New Classical Model Lras Econstudy рџћ
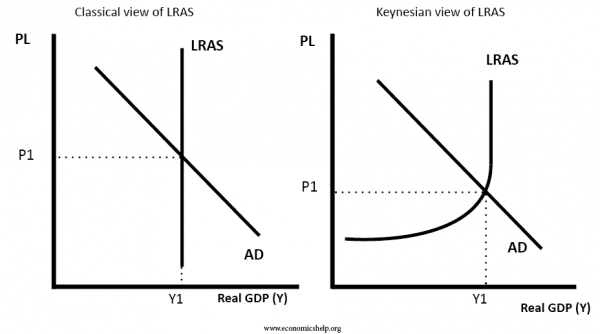
Aggregate Supply Economics Help October 29, 2022. the lras is an addition to the ad as model, which is used to examine the theoretical perspective of new classical economists. the long run aggregate supply (lras) is a curve which shows the total quantity of goods and services in an economy (real gdp) and the price level during a time period when resource prices are flexible. Classical theory is the basis for monetarism, which only concentrates on managing the money supply, through monetary policy. keynesian economics suggests governments need to use fiscal policy, especially in a recession. (this is an argument to reject austerity policies of the 2008 13 recession. 3. government borrowing.
Ppt Aggregate Supply Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4329610 Study with quizlet and memorise flashcards containing terms like state the key principles on which the monetarist new classical model is based, define the lras, explain the monetarist new classical perspective on the lras curve and others. Equilibrium in the monetarist new classical model. the diagram illustrates what takes place in an economy according to a monetarist when aggregate demand increases. assume the economy is in equilibrium at y1p1, where ad1 = sras1 = lras. ad shifts ad1 > ad2. firms respond to this increase in demand by increasing their output (gdp y1 > y2). Aggregate supply classical and keynesian interpretation. a video covering aggregate supply classical and keynesian interpretationinstagram: @econplusdalt. Saddique ansari • january 28, 2020 • 5 min read. the long run aggregate supply (lras) curve depicts the relationship between the price level and the real gdp when there has been time for input prices to adjust to fluctuations in aggregate demand. there are two types of long run aggregative supply curves. the keynesian lras.
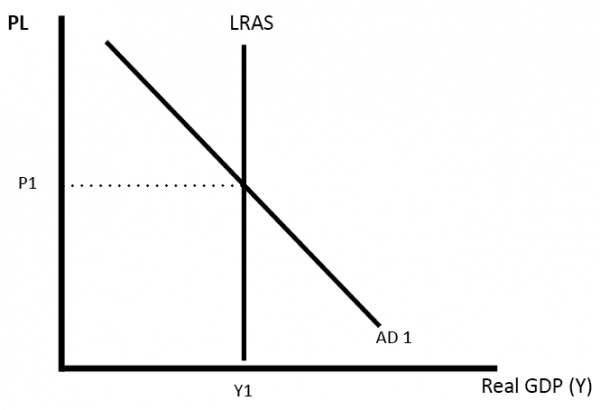
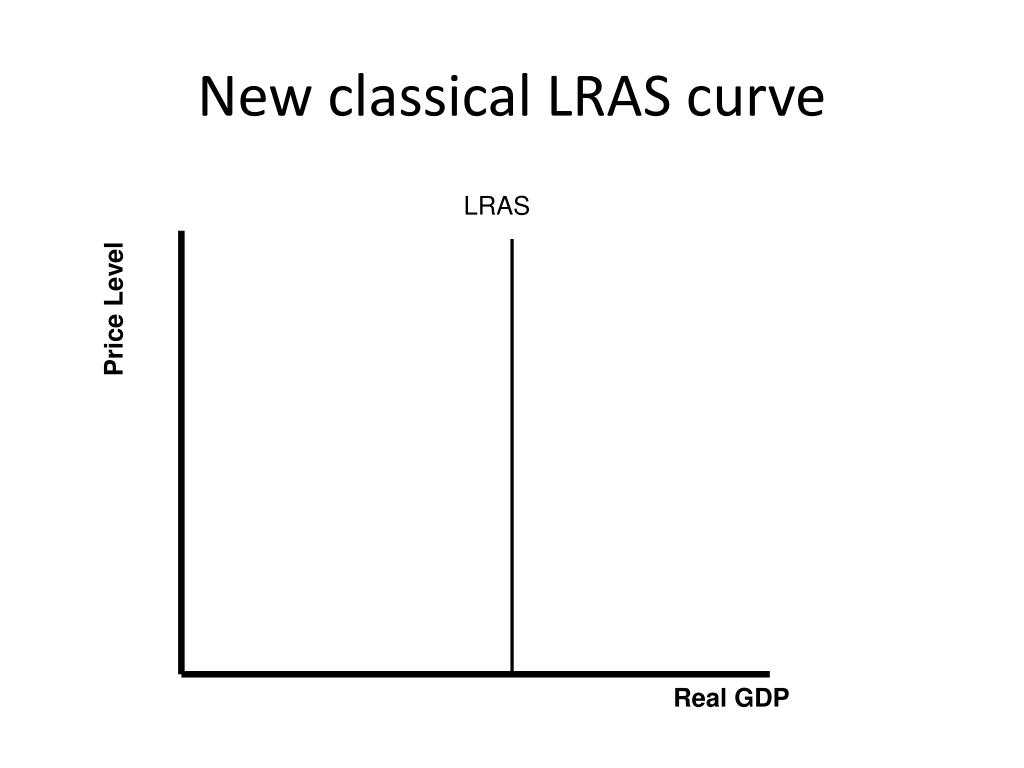
Aggregate Supply Economics Help Aggregate supply classical and keynesian interpretation. a video covering aggregate supply classical and keynesian interpretationinstagram: @econplusdalt. Saddique ansari • january 28, 2020 • 5 min read. the long run aggregate supply (lras) curve depicts the relationship between the price level and the real gdp when there has been time for input prices to adjust to fluctuations in aggregate demand. there are two types of long run aggregative supply curves. the keynesian lras. Long run aggregate supply (lras): monetarist view the lras curve is vertical at a country’s full employment level of output, or the real gdp that would be produced when all resources are fully utilized and wages have fully adjusted to the price level in the economy. i according to the monetarist new classical perspective, the long run. The arrows with the 3 next to them show how we move along the ad curve back to lras as the labor market also re approaches equilibrium. eventually we will attain a new equilibrium where ad' and lras cross. at this new equilibrium point, real gdp will be the same, but the price level in the economy will be higher.

Comments are closed.