Newton S Laws Of Motion Equations And Applications
юааnewtonтащsюаб юааlawsюаб юааof Motionюаб юааformulaюаб юааapplicationsюаб тау Studiousguy 6.4: friction (part 1) when a body is in motion, it has resistance because the body interacts with its surroundings. this resistance is a force of friction. friction opposes relative motion between systems in contact but also allows us to move, a concept that becomes obvious if you try to walk on ice. 6.1 solving problems with newton’s laws. newton’s laws of motion can be applied in numerous situations to solve motion problems. some problems contain multiple force vectors acting in different directions on an object. be sure to draw diagrams, resolve all force vectors into horizontal and vertical components, and draw a free body diagram.
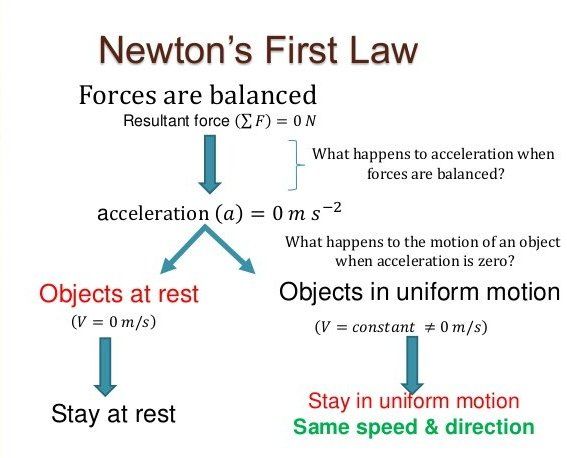
юааnewtonтащsюаб юааlawsюаб юааof Motionюаб юааformulaюаб юааapplicationsюаб тау Studiousguy Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. these laws, which provide the basis for newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: a body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, except insofar as it is acted upon by. Newton’s laws of motion relate an object’s motion to the forces acting on it. in the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. in the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. in the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude. 1= 60:0 n, and t. 2= 79:8 n. lecture 7: newton’s laws and their applications 6. accelerated motion f = ma a extremely common example of the accelerated motion type of problem is given in ex. 4.3 (page 123). a sled of mass mis placed on a frictionless hill (inclined plane) which is at an angle with the horizontal. Figure 4.4 the force exerted by a stretched spring can be used as a standard unit of force. (a) this spring has a length x when undistorted. (b) when stretched a distance Δx , the spring exerts a restoring force, frestore , which is reproducible. (c) a spring scale is one device that uses a spring to measure force.
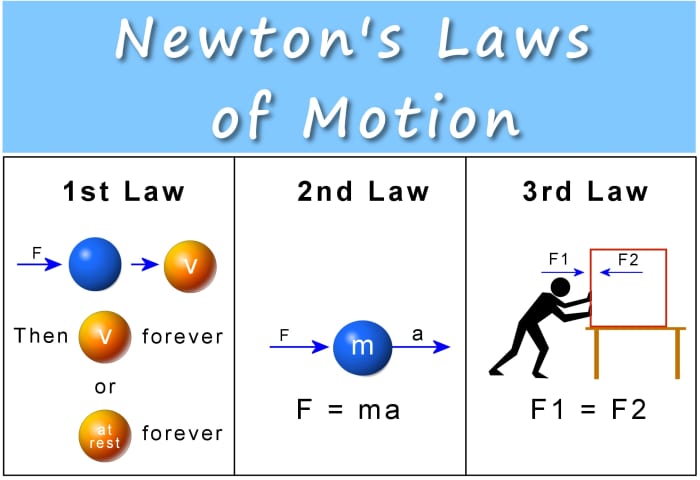
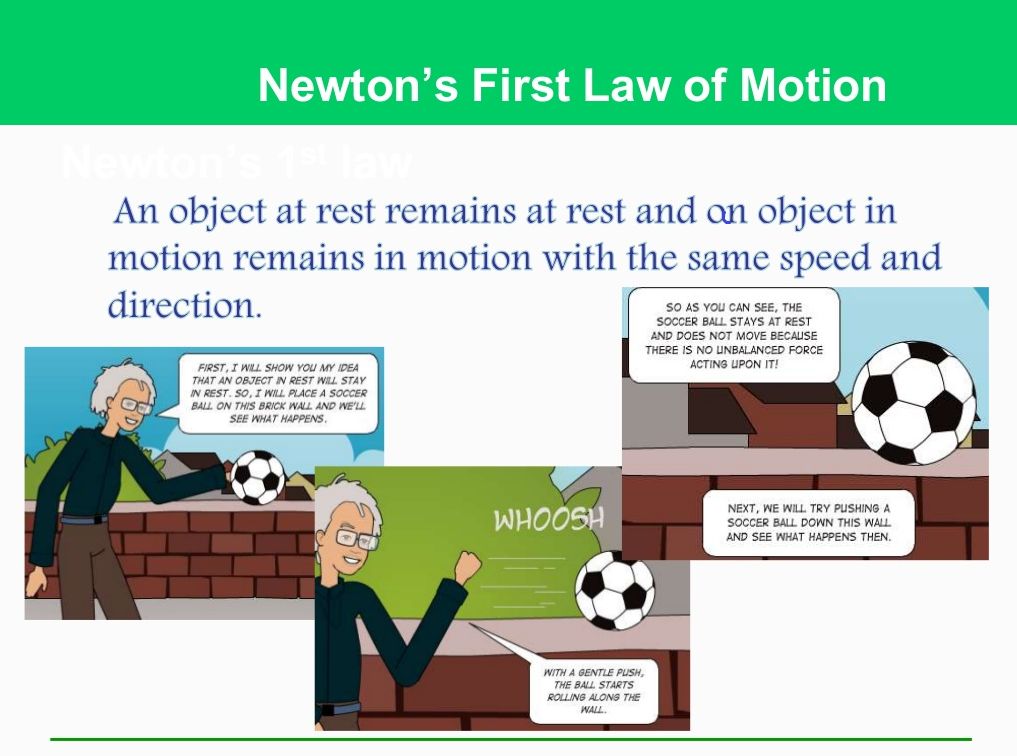
Newton S 3 Laws Of Motion Force Mass And Acceleration Owlcation 1= 60:0 n, and t. 2= 79:8 n. lecture 7: newton’s laws and their applications 6. accelerated motion f = ma a extremely common example of the accelerated motion type of problem is given in ex. 4.3 (page 123). a sled of mass mis placed on a frictionless hill (inclined plane) which is at an angle with the horizontal. Figure 4.4 the force exerted by a stretched spring can be used as a standard unit of force. (a) this spring has a length x when undistorted. (b) when stretched a distance Δx , the spring exerts a restoring force, frestore , which is reproducible. (c) a spring scale is one device that uses a spring to measure force. Therefore, this law is also known as action reaction law. example 1: the thrust of a rocket produces the force required to lift the rocket from earth. here, the thrust is the action, and the lift of the rocket is the reaction. example 2: when a person stands on earth’s surface, they experience a force due to gravity. The study of motion is kinematics, but kinematics only describes the way objects move—their velocity and their acceleration. dynamics considers the forces that affect the motion of moving objects and systems. newton’s laws of motion are the foundation of dynamics. these laws provide an example of the breadth and simplicity of principles.

Newton S Laws Of Motion Therefore, this law is also known as action reaction law. example 1: the thrust of a rocket produces the force required to lift the rocket from earth. here, the thrust is the action, and the lift of the rocket is the reaction. example 2: when a person stands on earth’s surface, they experience a force due to gravity. The study of motion is kinematics, but kinematics only describes the way objects move—their velocity and their acceleration. dynamics considers the forces that affect the motion of moving objects and systems. newton’s laws of motion are the foundation of dynamics. these laws provide an example of the breadth and simplicity of principles.

Newton S Laws Of Motion Equations And Applications

Comments are closed.