Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle
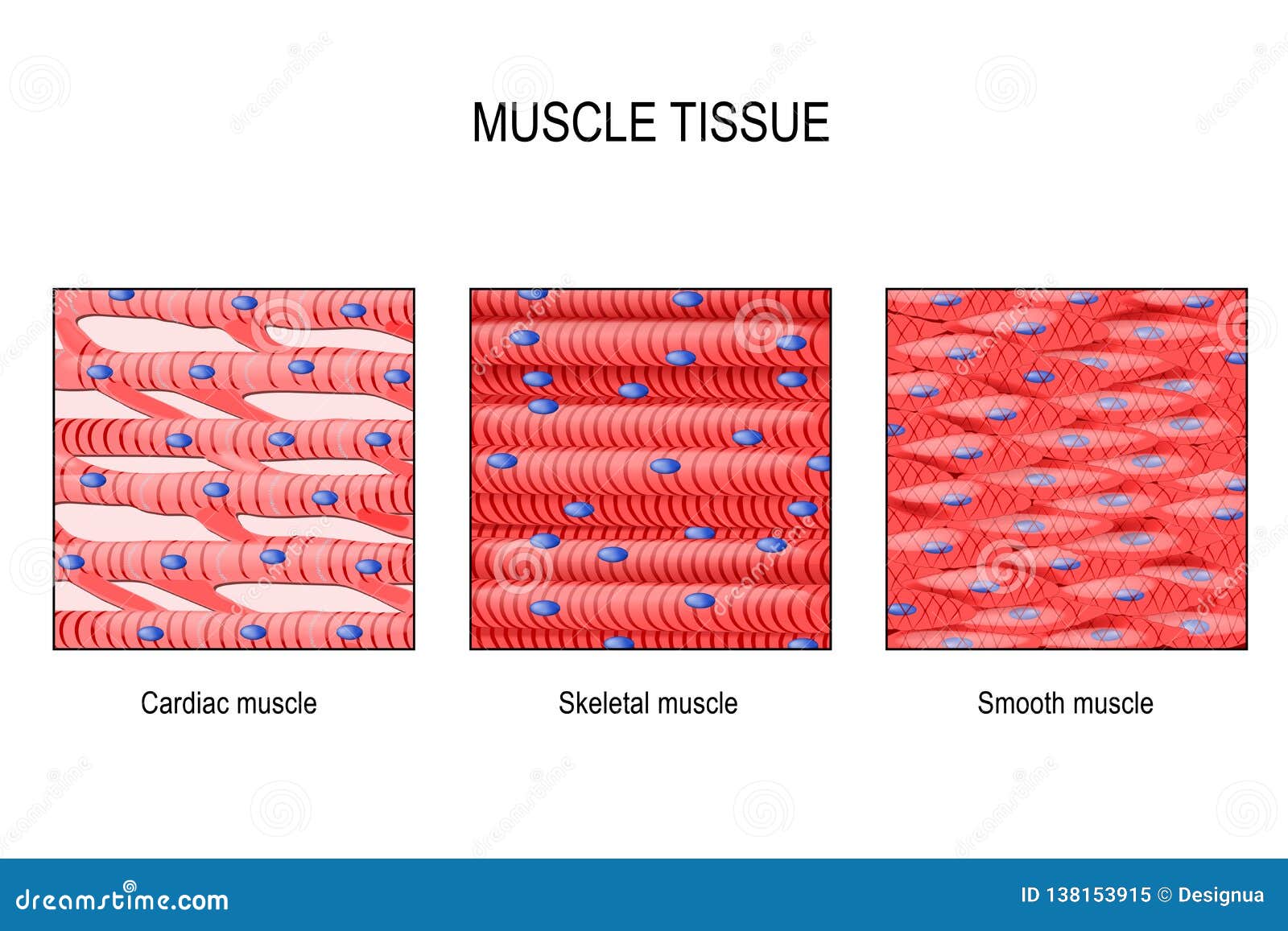
Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Stock Vector Illustration Muscular tissue is the third of the four major categories of animal tissue. muscle tissue is subdivided into three broad categories: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. the three types of muscle can be distinguished by both their locations and their microscopic features. skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. Cardiac muscle is found only in the walls of the heart. when cardiac muscle contracts, the heart beats and pumps blood. cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce atp for energy. this helps the heart resist fatigue. contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscle.
Muscular Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Muscle Online Biology Notes In the muscular system, muscle tissue is categorized into three distinct types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role. skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures. cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. the smooth muscle tissue that forms organs. Figure 4.4.1 – muscle tissue: (a) skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. (b) smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. (c) cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. from top, lm × 1600, lm × 1600, lm × 1600. Muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. there are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multi nucleated and striated. each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Similarities between cardiac skeletal and smooth muscles. cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles collectively form the muscular tissue of the animal body. each and every muscle type is involved in the internal and external movements of the body. the regulation of each type of muscles is done by the nervous system of the body.

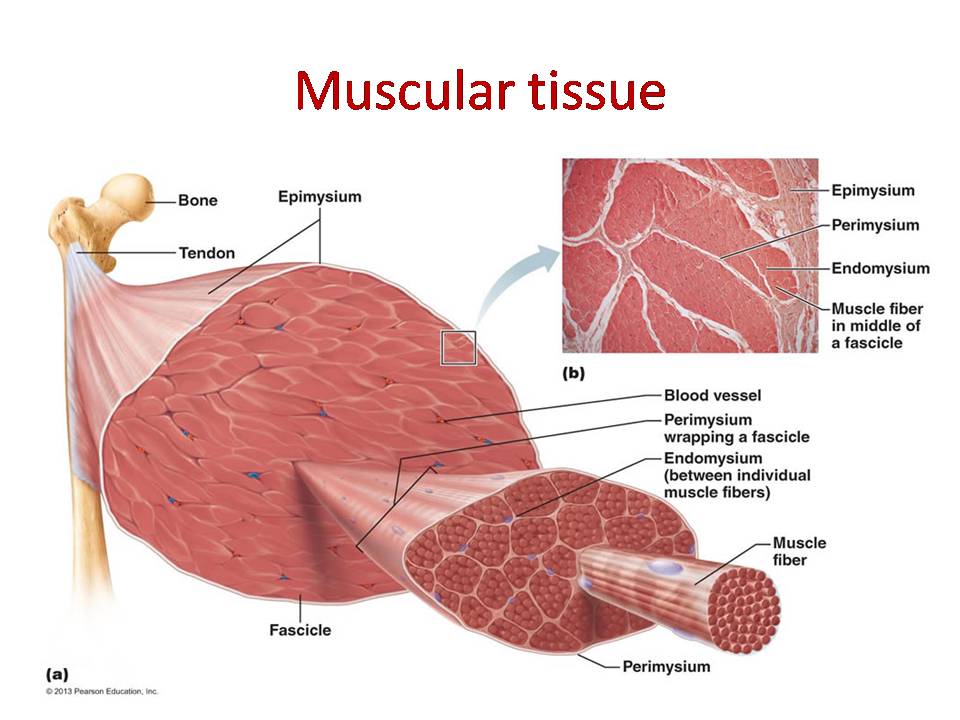
Structure Of Three Basic Muscle Types Muscle System Mcat Content Muscle cells, commonly known as myocytes, are the cells that make up muscle tissue. there are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body; cardiac, skeletal, and smooth. skeletal muscle cells are long, cylindrical, multi nucleated and striated. each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Similarities between cardiac skeletal and smooth muscles. cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles collectively form the muscular tissue of the animal body. each and every muscle type is involved in the internal and external movements of the body. the regulation of each type of muscles is done by the nervous system of the body. There are three major muscle types found in the human body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. each muscle type has unique cellular components, physiology, specific functions, and pathology. skeletal muscle is an organ that primarily controls movement and posture. cardiac muscle encompasses the heart, which keeps the human body alive. smooth muscle is present throughout the gastrointestinal. One of the primary differences between smooth muscle and skeletal cardiac muscle cells is the fact that the contractile proteins (actin myosin) are not organized into sarcomeres; therefore they lack striations as seen in other muscle tissue types. instead, actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments are scattered across the sarcoplasm of the cell.

Comments are closed.