Operons Prokaryotic Gene Expression Part 1 Mcat Biology
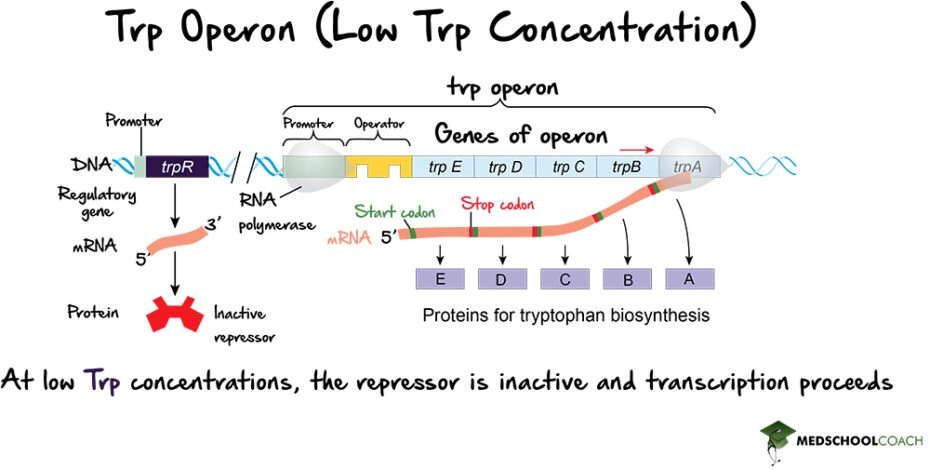
Operons Prokaryotic Gene Expression Part 1 вђ Mcat Biology Understanding prokaryotic gene expression is essential for the mcat exam. in prokaryotes, gene expression is tightly regulated. structural proteins that have related functions are encoded together within the genome in various blocks called operons. an operon is a dna sequence that includes a promoter, an operator, and the genes that are. The operon concept states that the set of genes that are transcribed in the prokaryotes are under the control of operons. jacob and monod showed the organization of bacterial genes into operons. in bacteria and archaea, structural proteins with related functions are usually encoded together within the genome in a block called an operon and are.
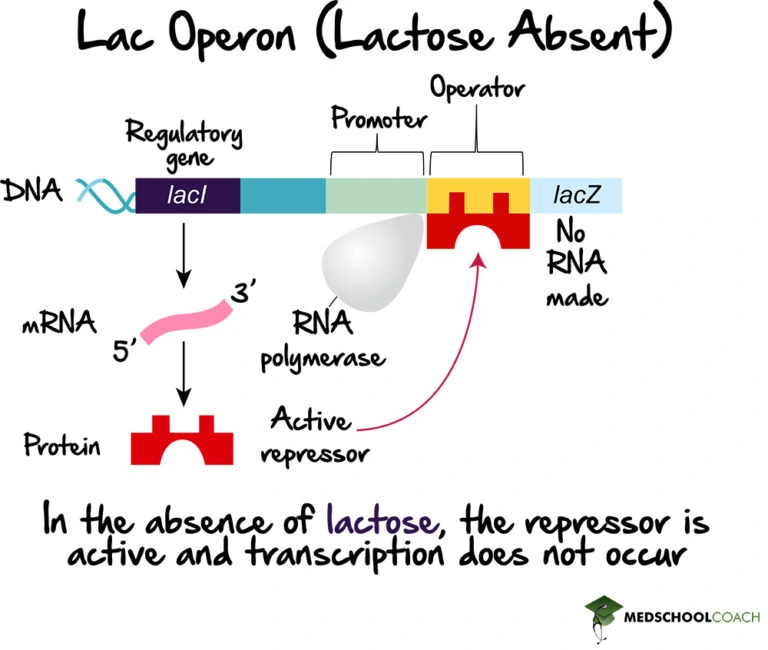
Operons Prokaryotic Gene Expression Part 1 вђ Mcat Biology Gene repression in bacteria. prokaryotic operons are commonly controlled by the binding of repressors to operator regions, thereby preventing the transcription of the structural genes. these prokaryotic operons are classified as either repressible operons or inducible operons. repressible operons, like the tryptophan (trp) operon, typically. The operon model of prokaryotic gene expression refers to the cluster of gene sequences and regions which work together to produce a mrna transcript, probably better explained via the visual below. there are 2 genes within the model: the repressor gene, which codes for a repressor protein, and the structural gene, which codes for the actual. Figure 11.7.6 11.7. 6: (a) in the presence of camp, cap binds to the promoters of operons, like the lac operon, that encode genes for enzymes for the use of alternate substrates. (b) for the lac operon to be expressed, there must be activation by camp cap as well as removal of the lac repressor from the operator. In terms of regulation, prokaryotic genes are typically organized into operons, allowing for coordinated regulation of functionally related genes. eukaryotic genes, on the other hand, tend to be individually regulated by specific enhancers and silencers. what is the role of the lac operon in e. coli gene expression?.

Operons Prokaryotic Gene Expression Part 1 вђ Mcat Biology Figure 11.7.6 11.7. 6: (a) in the presence of camp, cap binds to the promoters of operons, like the lac operon, that encode genes for enzymes for the use of alternate substrates. (b) for the lac operon to be expressed, there must be activation by camp cap as well as removal of the lac repressor from the operator. In terms of regulation, prokaryotic genes are typically organized into operons, allowing for coordinated regulation of functionally related genes. eukaryotic genes, on the other hand, tend to be individually regulated by specific enhancers and silencers. what is the role of the lac operon in e. coli gene expression?. The diagram shown here is a model of the gene regulatory circuit for light production by v. fischeri cells. the lux operon contains genes for luminescence (luxcdabe) and a gene, luxi, that encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the production of an inducer. First, the level of glucose must be very low or non existent. second, lactose must be present. only when glucose is absent and lactose is present will the lac operon be transcribed (figure 16.6). in the absence of glucose, the binding of the cap protein makes transcription of the lac operon more effective.
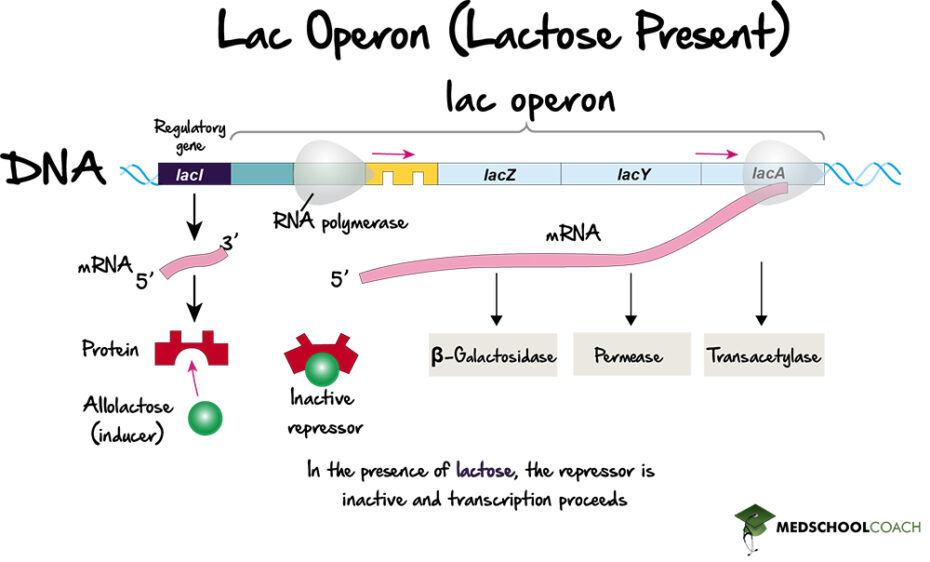
Operons Prokaryotic Gene Expression Part 1 вђ Mcat Biology The diagram shown here is a model of the gene regulatory circuit for light production by v. fischeri cells. the lux operon contains genes for luminescence (luxcdabe) and a gene, luxi, that encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the production of an inducer. First, the level of glucose must be very low or non existent. second, lactose must be present. only when glucose is absent and lactose is present will the lac operon be transcribed (figure 16.6). in the absence of glucose, the binding of the cap protein makes transcription of the lac operon more effective.

Mcat Masterclass Medschoolcoach

Comments are closed.