic info. us output gap is at 11.71%, compared to 11.41% last quarter and 10.30% last year. this is higher than the long term average of 6.94%. the us output gap is the difference between actual gdp or actual output and potential gdp. the calculation for the output gap is y–y* where y is actual output and y* is potential output. The difference between potential output and actual output—or, in other words, the difference between where the economy would be normally and where it is now—is known as the output gap. 3 the output gap is one of many economic measures that policymakers use to evaluate our economic performance. u.s. real gdp versus potential real gdp.

Output Gaps вђ The Tutor Academy Basic info. us output gap is at 11.71%, compared to 11.41% last quarter and 10.30% last year. this is higher than the long term average of 6.94%. the us output gap is the difference between actual gdp or actual output and potential gdp. the calculation for the output gap is y–y* where y is actual output and y* is potential output. The difference between potential output and actual output—or, in other words, the difference between where the economy would be normally and where it is now—is known as the output gap. 3 the output gap is one of many economic measures that policymakers use to evaluate our economic performance. u.s. real gdp versus potential real gdp.

Aggregate Supply Topslenak

Comments are closed.